Introduction
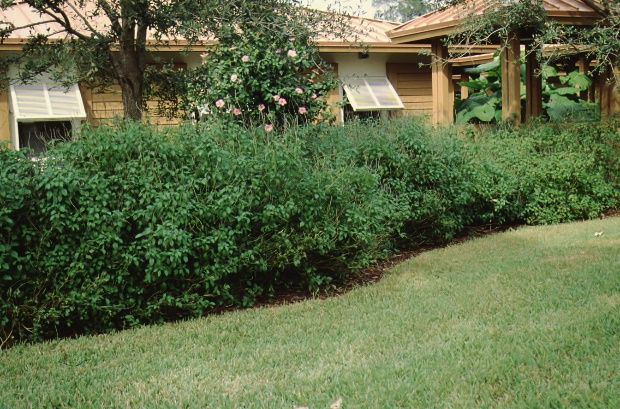
Porterweed is a small perennial shrub that becomes woody toward the base of the stem as it grows to about one year old. Plants grow about 4 feet tall by 6 feet wide before stems droop and touch the ground. Blue or pink flowers are borne terminally on long, stringy spikes at the ends of the stems. They attract butterflies to the landscape. Rich, dark green foliage displayed on square, green stems makes porterweed a nice addition to any sunny landscape.

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS
General Information
Scientific name: Stachytarpheta jamaicensis
Pronunciation: stake-kee-tar-FEE-tuh jah-may-SEN-sis
Common name(s): blue porterweed, light-blue snakeweed, joee
Family: Verbenaceae
Plant type: shrub; perennial; herbaceous
USDA hardiness zones: 10 through 11 (Figure 4)
Planting month for zone 10 and 11: year-round
Origin: not native to North America
Invasive potential: not known to be invasive
Uses: hedge; border; mass planting; attracts butterflies
Availability: somewhat available, may have to go out of the region to find the plant
Credit:
Description
Height: 4 to 8 feet
Spread: 4 to 8 feet
Plant habit: round
Plant density: dense
Growth rate: fast
Texture: medium
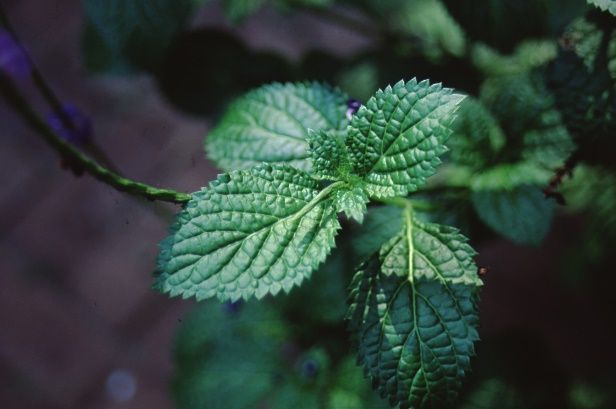
Foliage
Leaf arrangement: opposite/subopposite
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: serrate
Leaf shape: ovate
Leaf venation: pinnate; reticulate
Leaf type and persistence: semi-evergreen
Leaf blade length: less than 2 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: no fall color change
Fall characteristic: not showy
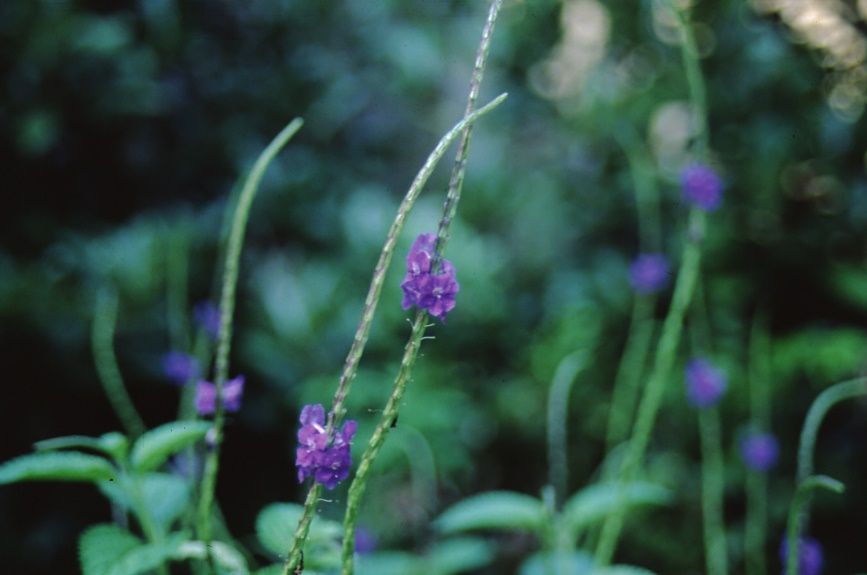
Flower
Flower color: pink; blue
Flower characteristic: summer flowering; fall flowering
Fruit
Fruit shape: unknown
Fruit length: unknown
Fruit cover: unknown
Fruit color: unknown
Fruit characteristic: inconspicuous and not showy
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: not particularly showy; typically multi-trunked or clumping stems
Current year stem/twig color: green
Current year stem/twig thickness: thin
Culture
Light requirement: plant grows in part shade/part sun
Soil tolerances: acidic; alkaline; sand; loam; clay
Drought tolerance: high
Soil salt tolerances: unknown
Plant spacing: 36 to 60 inches
Other
Roots: usually not a problem
Winter interest: no special winter interest
Outstanding plant: plant has outstanding ornamental features and could be planted more
Pest resistance: long-term health usually not affected by pests
Use and Management
Porterweed is frequently used in a mass planting along a foundation, or as a clipped or natural unclipped hedge to provide continuous color to the landscape. Space plants about 3 to 4 feet apart. A row will maintain a nice uniform shape for 6 or more months without pruning. Regular clipping can maintain a uniform shape for more than a year before the plant needs to be cut back to thicken the growth. Unclipped plants begin to open up as stems droop to the ground. For this reason, they are usually cut back each year, or any time the plant becomes leggy. This allows new growth to fill in and thicken the plant.
Locate porterweed in a sunny location in any soil. Provide irrigation during establishment and then in extended drought in the summer. Fertilize about twice each year to maintain foliage color and provide for continuous growth.
Pest and Diseases
No serious pests or diseases are known to affect porterweed.