Selling additional pounds of calf is a desirable objective in any beef cattle enterprise. One way to do this in a cow-calf operation is through creep grazing. Creep grazing is the use of high-quality forage that only calves have access to while grazing with their mothers during the time before weaning. Creep grazing is also one way of more efficiently using limited acreage of improved forages with livestock with greater nutritional demands. Through creep grazing nursing calves gain additional weight, often 30 to 50 pounds more per calf than those calves that did not creep graze.
The concept of creep grazing is based on the fact that the nutritional requirements of suckling calves are much higher than those of cows. Calves creep grazing on high-quality forage that provides high intake of digestible energy and protein make extra growth while the cows are grazing lower quality pasture. For instance, creep grazing makes a difference with Brahman crossbred cows when the milking ability of the mothers is low.
The Creep Pasture
Permanent pastures in Florida are generally nutritionally adequate for pregnant and lactating beef cows but are low-to-marginal for rapidly growing calves. Thus, it is desirable to provide the calves with more nutritious forage if possible. This can be done by fencing off a small part of the herd pasture and planting it with high quality forage. This area is called the creep pasture. Calves are allowed to graze the creep pasture via special access. The special access, or gate, allows the calves to pass through but prohibits the cows from entering the area.
The Calf
Although calves may start grazing at two months, they will not utilize a significant amount of forage for weight gain until they are 3 to 4 months old. They will continue to use increasing amounts of forage as they grow older. To obtain the best gains the creep pasture should be available for limited grazing when the oldest calves in the herd are 3 to 4 months old. Once creep grazing is started, it should be continued until the calves are weaned. Creep grazing can be provided for both spring calves as well as fall calves. Fall calves would graze cool-season forages, and spring calves would graze warm-season forages.
The Cows
While the cows do not get to creep graze, their reproduction is likely to improve because of less lactation demand by the calves. Another benefit for cows is a decrease in loss of weight and body condition during lactation, which shortens the calving interval.
What plants to use?
Legumes or grasses can be used in creep pastures. Producers should select adapted forages that are known to be high in digestibility and protein. Several warm-season legumes that may fit into creep grazing programs are Aeschynomene americana, adapted to poorly drained soils, as well as perennial peanut and cowpea, both adapted to well-drained soils. Aeschynomene has given good results in Florida research studies (Table 1). Results also show that cowpea creep provided adequate daily gains for the calf and improved the status (body condition score) of the lactating cow (Table 2).
Other forages that could be used in the warm season are alyceclover, hairy indigo, Savanna stylo, and pearl millet. The warm-season annual legumes are usually ready for grazing 6 to 8 weeks after planting and continue to grow into September. An early spring planting of pearl millet will provide forage from spring into the fall. Thus, pearl millet could be used to start or finish a creep grazing program where most of the creep pasture is planted to a legume.
If fall calves are 3 to 4 months old in January or February, then the cool-season annual grasses (ryegrass, small grains), as well as alfalfa, white clover, and other adapted cool-season legumes (crimson, red, and arrowleaf clover), can be used in creep pastures.
Managing the Creep Pasture
The size of the creep pasture will depend on the stocking rate and the productivity of the forages used. As a rule of thumb, take 10 percent of the herd pasture and put it into a creep pasture for Aeschynomene and other legumes. One acre will usually be sufficient for 6 calves. Creep pastures containing nitrogen-fertilized grasses such as pearl millet may require less area. If excess creep forage develops, the cow herd can be permitted to graze it.
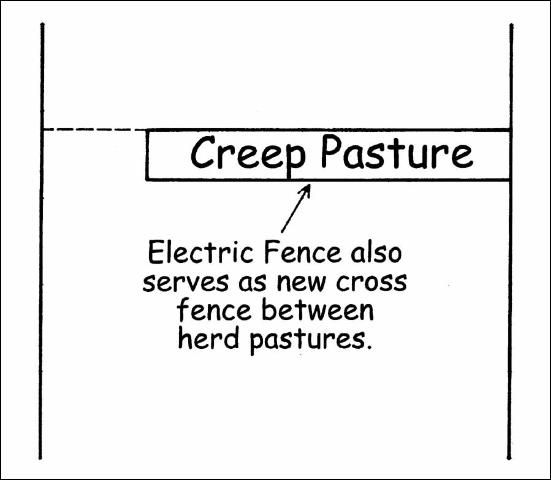
In pasture systems where cattle are rotated across two or more pastures, each herd pasture should have a creep pasture available to it. One creep pasture, if strategically located, may be grazed from two or more herd pastures (Figure 1).
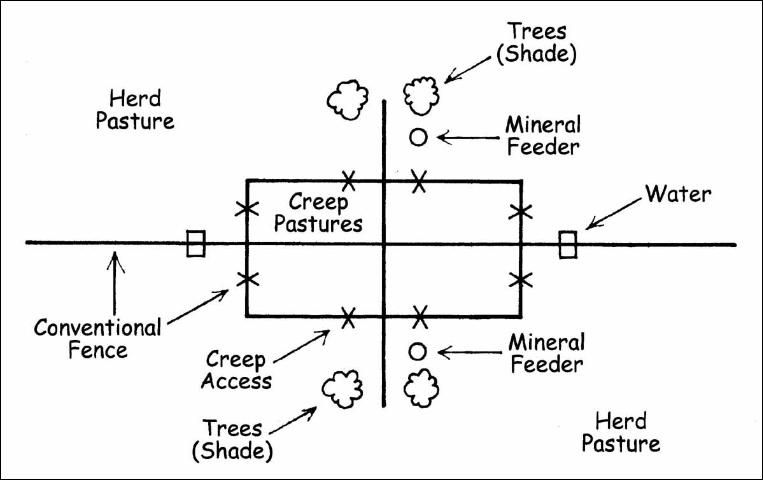
Many factors must be considered when choosing a site for the creep pasture. If annuals need to be planted each year, then the land must be farmable on a timely basis. The site must be compatible with the forage you plan to grow.
Calves must learn to go in and out of the creep pasture. It is helpful to locate the creep pasture and/or creep access in an area where the cows congregate. This can be accomplished by locating the creep access near water, salt, minerals, and/or shade, or the water trough and/or mineral feeder needs to be moved near the creep access. Calves can be initially introduced to the creep pasture by moving the entire herd into the creep for a short period of time each day over a 3- or 4-day period. Calves will learn to use the creep pasture if there is more forage available and if it is more palatable than that in the herd pasture. If plenty of palatable, high-quality forage is available for the calves in the herd pastures, then they will have less of a tendency to use the creep pasture. If the herd pasture is low quality and/or heavily stocked, then calves should make profitable use of creep grazing.
An example of where a creep grazing pasture would most likely increase calf weight is when a bahiagrass pasture is harvested for seed. The bahiagrass is deliberately allowed to mature in order to produce seed, thus when cattle are moved into these pastures after seed harvest, the forage is low in quality.
Construction of a Creep Access
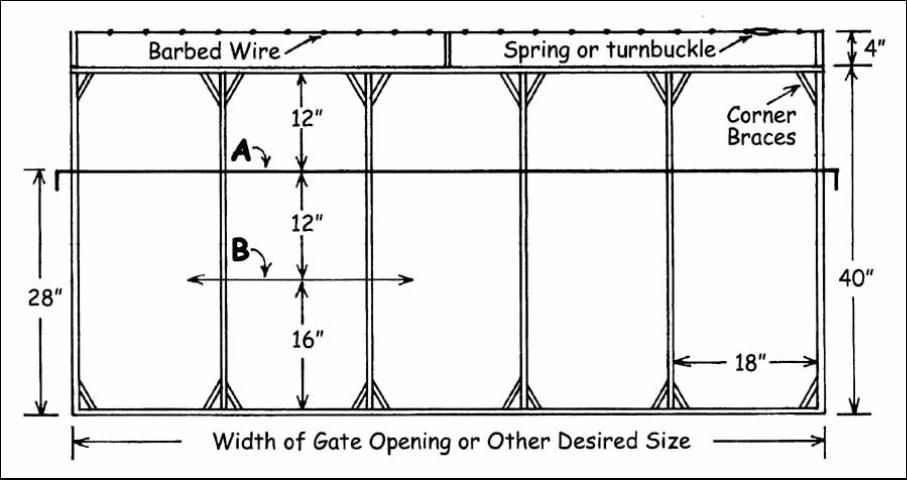
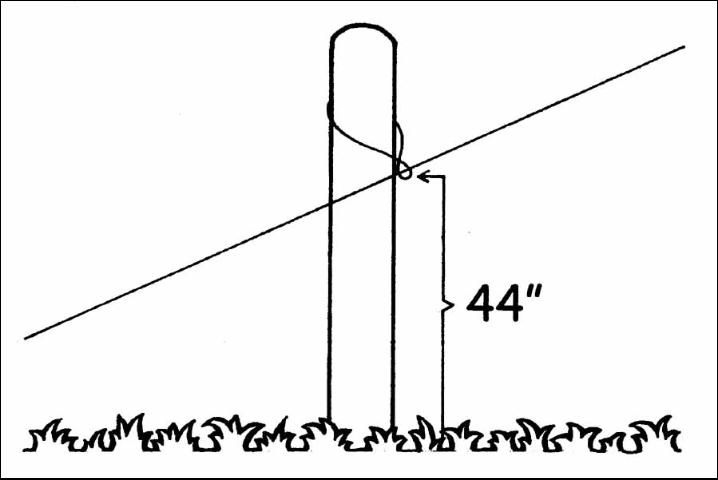
An access to the creep pasture may be placed in a gate opening of a conventional fence by opening the gate and setting a post so that there are 17 to 18 inches between the new post and the original latch post. Then tie the gate to the new post and nail a brace from the new post to the latch post at 36 to 48 inches above the ground. The gate could be opened or removed and replaced with a single electric wire to provide the creep access. A specially constructed creep gate (panel) could be used to replace the original gate, or a simple opening in the fence may be constructed with posts. The creep opening should be 17 to 18 inches wide and 36 to 48 inches high (height above ground) (Figures 2 and 3). Additional information on the construction of a creep gate can be found at the following website: https://extension.colostate.edu/publications-2/blueprints-and-housingequipment-plans/blueprints-pasture-and-range-equipment-plans/. There should be more than one access into the creep pasture if possible.
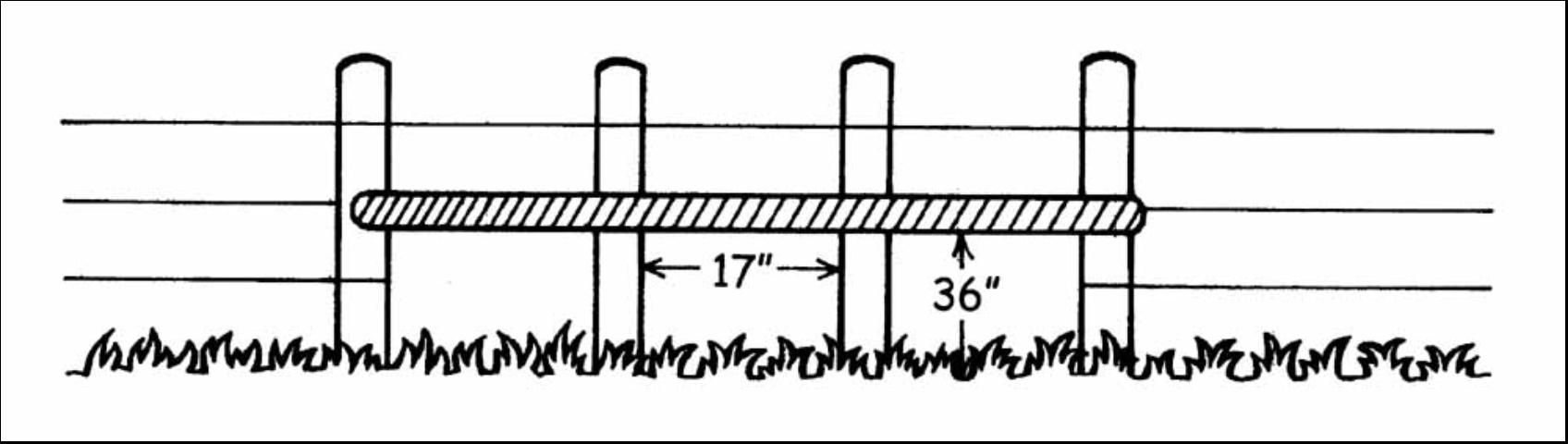
Portions of a large herd pasture may be economically fenced off and planted to a creep forage by using a single wire electric fence placed at a height of 36 to 48 inches (Figures 4, 5, and 6). High tensile smooth wire can be used and will require minimum maintenance as compared to the lightweight temporary type of electric fencing wire. Where electric current is not available, solar-powered electric fencers can be used. Calves can walk under the wire at any point and no special creep opening will be needed.
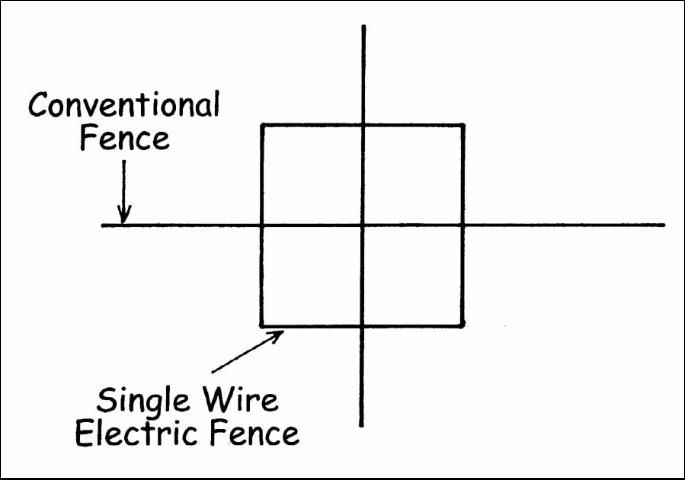
If a producer does not desire to develop separate creep pastures, some advantage may be gained by constructing creep access to each herd pasture so that calves can graze ahead of the mature cows. This allows the calves to select the highest quality forage before the mature cows have an opportunity to graze it.
Summary
Creep grazing is a management practice for economically increasing the weaning weight of calves. To successfully use this practice:
- Establish creep pastures in locations that will be used by the calves.
- Use adapted high quality forages in the creep pastures.
- Induce calves to use the creep pasture by placing mineral feeders, water, and/or shade near the creep access.
- Have creep grazing available by the time the oldest calves in the herd are 3 to 4 months old.
- Make the creep access or opening through which the calf passes 17 to 18 inches wide and 36 to 48 inches high.
Before setting up a creep pasture, a producer should determine what it will cost and compare the cost to expected increase in weight gain of calves and the value of the increased weight.
Creep grazing may not work for all herds. Cows that are heavy milkers may provide their calves with all of the energy they can use, and no additional gain will result from creep grazing.
References
Foster, J.L. 2008. Improving the productivity of livestock with warm-season legumes. PhD diss., University of Florida, Gainesville, FL.
Ocumpaugh, W.R., and G.A. Dusi. 1981. Creep grazing for calves using warm-season legumes. Forage and Grassland Progress. 22: 3–4.
Williams, M.J., C.C. Chase, Jr., and A.C. Hammond. 2004. Performance of cows and their calves creep-grazed on rhizome perennial peanut. Agronomy Journal. 96:671–676.