Introduction
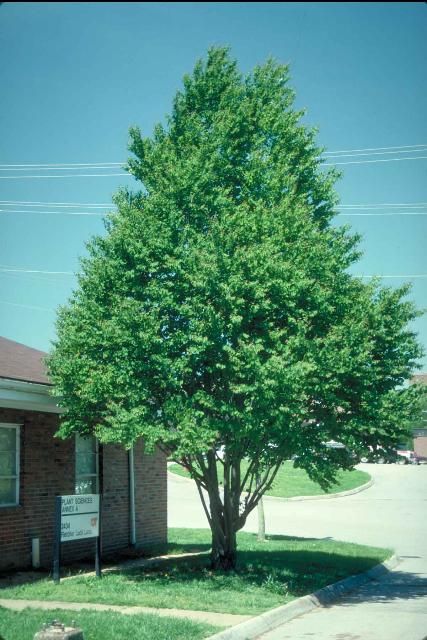
Katsuratree grows best in a sunny exposure and in a moist soil, but is considered drought-tolerant once established. The tree reaches a mature height and spread of 40 to 60 feet with a symmetrical canopy and new growth is reddish turning a light pale green. Fall color is a spectacular yellow, with some red. The growth rate is moderately rapid when young but slows down with age. The tree has a shallow root system and some of the roots can grow to 6 inches in diameter or more above the soil. The trunk normally flares out at the base, gracefully dividing into the numerous shallow roots often prominent at the soil surface.

Credit: Ed Gilman
General Information
Scientific name: Cercidiphyllum japonicum
Pronunciation: ser-sih-dih-FILL-um juh-PAWN-ih-kum
Common name(s): Katsuratree
Family: Cercidiphyllaceae
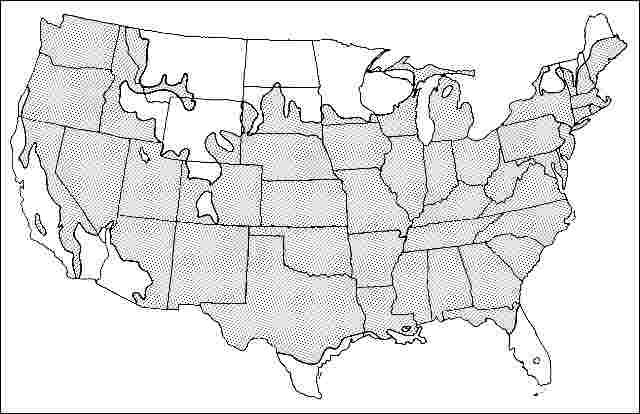
USDA hardiness zones: 4B through 8B (Fig. 2)
Origin: not native to North America
Invasive potential: little invasive potential
Uses: shade; street without sidewalk; specimen; parking lot island 100–200 sq ft; parking lot island > 200 sq ft; tree lawn 4–6 feet wide; tree lawn > 6 ft wide; highway median
Availability: not native to North America
Description
Height: 40 to 60 feet
Spread: 35 to 60 feet
Crown uniformity: symmetrical
Crown shape: oval, upright/erect, pyramidal, spreading
Crown density: moderate
Growth rate: fast
Texture: medium
Foliage
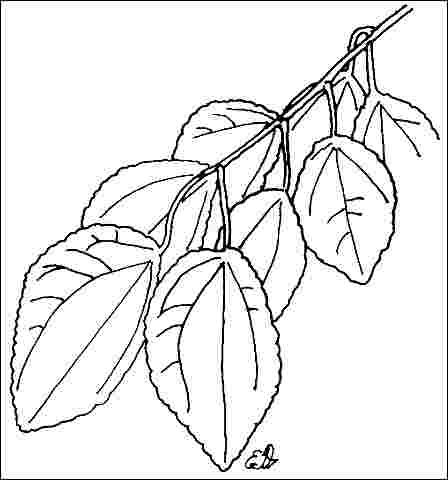
Leaf arrangement: opposite/subopposite (Fig. 3)
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: crenate
Leaf shape: ovate, orbiculate
Leaf venation: palmate, reticulate
Leaf type and persistence: deciduous
Leaf blade length: 2 to 4 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: yellow
Fall characteristic: showy
Flower
Flower color: green
Flower characteristics: not showy
Fruit
Fruit shape: pod or pod-like, elongated
Fruit length: .5 to 1 inch
Fruit covering: dry or hard
Fruit color: unknown
Fruit characteristics: does not attract wildlife; not showy; fruit/leaves not a litter problem
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: branches droop; showy; typically multi-trunked; thorns
Pruning requirement: needed for strong structure
Breakage: susceptible to breakage
Current year twig color: brown
Current year twig thickness: thin
Wood specific gravity: unknown
Culture
Light requirement: full sun, partial sun, or partial shade
Soil tolerances: clay; sand; loam; slightly alkaline; acidic; well-drained
Drought tolerance: moderate
Aerosol salt tolerance: moderate
Other
Roots: can form large surface roots
Winter interest: yes
Outstanding tree: yes
Ozone sensitivity: unknown
Verticillium wilt susceptibility: resistant
Pest resistance: free of serious pests and diseases
Use and Management
Katsuratree has an oval or pyramidal form in youth becoming more upright spreading with age and makes a good shade tree for residential property due to the medium stature. Male trees are more upright, female trees are more spreading. It may also have uses as a street tree where there is adequate soil space to prevent surface roots from raising walks and curbing. Select single stemmed specimens for street tree use and be sure that the major limbs are well spaced along a central trunk to prevent branches from splitting from the tree. Multi-stemmed trees are also sold and they make nice specimens for lawn and park areas, not street trees. Katsuratree has proven to be fairly pest free. Transplant in spring.
Katsuratree is intolerant of drought and should be protected from direct exposure to wind. Leaves often drop in mid to late summer in response to dry weather. Not suited for compacted soil since the shallow roots will be a nuisance for lawn and sidewalk maintenance. Provide irrigation and keep the soil beneath the canopy mulched. Coarse root system calls for production in fabric containers, frequent root pruning field-grown stock, or growing in air root-pruned containers.
The cultivar 'Pendula' grows 15 to 25 feet tall and displays a beautifully graceful, weeping form but it is hard to find.
Pests and diseases
None serious. Occasionally chewing insects eat the foliage.