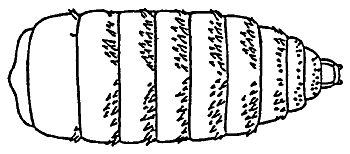
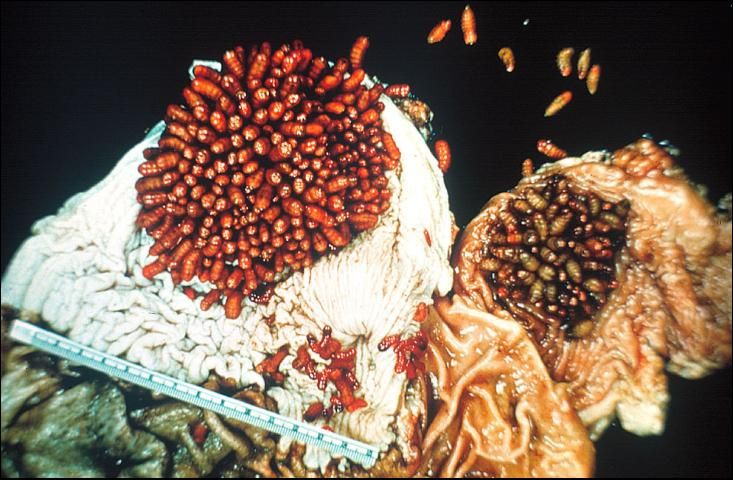
Horse bots (Figure 1), are fly larvae that are internal parasites of horses. The horse bot larvae develop in the stomach and intestines of horses (Figure 2), causing symptoms ranging from stomach ulcers to esophageal paralysis.
Biology
The adult bot fly (Figure 3) is a bee-like fly about 3/4 inch in length. Bot flies are covered with black and yellow hairs and do not feed as adults. There are 3 species of horse bot flies in North America, the common horse bot fly, Gasterophilus intestinalis, is the most widely distributed, the throat horse bot, G. nasalis, and the rarer nose bot, G. haemorrhoidalis. In Florida 2 species of adult bot flies may be active throughout the year, although they are more abundant from late spring to early winter.
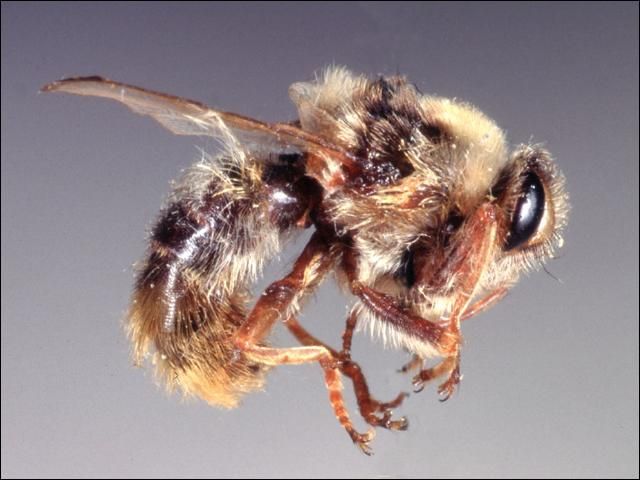

Credit: J. F. Butler, University of Florida
Female bot flies lay from 150–1,000 yellowish eggs. The common bot fly glues eggs to the hairs of the forelegs. The throat bot lays eggs under the chin and lower jaw, while the nose bot prefers the hairs of the nose and lips. The eggs are ready to hatch 7–10 days after oviposition, and will hatch only if the horse licks or bites the area where they have been glued. It is believed that the sudden increase in temperature and moisture from the tongue stimulates the young maggots to hatch.
Once inside the horse's mouth the larvae burrow into the mucous linings of the mouth and tongue and remain there for 3–4 weeks. From the mouth, the larvae pass to the stomach and intestine where the 2nd and 3rd instar larvae remain attached with no change in position until the following summer.
When fully mature, the 3rd stage larvae detach from the stomach or intestine and are passed in the droppings. When they reach the soil, the larvae burrow under the surface of the soil, pupate, and remain there for 1–2 months. The adult fly emerges in late summer or fall. Only one generation is completed per year.
Seasonal Abundance
In South Florida, adult bot flies have been found to be active year-round. In Central and North Florida adults are found from late spring to early winter. Highest populations of adults are recorded from August through September.
Larval populations sampled in horses in October and November ranged from 1-184 larvae per stomach in Central and North Florida. The horse bot is an abundant parasite throughout Florida.
Symptoms
A few bots will cause little damage; however, increasing populations cause gastrointestinal disturbances. Infestations can produce symptoms varying from mild to severe, such as irritation of stomach membranes; ulceration of stomach; peritonitis; perforated ulcers; colic; mechanical blockage of stomach resulting in stomach rupture; esophageal paralysis; and squamal cell tumors. In addition to the previous pathogenicity, the first stage larvae migrating in the tongue and gums have been shown to cause pus pockets in the mouth. The larvae developing in the stomach have also been shown to cause severe anemia.
Cases have also been reported of horse bots in humans. The 1st stage larvae have been found migrating in the skin of humans (cutaneous myiasis), in the eye (ocular myiasis), and horse bots have also been reported in the stomach of humans.
Control
Effective control of horse bots requires breaking the life cycle of the fly. Grooming may aid in removal of eggs, but effectiveness of control is questionable. Human myiasis infections may occur when warm moist grooming aids cause eggs to hatch and larvae to penetrate the skin.
For internal treatment of horse bots, consult a veterinarian. Insecticides are labeled as liquids, gels, boluses, and feed additives for horse bot control. Internal medications will usually control 2nd stage but may not control 3rd stage larvae. Most effective treatments should be applied 1 month after first sighting of eggs to control 2nd stage larvae. Materials which control both 2nd and 3rd stage larvae should be applied in the fall of the year. Refer to Veterinary Medicine for additional information on internal treatment.
Selected References
Catts, E. P. and G. R. Mullen. 2002. Myiasis (Muscoidea, Oestroidea), In: Medical and Veterinary Entomology, (G. R. Mullen and L. A. Durden, Eds.), pp.318–348. Elsevier Science, San Diego, CA.
Knapp, F. W. 1985. Arthropod pests of horses. In: Livestock Entomology (R. E. Williams, R. D. Hall, A. B. Broce and P. J. Scholl, eds.), pp. 297–322. Wiley, New York.
Medownick, M., M. Lazarus, E. Finkelstein, and J. M. Weiner. 1985. Human external ophthalmomyiasis caused by the horse bot fly larva (Gasterophilus spp.). Aust. N. Z. J. Ophthalmol. 13: 387–390.
Price, R. E. and P. C. Stromberg. 1987. Seasonal occurrence and distribution of Gasterophilus intestinalis and Gasterophilus nasalis in the stomachs of equids in Texas. Am. J. Vet. Res. 48: 1225–1232.
Reinemeyer, C. R., P. J. Scholl, F. M. Andrews and D. W. Rock. 2000. Efficacy of moxidectin equine oral gel against endoscopically-confirmed Gasterophilus nasalis and Gasterophilus intestinalis (Diptera: Oestridae) infections in horses. Vet. Parasitol. 88: 287–291.
Sukhapesna, V., F. W. Knapp, E. T. Lyons and J. H. Drudge. 1975. Effect of temperature on embryonic development and egg hatchability of the horse bot, Gasterophilus intestinalis (Diptera: Gasterophilidae). J. Med. Entomol. 12: 391–392.