Introduction
This deciduous tree is a selection from one of the parents of the popular London Planetree ( Platanus x acerifolia ) and has more deeply lobed leaves than the species. The leaves roll up on the ground and do not blow around in the fall like other Platanus spp. Leaves are almost silver maple-like. Capable of reaching perhaps 80 feet in height, the Oriental Planetree has very strong branches and was quite useful as a shade tree until disease struck. The wood of Platanus spp. is so tough, dense and hard it is often used for butcher's blocks and furniture. The springtime flowers are followed by fruits which are found on stalks in groups of three to 6. The attractive bark is cream colored and flaky and very striking in the winter.
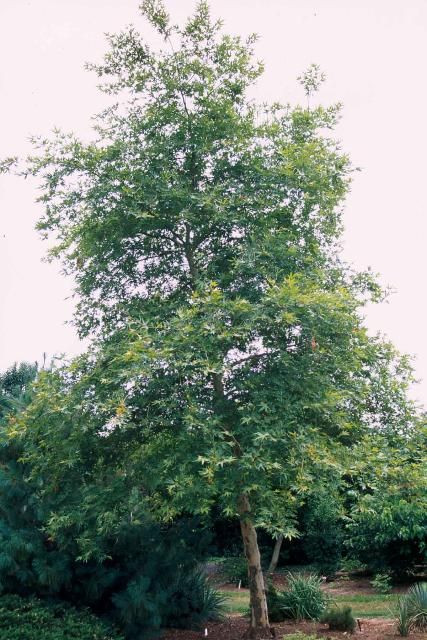

Credit: Ed Gilman
General Information
Scientific name: Platanus orientalis var. digitata
Pronunciation: PLAT-uh-nus or-ee-en-TAY-liss variety dij-ih-TAY-tuh
Common name(s): Cut-Leaf Oriental Planetree
Family: Platanaceae
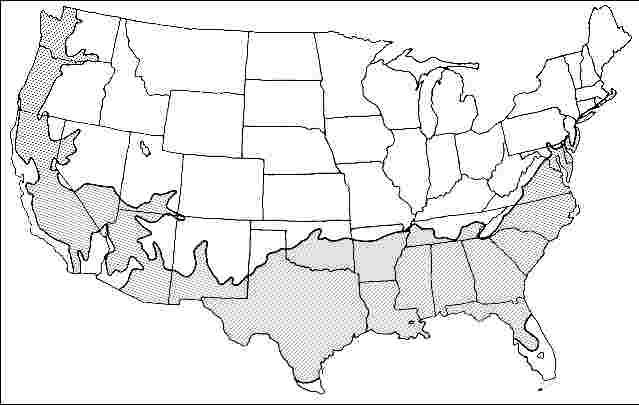
USDA hardiness zones: 7A through 9A (Fig. 2)
Origin: not native to North America
Invasive potential: little invasive potential
Uses: shade
Availability: not native to North America
Description
Height: 50 to 80 feet
Spread: 40 to 70 feet
Crown uniformity: symmetrical
Crown shape: round, pyramidal
Crown density: moderate
Growth rate: fast
Texture: coarse
Foliage
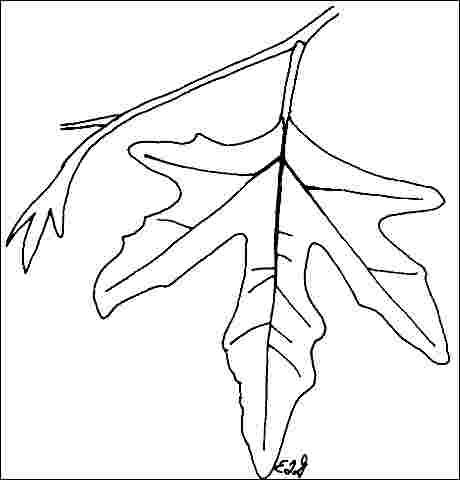
Leaf arrangement: alternate (Fig. 3)
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: incised, serrate, lobed
Leaf shape: ovate
Leaf venation: palmate
Leaf type and persistence: deciduous
Leaf blade length: 4 to 8 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: yellow
Fall characteristic: not showy
Flower
Flower color: unknown
Flower characteristics: not showy
Fruit
Fruit shape: round
Fruit length: .5 to 1 inch
Fruit covering: dry or hard
Fruit color: brown, tan
Fruit characteristics: does not attract wildlife; showy; fruit/leaves not a litter problem
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: branches droop; showy; typically one trunk; thorns
Pruning requirement: little required
Breakage: resistant
Current year twig color: brown
Current year twig thickness: medium
Wood specific gravity: unknown
Culture
Light requirement: full sun, partial sun or partial shade
Soil tolerances: clay; sand; loam; alkaline; acidic; occasionally wet; well-drained
Drought tolerance: high
Aerosol salt tolerance: unknown
Other
Roots: can form large surface roots
Winter interest: yes
Outstanding tree: no
Ozone sensitivity: unknown
Verticillium wilt susceptibility: resistant
Pest resistance: sensitive to pests/diseases
Use and Management
Naturally found along streams and floodplain riverbeds, Oriental Planetree should be grown in full sun or partial shade on moist soils. It grows on acid or alkaline soil, wet or dry. Leaves may drop early in dry years. Should be grown primarily for its resistance to anthracnose disease which can be devastating to American Sycamore, but it is rare in the trade.
Propagation is by cuttings which root easily but they transpire fast so they need lots of mist in the first week after being inserted into the growing media.
Pests
Pests are probably lace bug, and others.
Diseases
The cultivar probably will be subjected to the same disease problems as the species.