Introduction
Accurate estimation of cotton yield while in the field is an important skill for growers, consultants, and Extension agents. Preharvest estimation of cotton yield can help growers to determine their return on investment, assess weather-related damages, and adjust crop management. Although experienced eyes can provide a rough estimate by simply scanning the field, taking a few simple in-field measurements can reduce inaccuracies. This publication will outline the steps to calculate a reliable estimate of cotton yield.
The Field Procedure
Step 1: Count Bolls
For accurate estimation, you will need several representative areas in the field for sampling. The number of areas needed to accurately estimate yield will depend on field variability. In theory, a field that is perfectly uniform will need only one sampling area. On the other hand, a field with a lot of variability needs more sampling areas. It is recommended to stay away from field borders and other areas that are not representative of the field as a whole.
Identify and mark a 10-foot section of row. Count each harvestable boll, or bolls that will be harvestable when the picker runs through the field. This count should not include hardlocked or rotted bolls, or those that will not open by harvest (Figure 1).

Credit: M. Mulvaney, UF/IFAS
Step 2: Estimate Boll Weight
Next, estimate the average weight per boll. Bolls tend to weigh between 2–6 grams (0.07–0.21 oz). A true weight can be estimated by hand-picking a representative number of harvestable bolls in various parts of the field, counting them, weighing them, then dividing the weight by the number of bolls. This will give a more accurate average boll weight and will improve the accuracy of the yield estimate. Doing so, however, requires having a small scale in the field, or transporting the bolls to an indoor scale, which may not be practical. In those cases, using 4 g (0.14 oz) per boll as an average is a reasonable estimate (Figure 2).
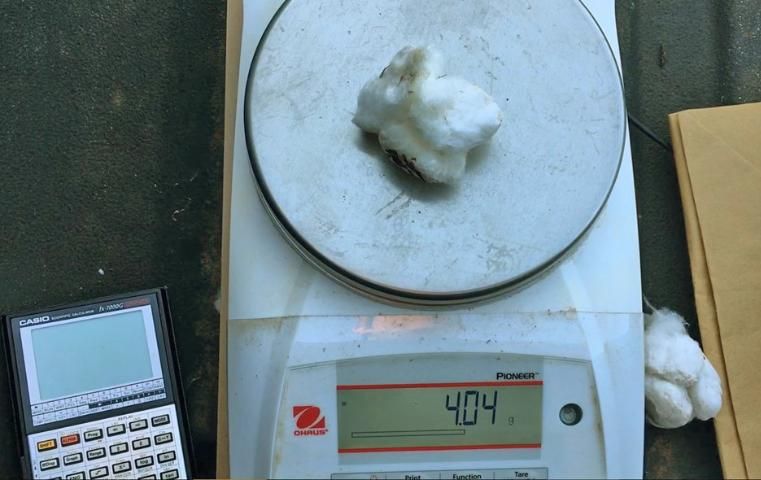

Credit: M. Mulvaney, UF/IFAS
Step 3: Estimate Picker Efficiency
Picker efficiency typically ranges between 75% and 95%. Under typical conditions, efficiency is expected to be between 85% and 90% (Goodman and Monks 2003). However, adverse growing conditions such as extreme weather, disease, lodging, or rank growth will reduce harvest efficiency and yield (Figure 3).

Credit: M. Mulvaney, UF/IFAS
In the Southeast, where storms are a major factor, leaning or lodged cotton with intertwined branches is fairly common. These factors should be considered when estimating picker efficiency. In these cases, use the lower end of the expected harvest efficiency range. On the other hand, new or well-maintained pickers will have higher harvest efficiencies, in which case the upper range should be used.
Step 4: Estimate Turnout
Turnout is the proportion of lint in seed cotton as determined by ginning. It is commonly between 35% and 40% of seed cotton. Crop health, environmental conditions, variety, and boll quality will impact ginning efficiency. A commercial gin generally operates near 38% turnout, which provides a reasonable estimate for yield estimation. If turnout data from previous harvests of the same cultivar at the same gin are available, then it is appropriate to use those values.
Determine Row Spacing
The row spacing is as simple as measuring the distance between rows, in inches.
Estimating Cotton Yield
At this stage, the variables are:
- Number of bolls in a 10-foot row
- Weight per boll
- Picker efficiency (percentage; as a decimal for calculation)
- Lint turnout (percentage; as a decimal for calculation)
- Row spacing (inches)
The equation uses the decimal form of picker efficiency and lint turnout (e.g., 87% written as 0.87 and 38% as 0.38). The formulas below have constants based on empirical data. These constants will differ depending on whether the boll weight was measured in grams or ounces. The constant is simply a value that has been derived from field observations to link the variables to yield (Goodman and Monks 2003). A sample calculation is given in Example 1.

If boll weight is in grams, then Equation 1 should be used to determine cotton lint yield in lb/acre.
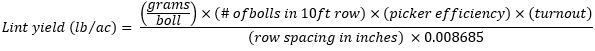
If the boll weight was measured in ounces, the formula requires a simple change of the boll weight input and the constant used to determine cotton lint yield in lb/acre, as shown in Equation 2.
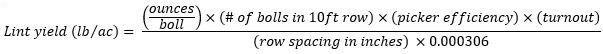
Economics to Inform Crop Management
The economic value of a boll can be used to inform crop management directly before harvest. The number of harvestable bolls can often be increased by a late-season application of a boll opener. It is useful to know how many additional bolls need to be opened to pay for an application.
Will the boll opener application be worth it?
Boll openers may increase the number of open, harvestable bolls. They can also help defoliate the crop, reducing leaf trash and staining of lint, thereby maintaining lint quality.
To find the minimum number of bolls needed to open to make a boll opener application worth the investment, first total the costs. The cost of a common boll opener in the Florida Panhandle in 2020 was $28/gallon. When applied at the labeled rate of 2 pints/acre, the cost comes to $7/acre. Assuming fuel and labor costs of $6/acre, there is a total cost of $13/acre for the application.
We also need to know how much we stand to gain from the application. The market price for cotton lint at the time of writing is $0.79/lb of lint. The farm gate value of lint is dependent on market forces and lint quality. Determining the number of additional bolls that need to open to pay for the application cost requires the same estimates of boll weight, picker efficiency, and lint turnout. Equation 3 shows the number of additional bolls needed to open in a 10-foot row. A sample calculation is given in Example 2.
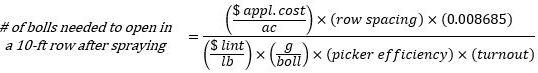

Using the example above, if 3.9 bolls are needed to open per 10-ft row to pay for the spray application, that number can be contextualized in terms of plant density. For example, if there are 3 plants/ft, totaling 30 plants in a 10-ft row, only one extra boll will need to open per 7.7 plants to cover the cost of the boll opener. Since upper bolls tend to weigh less than lower bolls, one should assume that those bolls are lighter on average, say 3 grams each. In that case, there will need to be an additional 5.2 bolls opened in a 10-foot row, or one extra boll opened for every 5.8 plants.
What is a boll worth?
The price per pound of cotton lint can be used to evaluate the value of a single boll, which can provide another tool, mainly of academic interest, for value assessment in the field. Given that there are 454 grams in one pound:
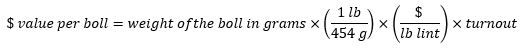
Using the current market price of lint cotton of $0.79/lb and assuming a 38% turnout:
A 2-gram boll is worth:
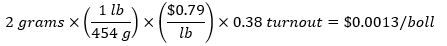
A 4-gram boll is worth:
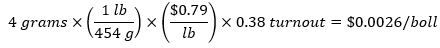
A 6-gram boll is worth:
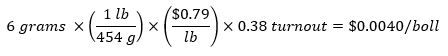
Considering the value of individual bolls provides some perspective regarding which bolls are worth protecting, boll value based on position on the plant, and the importance of boll size. Taken altogether, understanding the value of additional bolls supports cost-effective, yield-based decisions for cotton management.
Skip the Math
To skip the math and use a spreadsheet that will automatically estimate cotton lint yield and the economics for boll opener applications, click here, scan the QR Code below, or copy and paste this link into your search engine: https://wfrec.ifas.ufl.edu/media/wfrecifasufledu/docs/doc/Cotton-yield-estimate.xlsx

Credit: UF/IFAS
To watch this method in action as a step-by-step video, visit https://youtu.be/4u0gK_MoOOI.
Conclusion
Counting harvestable bolls provides an estimation of cotton lint yield that is more robust than observation alone. The benefits of this method are increased accuracy, improved confidence, cost-benefit analysis for boll opener applications, and the ability to calculate returns on investment. It can also provide reliable estimates of harvest before and after storms for insurance claims. Despite the relative improvements over visual estimation, this method provides an estimation only. Mechanical efficiencies, field variability, and boll weight can vary greatly over time and throughout the field. Nevertheless, this method of yield estimation is easy to use during field visits and provides improved reliability.
Reference
Goodman, W. R., and C. D. Monks. 2003. "A Farm Demonstrations Method for Estimating Cotton Yield in the Field for Use by Extension Agents and Specialists." Journal of Extension (41)6. https://archives.joe.org/joe/2003december/iw3.php