Acer japonicum 'Vitifolium': Vitifolium Fullmoon Maple
Introduction
Fullmoon maple is a small, deciduous tree that reaches 10 to 15 feet in height and width, creating a smooth, rounded canopy. It fits well into the oriental garden due to the exotic silhouette. The deeply divided, soft green leaves have 9 to 11 lobes and are delicately displayed on thin, drooping branches. The cultivar 'Vitifolium' leaves are less divided, providing a coarse texture in the landscape. Leaves take on a beautiful yellow to red coloration in the fall before dropping, making this small, dense plant really stand out in the landscape. Fall color has been described as exceptional. The hanging clusters of showy, purple/red flowers appear in late spring and are followed by the production of winged seeds. The flowers stand out among the maples.
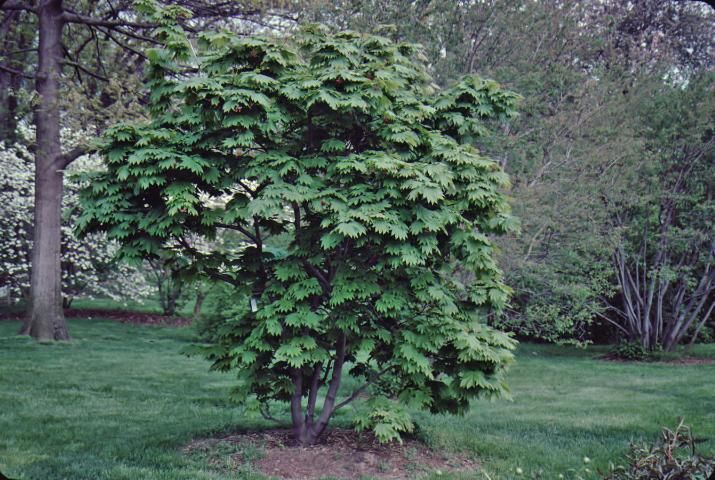

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS
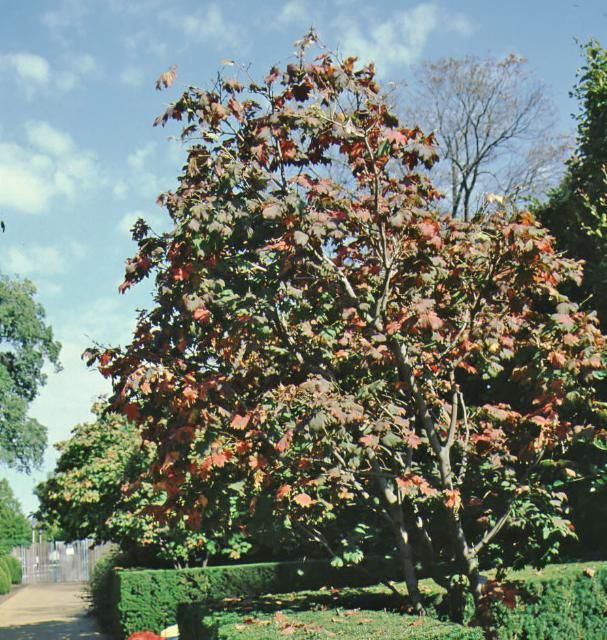

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS
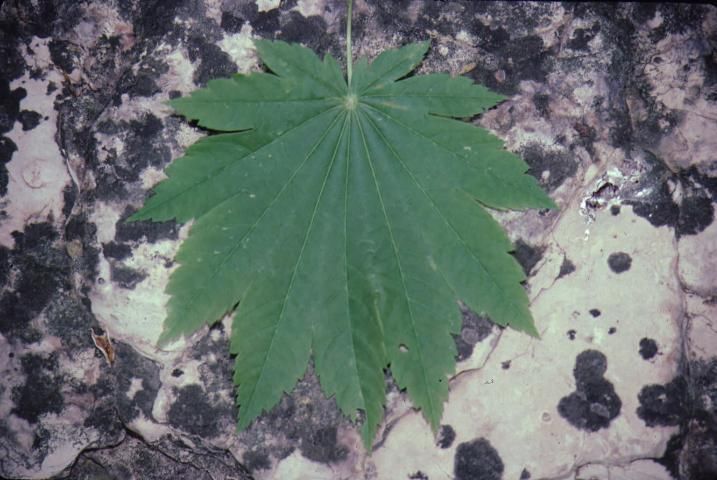

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS
General Information
Scientific name: Acer japonicum 'Vitifolium'
Pronunciation: AY-sir juh-PAW-nick-um
Common name(s): 'Vitifolium' fullmoon maple
Family: Aceraceae
Plant type: tree
USDA hardiness zones: 4B through 7 (Figure 4)
Planting month for zone 7: year round
Origin: not native to North America
Invasive potential: not known to be invasive
Uses: near a deck or patio; container or above-ground planter; trained as a standard; bonsai
AvailabiIity: grown in small quantities by a small number of nurseries
Description
Height: 10 to 15 feet
Spread: 6 to 10 feet
Plant habit: round
Plant density: moderate
Growth rate: slow
Texture: coarse
Foliage
Leaf arrangement: opposite/subopposite
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: lobed; parted
Leaf shape: star-shaped
Leaf venation: palmate
Leaf type and persistence: deciduous
Leaf blade length: 2 to 4 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: orange
Fall characteristic: showy
Flower
Flower color: red
Flower characteristic: showy
Fruit
Fruit shape: oval
Fruit length: 1/2 to 1 inch
Fruit cover: dry or hard
Fruit color: green
Fruit characteristic: inconspicuous and not showy
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: not particularly showy; no thorns
Current year stem/twig color: green
Current year stem/twig thickness: medium
Culture
Light requirement: plant grows in the shade
Soil tolerances: clay; acidic; well-drained; sand; loam
Drought tolerance: moderate
Soil salt tolerance: unknown
Plant spacing: not applicable
Other
Roots: usually not a problem
Winter interest: no special winter interest
Outstanding plant: plant has outstanding ornamental features and could be planted more
Invasive potential: not known to be invasive
Pest resistance: long-term health usually not affected by pests
Use and Management
This maple is at home in the residential landscape as well as the commercial setting. Planted near a patio or deck, it will generate many comments from friends and other visitors. It is probably best used as a specimen, planted to attract attention to an area. It should live for at least 20 years. Nice specimens can be viewed at arboreta, but few nurseries currently offer these cultivars for sale. This may change as nursery operators and homeowners discover the trees.
Fullmoon maple can be grown in sun to almost full shade. Nice specimens can be seen growing in the filtered shade of tall, overstory trees, or with 2 to 6 hours of direct sun. Where the sunlight is intense, the tree will benefit from having its roots shaded or mulched to help keep the soil cool. A generous helping of mulch out to the edge of the canopy is beneficial.
Design Considerations
As a specimen plant the Fullmoon maple should be located to create a focal point. Background plants should have a simple form and full foliage to create a solid mass that highlights the form of the maple. Low-growing shrubs and groundcover plants with dark green, glossy leaves would contrast well with the light green foliage of the maple plant. Pair with plants with simple forms and fine texture such as mounding grasses with narrow strap blades or the sprawling forms of juniper with fine little needles. White and pink flowers in surrounding plants will highlight the purple/red flowers and red fall color of the foliage.
Pests and Diseases
None of major concern except for verticillium wilt.


