Introduction
Growing 20 to 40 feet in height, Hong Kong orchid tree creates a rounded, spreading canopy composed of large, 6- to 8-inch-diameter, gray/green leaves. Since young trees can be irregularly shaped, pruning during the first several years after propagation is often needed to develop a more uniform crown. It is the beautiful display of orchid-like blooms, though, which make Hong Kong orchid tree so desirable for the landscape, the large, six-inch blossoms appearing in multiple shades of purple, rose, and pink during the summer, fall, and early winter months, when little color is usually present in the garden. These flowers are sterile and will not set seed, so the plant will not drop long pods as other orchid trees do, and they will not become a pest in the landscape. This is often the orchid tree of choice for planting in urban landscapes.
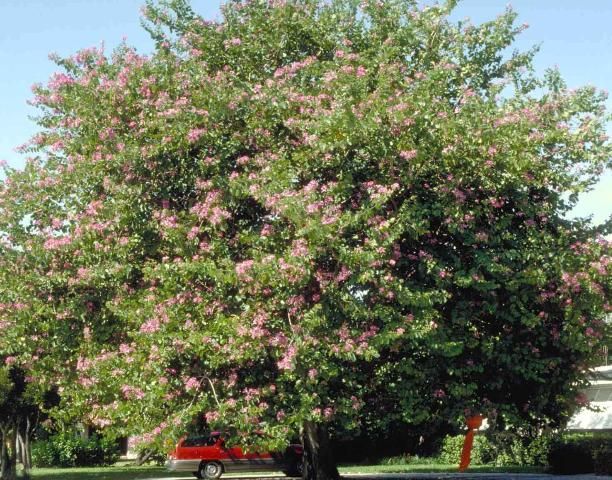

Credit: Ed Gilman
General Information
Scientific name: Bauhinia blakeana
Pronunciation: bah-HIN-ee-uh blay-kee-AY-nuh
Common name(s): Hong Kong orchid tree
Family: Leguminosae
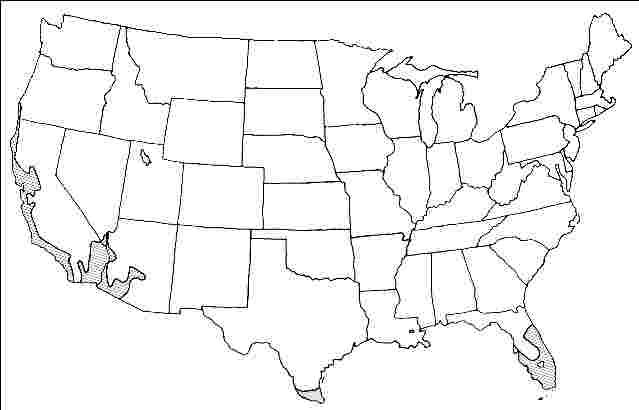
USDA hardiness zones: 9B through 11 (Fig. 2)
Origin: not native to North America
Invasive potential: has been evaluated using the UF/IFAS Assessment of the Status of Non-Native Plants in Florida's Natural Areas (Fox et al. 2005). This species is not documented in any undisturbed natural areas in Florida. Thus, it is not considered a problem species and may be used in Florida.
Uses: shade; sidewalk cutout (tree pit); reclamation; street without sidewalk; deck or patio; specimen; parking lot island < 100 sq. ft.; parking lot island 100–200 sq. ft.; parking lot island > 200 sq. ft.; tree lawn 3–4 feet wide; tree lawn 4–6 feet wide; tree lawn > 6 ft. wide; highway median
Availability: not native to North America
Description
Height: 20 to 40 feet
Spread: 20 to 25 feet
Crown uniformity: irregular
Crown shape: vase
Crown density: moderate
Growth rate: fast
Texture: coarse
Foliage
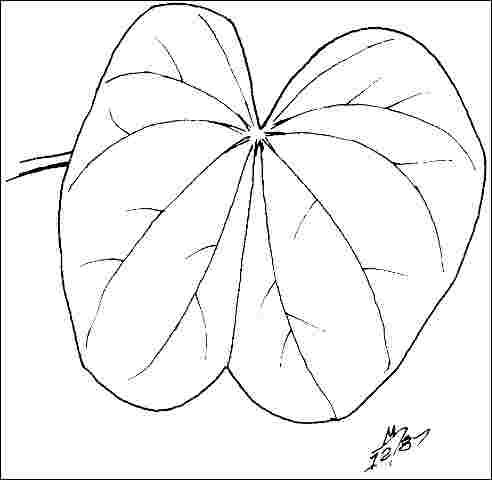
Leaf arrangement: alternate (Fig. 3)
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: cleft, lobed
Leaf shape: orbiculate
Leaf venation: palmate
Leaf type and persistence: evergreen, broadleaf evergreen
Leaf blade length: 2 to 4 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: no color change
Fall characteristic: not showy
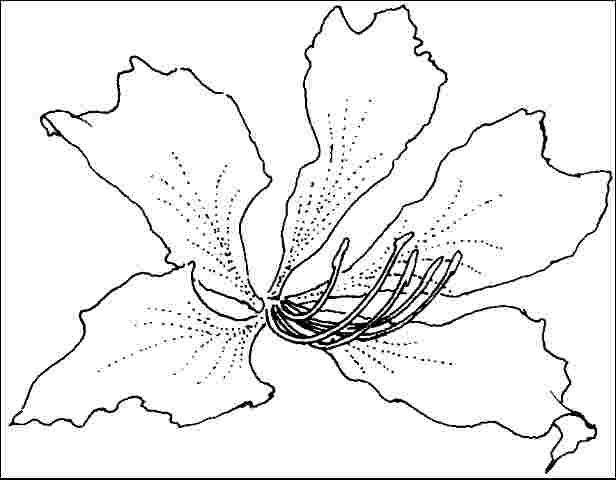
Flower
Flower color: red, purple
Flower characteristics: very showy
Fruit
Fruit shape: no fruit
Fruit length: no fruit
Fruit covering: no fruit
Fruit color: no fruit
Fruit characteristics: no fruit
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: branches droop; not showy; can be trained to one trunk; thorns
Pruning requirement: needed for strong structure
Breakage: susceptible to breakage
Current year twig color: brown
Current year twig thickness: medium, thin
Wood specific gravity: unknown
Culture
Light requirement: full sun, partial sun, or partial shade
Soil tolerances: clay; sand; loam; acidic; slightly alkaline; well-drained
Drought tolerance: high
Aerosol salt tolerance: moderate
Other
Roots: not a problem
Winter interest: yes
Outstanding tree: yes
Ozone sensitivity: unknown
Verticillium wilt susceptibility: unknown
Pest resistance: free of serious pests and diseases
Use and Management
Some people object to the debris which always seems to be falling from other orchid trees, but this one produces no fruit. It makes a beautiful specimen planted in parks or on large properties. They are well suited for planting along streets and in wide medians along a boulevard.
Hong Kong orchid tree grows in full sun on well-drained soil. Trees are very drought-tolerant and actually flower best on dry soils. Problems include a tendency to show nutritional deficiencies, especially potassium; the weak wood, which is susceptible to breakage in storms; and the litter problem created by the falling leaves and flowers. Orchid tree may need occasional pruning to maintain its shape.
Propagation is by cuttings or air-layering.
Pests
Borers, caterpillars, mites.
Diseases
Leaf spot, leaf scorch diseases.
Literature Cited
iversity of Florida, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences. 2018. "Assessment of Non-native Plants in Florida's Natural Areas" (https://assessment.ifas.ufl.edu, 4/29/2019) Gainesville, FL, 32611-4000, USA.