Asimina triloba: Pawpaw1
Introduction
A native deciduous tree, the coarse-textured pawpaw ultimately reaches 30 feet in height (more commonly 15- to 20-feet) with an equal spread, and creates an upright, wide pyramidal silhouette. The large, dark green leaves, 6- to 12-inches in length and 3- to 5-inches wide, seem to droop from their weight at branch tips, giving the plant a distinctive, almost wilted appearance. Leaves turn a sometimes-brilliant yellow before dropping in the fall. The two-inch-wide purple flowers with the less-than-pleasant perfume appear before the leaves unfurl in springtime, and are followed by the production of unusual, fleshy, 3- to 5-inch-long, round or oval fruits, green when young but ripening to a brown/black, wrinkled texture. When fully ripe, the edible flesh becomes soft, almost custard-like, has a sweet, rich taste similar to bananas, and is surprisingly very nutritious. The fruits are popular with man and wildlife, especially raccoons and birds.
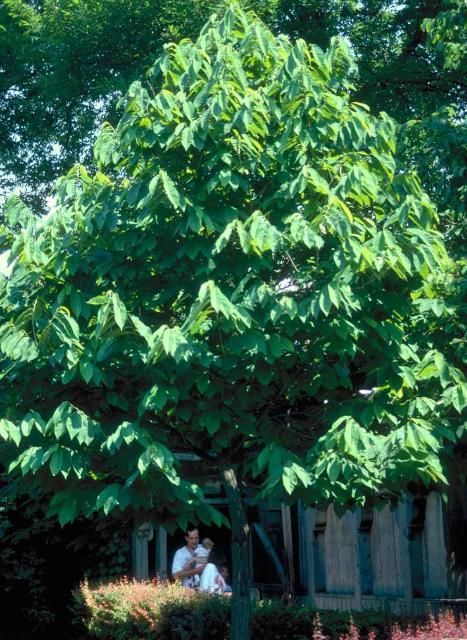

Credit: Ed Gilman
General Information
Scientific name: Asimina triloba
Pronunciation: uh-SIM-min-nuh try-LOE-buh
Common name(s): Pawpaw
Family: Annonaceae
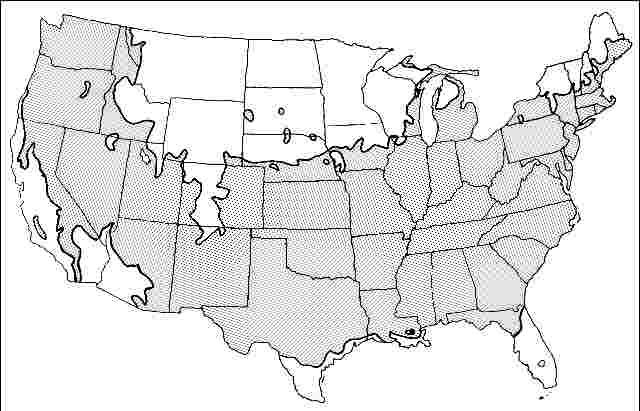
USDA hardiness zones: 5A through 8B (Fig. 2)
Origin: native to North America
Invasive potential: little invasive potential
Uses: reclamation; specimen; fruit
Availability: not native to North America
Description
Height: 15 to 20 feet
Spread: 15 to 20 feet
Crown uniformity: symmetrical
Crown shape: upright/erect, round
Crown density: moderate
Growth rate: moderate
Texture: coarse
Foliage
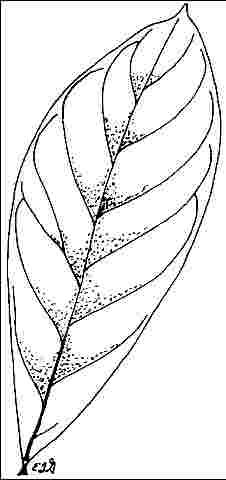
Leaf arrangement: alternate (Fig. 3)
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: entire
Leaf shape: obovate, oblong
Leaf venation: pinnate
Leaf type and persistence: deciduous
Leaf blade length: 4 to 8 inches, 8 to 12 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: yellow
Fall characteristic: showy
Flower
Flower color: purple
Flower characteristics: not showy
Fruit
Fruit shape: elongated
Fruit length: 3 to 6 inches
Fruit covering: fleshy
Fruit color: brown, black
Fruit characteristics: attracts birds; showy; fruit/leaves a litter problem
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: branches droop; not showy; typically multi-trunked; thorns
Pruning requirement: needed for strong structure
Breakage: resistant
Current year twig color: brown
Current year twig thickness: medium
Wood specific gravity: unknown
Culture
Light requirement: full sun, partial sun, or partial shade, shade tolerant
Soil tolerances: clay; sand; loam; acidic; slightly alkaline; occasionally wet; well-drained
Drought tolerance: moderate
Aerosol salt tolerance: unknown
Other
Roots: not a problem
Winter interest: no
Outstanding tree: yes
Ozone sensitivity: unknown
Verticillium wilt susceptibility: resistant
Pest resistance: free of serious pests and diseases
Use and Management
The pawpaw tree will grow in full sun or dense shade but will have denser growth in the sun. Branches arch and reach to the sun in shaded sites, often creating an open, irregularly shaped canopy. The soil should be rich, moist, and slightly acid, and the trees will even tolerate wet, soggy soils. It can be found in multi-stemmed thickets along stream banks and on flood plains in the wild. The tree is probably best used in a natural area for stabilizing stream banks and to add yellow fall color to a landscape. It also makes a great coarse-textured specimen.
Propagation is by seeds, layerings, or root cuttings.
Pests and Diseases
No pests or diseases are of major concern.


