Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Sessile Ciliates
Introduction
This publication is one in a series of pictorial guides that is designed to assist in the identification of common freshwater fish parasites. The publications included in this series are:
-
Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Sessile Ciliates
-
Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Motile Ciliates
-
Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Dinoflagellates, Coccidia, Microsporidians, and Myxozoans
-
Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Monogeneans
-
Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Digenean Trematodes
-
Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Nematodes
-
Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Acanthocephalans, Cestodes, Leeches, and Pentastomes
-
Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Crustaceans
The information provided in this guide is not intended to be a complete, detailed description of each parasite or parasite group and its characteristics but rather is intended to assist in the visual identification of some of the most common species or groups of parasites seen in freshwater fish. For further information on each parasite, refer to publications in the "Recommended Reading" and "Reference" sections below.
Guide Information
-
Target Tissue: provides the location on/in the fish where the parasite is most commonly found.
-
Characteristic: provides a brief description about the appearance of the parasite.
-
Size: provides the size or size range of the parasite. (1 µm = 0.001 mm = 0.0001 cm) (µm = micron or micrometer; mm = millimeter; cm = centimeter)
-
Movement: provides the type of movement, if any, of the parasite.
-
Note: provides a brief comment of interest about the parasite.
Sessile Ciliates
Ambiphrya (Formerly Scyphidia)
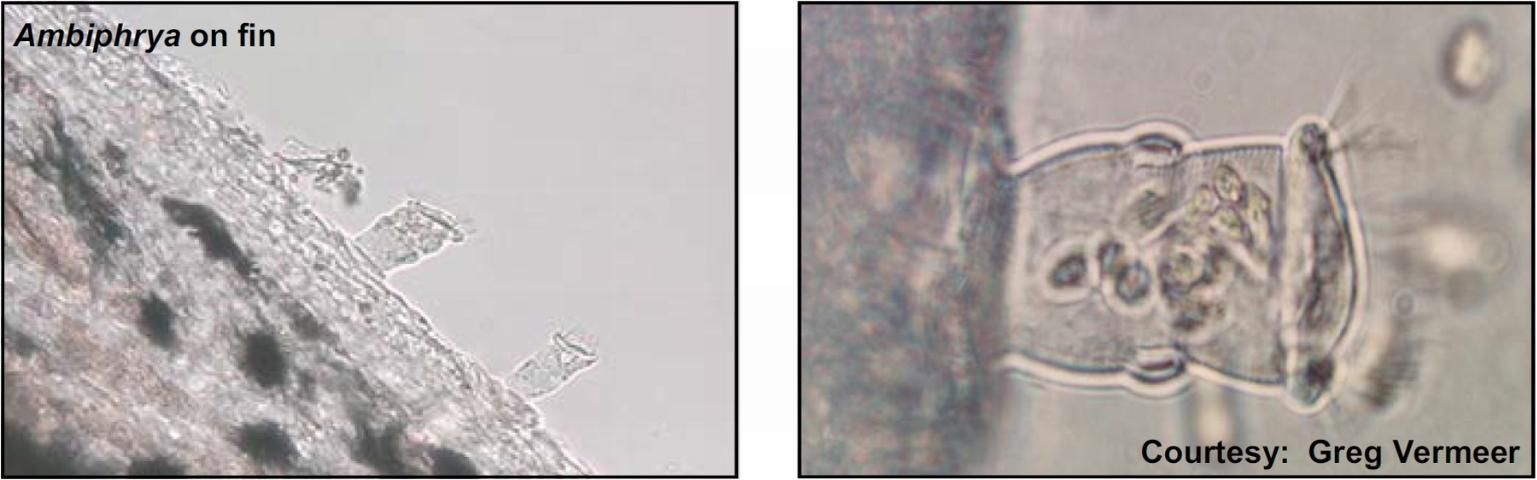
Target Tissues: Skin, fin, gills
Appearance: Barrel-shaped with row of oral and mid-line cilia
Size: Approx. 50–95 μm x 40–61 μm
Movement: Not free-moving on fish; may see cilia move
Note: Common in water with high organic concentration
Apiosoma (Formerly Glossatella)
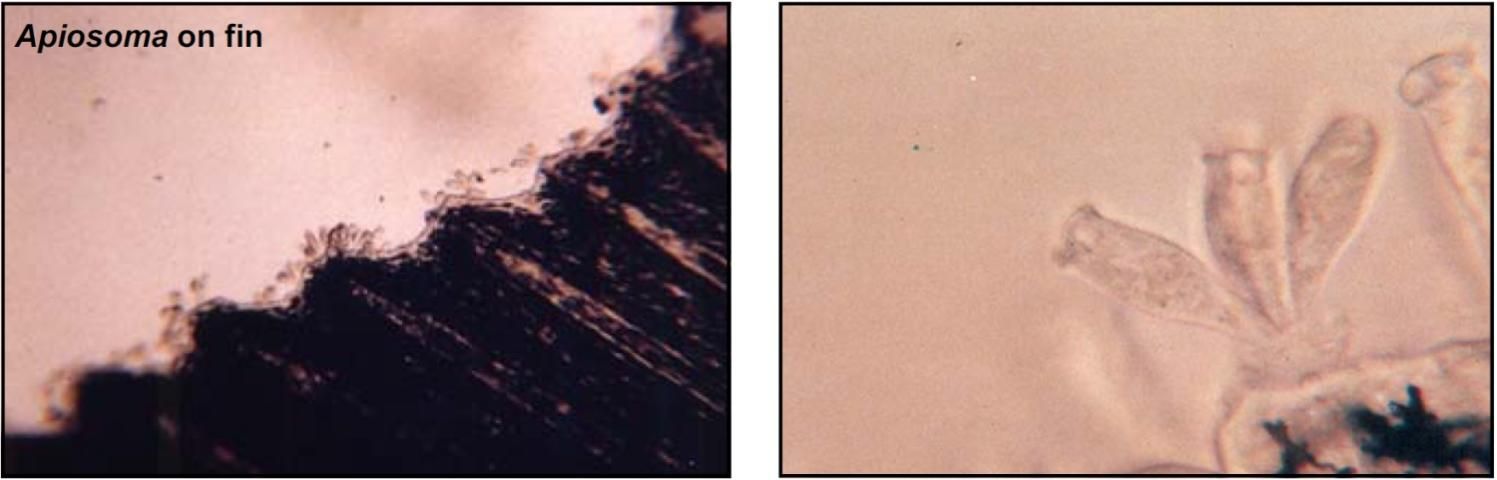
Target Tissues: Skin, fin, gills
Appearance: Vase-shaped with oral cilia
Size: Approx. 100 μm in length
Movement: Not free-moving on fish; may see cilia move
Note: Common in water with high organic concentration
Capriniana (Formerly Trichophrya)
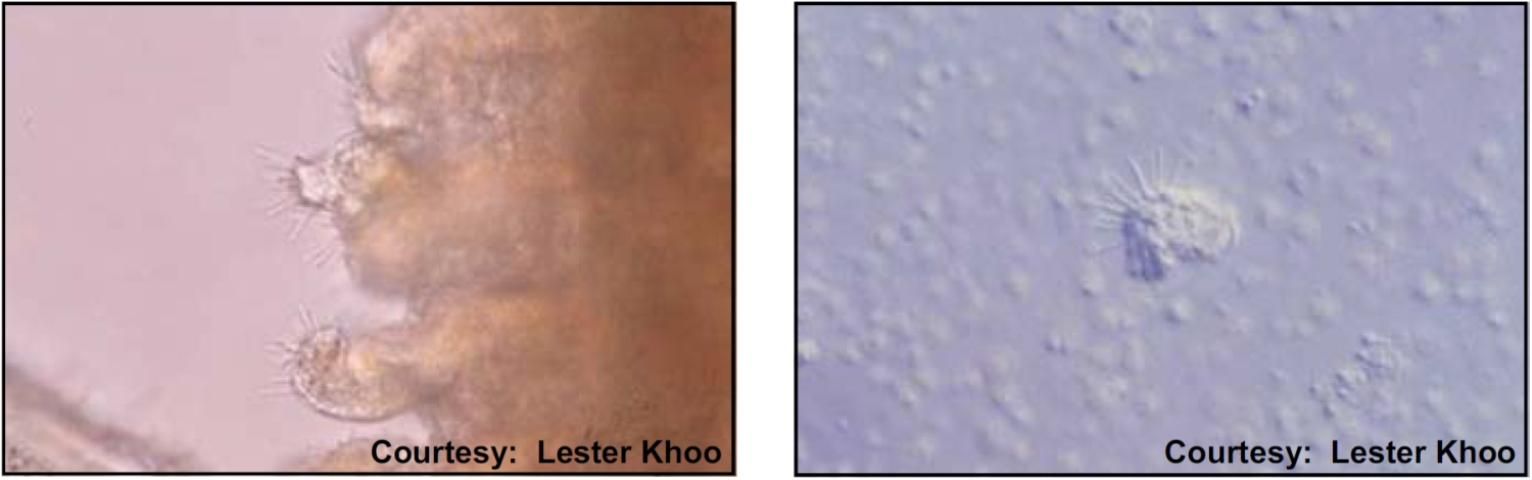
Target Tissues: Gills
Appearance: Amorphous shape with cilia which stick up like pins in pin cushion
Size: Approx. 40–110 μm x 25–70 μm
Movement: Not free-moving on fish
Note: Common in water with high organic concentration
Epistylis
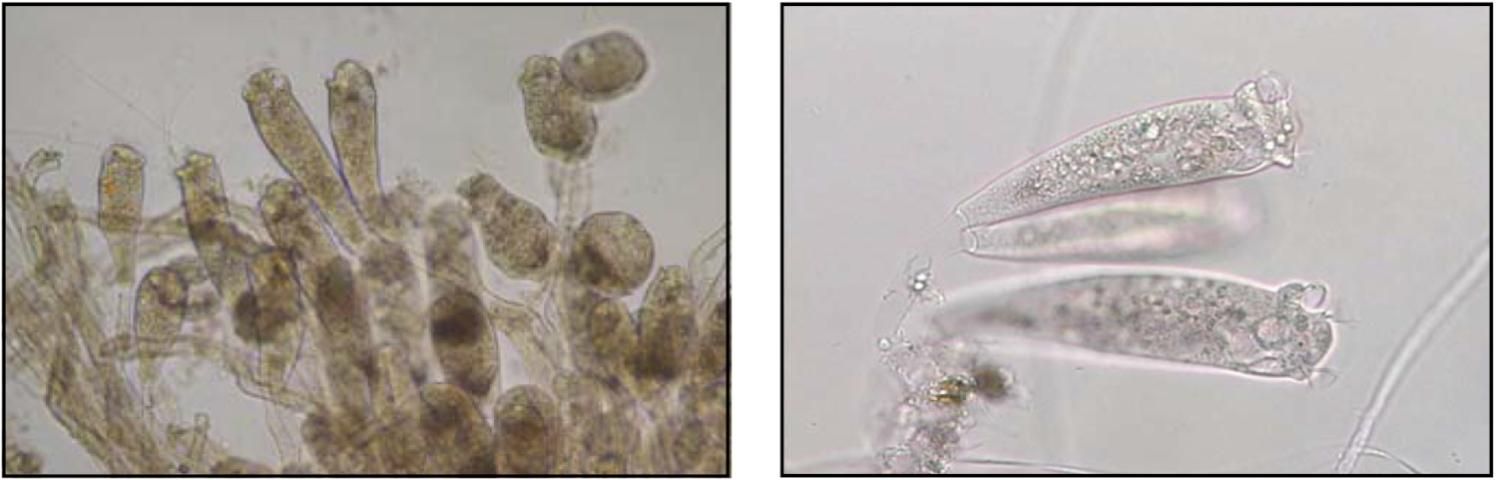
Target Tissues: Skin, fin, (less commonly) gills
Appearance: Elongated on stalks; forms colonies
Size: Zooids approx. 40–80 μm x 20–30 μm; stalks up to 1.2 mm in length
Movement: Not free-moving on fish; may see cilia move
Note: Common in water with high organic concentration; often found in combination with the bacteria Aeromonas sp.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Lester Khoo and Greg Vermeer for the photographs they contributed to this publication.
Recommended Reading
UF/IFAS Circular 91 Nematode (Roundworm) Infections in Fish. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa091
UF/IFAS Circular 120 Fish Health Management Considerations in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems - Part 1: Introduction and General Principles. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa099
UF/IFAS Circular 121 Fish Health Management Considerations in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems - Part 2: Pathogens. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa100
UF/IFAS Circular 122 Fish Health Management Considerations in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems - Part 3: General Recommendations and Problem Solving Approaches. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa101
UF/IFAS Circular 920 Ichthyophthirius multifiliis (White Spot) Infections in Fish. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa006
UF/IFAS Circular 921 Introduction to Fish Health Management. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa004
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-13 Use of Copper in Freshwater Aquaculture and Farm Ponds. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa008
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-90 Pentastomid Infections in Fish. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa090
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-108 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Motile Ciliates. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa108
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-109 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Flagellates. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa109
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-110 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Dinoflagellates, Coccidia, Microsporidians, and Myxozoans. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa110
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-111 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Monogeneans. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa111
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-112 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Digenean Trematodes. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa112
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-113 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Nematodes. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa113
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-114 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Acanthocephalans, Cestodes, Leeches, and Pentastomes. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa114
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-115 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Crustaceans. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/fa115
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet VM-104 Cryptobia iubilans in Cichlids. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/vm077
References
Hoffman, G. L. 1999. Parasites of North American Freshwater Fishes. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press. https://doi.org/10.7591/9781501735059
Longshaw, M., and S. W. Feist. 2001. Parasitic diseases. Pages 167–183 in W.H. Wildgoose, editor. BSAVA manual of ornamental fish, second edition. British Small Animal Veterinary Association, Gloucester, England. https://doi.org/10.22233/9781910443538.21
Noga, E. J. 1996. Fish Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment. St. Louis, MO: Mosby-Yearbook, Inc.
Stoskopf, M. K. 1993. Fish Medicine. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Company.
Woo, P. T. K., editor. 1995. Fish Diseases and Disorders, volume 1: protozoan and metazoan infections. CAB International, Wallingford, United Kingdom.



