Introduction
Deposition of pesticides on non-fruit or tree surfaces (non-target deposition) is both an economic loss to the grower and a potential environmental problem. Much research has documented factors and the possible magnitude of spray drift in agricultural production systems (Spray Drift Task Force 1997). Differences in canopy characteristics, wind, relative humidity, planting density, and other factors may all significantly affect spray drift (reviewed by Stover et al. 2003). Smaller droplets are generally more prone to drift, with ground deposits typically being greatest within 50 ft of the sprayer (Fox et al. 1993; Hobson et al. 1993; Johnson 1995; Salyani and Cromwell 1992; Walklate 1992). The percentage of material drifting off-site increases with both wind speed and decreased droplet size.
The potential for surface water contamination in flatwoods citrus production areas is not restricted to long-range drift of spray materials. Most of these groves are situated on poorly drained soils with shallow hardpans and perched water-tables. These groves are almost always bedded to expedite drainage and provide adequate rooting space for the trees. Groves are designed so that rainfall drains rapidly from the beds through a series of water furrows connected to drainage ditches and larger canals (Figure 1).

Credit: PCW
These ditches and canals represent a direct linkage to streams, rivers, lakes, and estuaries, making minimization of pesticide losses from production areas especially important. These ditches and canals also serve as aquatic habitat for a variety of invertebrate, fish, bird, and mammal species. Direct deposition of applied pesticides to the water surfaces of adjacent ditches and canals may present significant ecological risks, depending on the pesticide applied.
Since lateral drainage ditches and canals are often located perpendicular to tree rows, shutting off sprayer nozzles when approaching the end of tree rows should reduce drift of pesticides into these non-target surface water bodies. In practice, sprayer operators may not always turn sprayers off at the end of tree rows because of preoccupation with several aspects (scanning for oncoming traffic and obstacles, avoiding water furrow pipes, etc.) of safely exiting the row and making the 180° turn into the next row, especially if they are driving in a water furrow.
This document summarizes the results from a study evaluating the effectiveness of turning sprayer nozzles off at row ends as best management practice for preventing non-target deposition of pesticides in surface water connections such as irrigation and drainage ditches. It also estimates direct deposition on ground surfaces that translate into wasted product, as well as another potential source of surface water contamination through surface water runoff. More detailed information regarding this study can be found in Wilson et al. (2004).
Summary of Methods
Specific Row-End Spraying Strategies Evaluated
- Leaving both banks of nozzles on while turning;
- Turning the outside-facing nozzles off (leaving tree-facing nozzles on);
- Turning both banks of nozzles off at the tree trunk;
- Turning all nozzles off at the end of the foliage of the last tree within the row.
Site Description
This study was conducted within a commercial, double-bedded citrus grove located in St. Lucie County, FL. This grove was planted with white Marsh grapefruit (on sour orange rootstock) trees that were greater than 20 years old and were approximately 18 ft tall. Distance between tree rows averaged 28.5 ft both across bed tops and furrows. These studies were conducted along a drainage ditch that separated two blocks of citrus within the grove. This ditch was located approximately 23 ft from the edge of the last tree within each row. The ditch was 25 ft wide. The vertical distance from the ground surface down to the surface of the water within the ditch was approximately 5.4 ft.
Copper Applications
Copper hydroxide formulated product was used as a model pesticide because of its low human toxicity and its stable disposition, having few special handling and storage requirements for accurate analysis. Copper is routinely used in fungicidal applications to commercial citrus in the region. Copper applications were made in June and again in July 2001. A summary of application materials is shown in Table 1.
Evaluations were made with the tractor spraying only bed-tops. Within this type of double-bedded grove, pesticide applications to the furrow side of the trees were made after the sprayer was adjusted for tree elevation differences. Applications were started before 8:00 AM and lasted until approximately noon during both dates of the study.
Estimation of Non-Target Deposition
The area evaluated was divided into three distinct zones: 1) ground surfaces adjacent to the sprayer, 2) water surface within lateral canal, and 3) ground surfaces across the canal from the sprayer. Deposition directly on the ground or water surfaces was estimated by multiplying the average amount of copper on each set of targets (i.e., ground-sprayer side, water surface, ground-opposite side) by the grove surface area encompassed by each set of targets. The total ground surface areas encompassed 3,645 ft2, while the surface area of the water within the ditch was 4,050 ft2.
Deposition Results
Deposition during the June application was generally greater than that found in July. This was not unexpected since a variety of factors, including wind speed and direction, temperature, and humidity can influence droplet size and non-target deposition. These factors were reviewed by Stover et al. (2003). A summary of the deposition results obtained follows.
Adjacent to Sprayer
Copper deposition adjacent to the sprayer was more similar among the four treatments in June than in July (Figure 2). On both application dates, turning the outside nozzles off at the foliage edge through the turn resulted in less deposition than when leaving both sets of nozzles on. Turning both sets of nozzles off at the tree trunk and turning off only the outside-facing nozzles also reduced deposition on the ground surface adjacent to the sprayer. Deposition ranged from 142 to 369 mg (0.005 to 0.013 oz) in June. In contrast, deposition on the ground surface during the July application was significantly higher when both nozzles were left on through the turn, relative to all other treatments. In this case, leaving all nozzles on through the turn resulted in 142 mg (0.005 oz), compared to 28 mg (0.001 oz) for the other treatments.
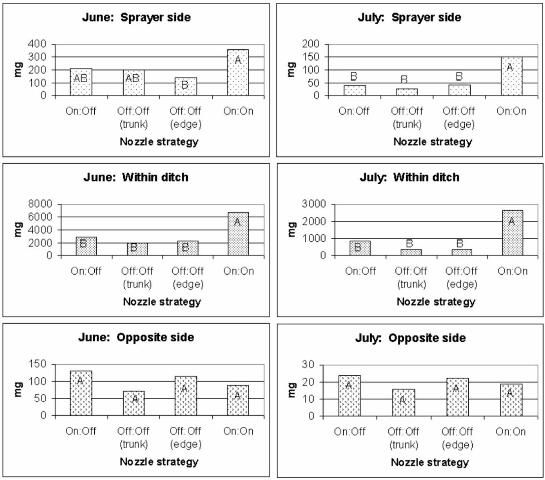
Credit: Wilson et al. (2004)
Within Lateral Canal
Similar deposition patterns were apparent for both application dates (Figure 2). However, deposition was generally greater during the June application. In both cases, deposition was significantly reduced when the outward-facing or both banks of nozzles were turned off, regardless of timing. During the June application, an estimated 6,747 mg (0.238 oz) was deposited directly on the water surface when all nozzles were left on through the turn, as compared to 2,013 to 2,892 mg (0.071 to 0.102 oz) with the other treatments. During the July study, 2,637 mg (0.093 oz) were deposited on the water surface when all nozzles were left on as compared to 340 to 879 mg (0.012 to 0.031 oz) with the other treatments. Turning all or the outside-facing nozzles off through turns reduced direct deposition on the water surface by 57–70% during the June application and 67–87% during the July application.
Opposite Side of Lateral Canal
Row-end spraying strategies did not influence copper deposition on ground surfaces on the opposite side of the drainage canal from the sprayer. Again, deposition during the June application was higher than in the July application. Deposition on the ground surface ranged from 72 to 130 mg (0.003 to 0.005 oz) during the June application and 16 to 24 mg (0.0006 to 0.0008 oz) during the July application.
Discussion
The row-end spraying techniques compared in this study are representative of those commonly used for citrus production in flatwoods areas. Continuing to spray from both sides of the sprayer while rounding the row ends, which resulted in highest deposition, has never been a recommended practice but is occasionally observed. These studies illustrate the importance of shutting off the outer nozzles to reduce off-target deposition on water and ground surfaces, but do not indicate a significant difference in the non-target deposition between any of the remaining techniques.
The difference in mean deposition measured on each of the two study dates is quite remarkable. Each of the study dates had very similar wind speed and relative humidity. The difference in deposition may have resulted from the very different wind direction on the two study dates. The wind direction during the June study date was primarily from the northeast, resulting in a mean wind speed of 3.4 mph in a southerly direction, which resulted in a greater wind movement between the North-South oriented rows. Even though wind speed was well within that considered suitable for foliar applications (Stover et al., 2003), it may have significantly influenced off-target deposition.
In practice, some managers may turn the sprayer nozzles off at the trunk of the last tree within rows while spraying a block, and then make a final pass around the outside perimeter with only the tree-side nozzles operating (wrapping). While our data indicate that turning off the nozzles at the end of the tree rows reduces non-target deposition, the wrapping application will almost certainly increase non-target deposition on both bed-tops and water furrows, and possibly water surfaces. In contrast, while leaving the inner nozzles on while rounding the tree row reduces non-target deposition, this practice is likely to result in much higher applications of the pesticides to the row end relative to the remaining trees in the row, suggesting inefficient use of spray material (Indian River growers, personal communication).
Therefore, these data and the accompanying discussion suggest that continuing to spray just to the end of the foliage on the row ends without the added step of wrapping the perimeter should be considered as a BMP to reduce non-target deposition of spray-applied pesticides. Growers should confirm adequate control at the row ends through scouting programs and make application adjustments if needed.
Summary
Considering that most groves in flatwoods citrus production areas have similar drainage systems, the possible environmental benefits of turning outside-facing nozzles off during turns can be significant. In addition to demonstrating the reduction in direct deposition of a pesticide on water and ground surfaces, these studies also demonstrated the inherent variability that can be expected in non-target deposition, even when applications are made at the same rates and under relatively similar climatic conditions.
Acknowlegements
We thank Jane Ferguson-Foos (Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services) for her support and guidance, and Peter Strimple, Robert Minerva, James Salvatore, Michael Boman, and Michael Poult for their technical assistance. This project was funded by USEPA R4 through FDACS.
References
Fox, R. D., D. L. Reichard, R. D. Brazee, C. R. Krause and F. R. Hall. 1993. "Downwind residues from spraying a semi-dwarf apple orchard." Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers 36:333–340.
Hobson, P. A., P. C. Miller, P. J. Walkgate, C. R. Tuck and N. M. Western. 1993. "Spray drift from hydraulic spray nozzles: the use of a computer simulation model to examine factors influencing drift." Journal of Agricultural Engineering and Research 54:293–305.
Johnson, D. R. 1995. Drift from orchard airblast applications: integration and summary of 1993 and 1994 field studies (Report no. I95-004). Spray Drift Task Force, Washington, D.C.
Salyani, M. and R. P. Cromwell. 1992. "Spray drift from ground and aerial applications." Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers 35:1113-1120. http://agricola.nal.usda.gov/
Spray Drift Task Force. 1997. A summary of airblast application studies. 31 May 2002. http://www.agdrift.com/PDF_FILES/Airblast.pdf.
Stover, E., D. Scotto, C. Wilson and M. Salyani. 2003. "Pesticide spraying in grapefruit: II. Overview of factors influencing spray efficacy and off-target deposition." HortTechnology 13:166–177.
Walklate, P. J. 1992. "A simulation study of pesticide drift from an air-assisted orchard sprayer." Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research 51:263–283.
Wilson, P. C., E. Stover, and B. Boman. 2004. "Minimizing direct deposition of pesticides into waterways associated with Indian River citrus production." HortTechnol. 14(4):545–550.