Key Plant: Southern Yew (Podocarpus macrophyllus)
Southern yew or podocarpus (Podocarpus macrophyllus) is a popular hedge used indoors and in landscapes, highway medians, shade hedges, and parking lot islands. Podocarpus’ dense foliage, evergreen color, and ease of growing in suboptimal soils make it an ideal plant for homeowners and commercial landowners alike. Though urban-tolerant, this hardy plant can quickly become a tree if left untrimmed, reaching heights of 30 to 40 feet (Figures 1 and 2). Native to southern China and Japan, this species can be found in USDA Hardiness Zones 8B–11 and is a slow-growing perennial (Gilman et al., 2019).

Credit: Brandon White, UF/IFAS

Credit: Brandon White, UF/IFAS
This publication provides information and general management recommendations to growers and homeowners for dieback, fusarium wilt, root nodules, root rot, aphids, eriophyid mites, and scale. For a more comprehensive guide of woody ornamental insect management, download “Professional Disease Management Guide for Ornamental Plants” or the “Integrated Pest Management in the Commercial Ornamental Nursery” guide. Additional information on pest management can be found in the 2017 Southeast Pest Control Guide for Nursery Crops and Landscape Plantings.
Key Infections and Their Potential Pests
Dieback (Botryodiplodia, Botryosphaeria, Phoma, and Phomopsis spp.)
Recognition
In the nursery, liners will progressively wilt to death as the pathogen girdles the stem. Terminals and side shoots die after a growth flush on larger plants, and the dieback may continue to the soil line. The symptoms may be confused with root rot, however, small, round, brown to black fruiting structures can be seen with a hand lens on the dead tissue at the point of invasion with dieback (Figure 3).
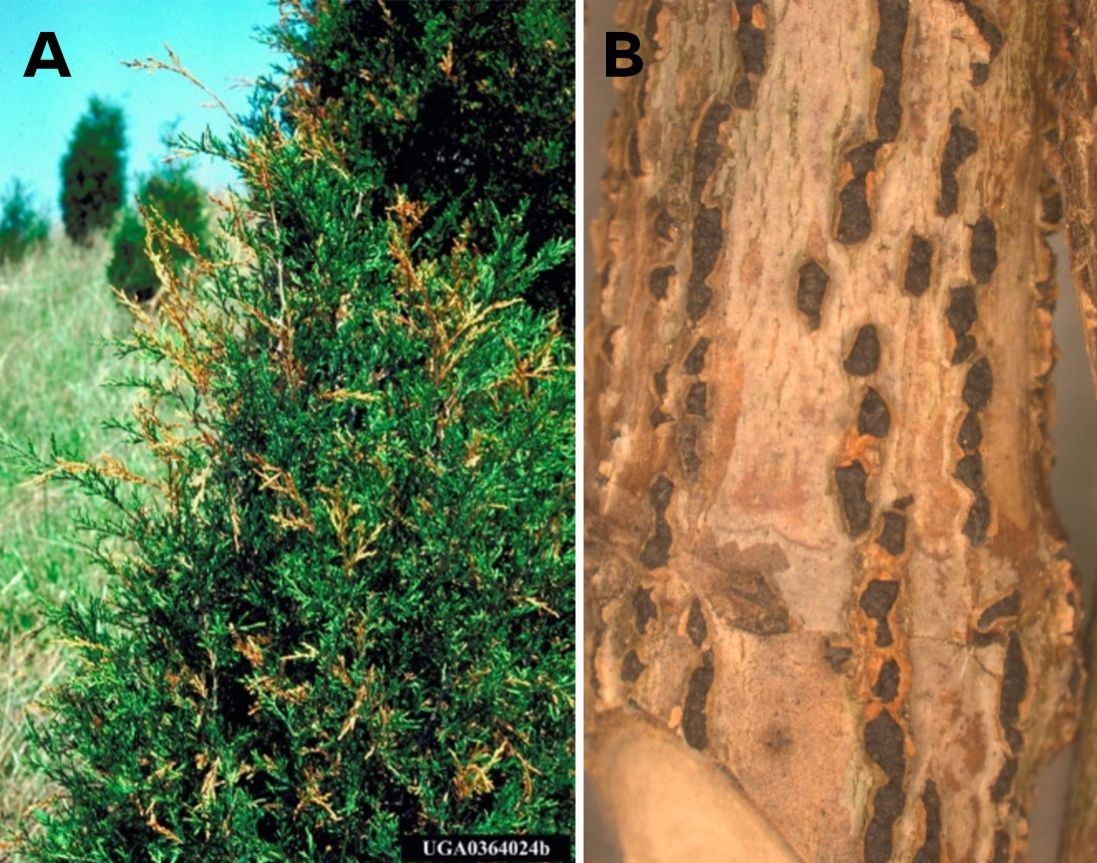

Credit: (A) Robert L. Anderson, United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service, Bugwood.org; (B) Nicholas Brazee, UMass Extension
Contributing Factors
Spores are spread through splashing water droplets. Frequent rainfall or irrigation triggers the release of spores from invaded bark or sapwood. Injury caused by shearing, sunscald, and cold-damaged, new growth increases chances of dieback infection.
Management Recommendations
Do not use diseased plants for propagation. You can prune out affected wood down to green wood on mature plants. Collect and dispose of the affected removed wood. If only one liner in a pot of several dies back, pruning out the dead wood is still needed to maintain the quality of the survivors. There are no effective fungicide treatments.
Fusarium Wilt (Fusarium oxysporum)
Recognition
Lower leaves develop a grayish-green cast and then turn brown. This may affect only one liner in a group or one side of a larger plant (Figure 4). A discoloration of the wood under the bark for several inches at or above the soil line can be seen. Root systems are discolored and deteriorated (Roberts et al., 2019).

Credit: Juanita Popenoe, UF/IFAS
Contributing Factors
Symptoms are worse in the summer when plant water demand is high. Fusarium is a soilborne pathogen that invades feeder roots. It is more likely to be a problem in field production but can also be found in container production when infested media or containers are reused without sterilization by heat or chemical fumigation.
Management Recommendations
Fungicides are not effective. At first diagnosis, move unaffected plants out of that area and do not put rooted liners on non-sterile soil that may contain the pathogen. Do not harvest seeds or cuttings from diseased plant material because the fungus may be present throughout the vascular system of the plant.
Root Rots (Phytophthora, Pythium spp.; Rhizoctonia solani)
Recognition
The first noticeable symptoms are discoloration and, thereafter, the death of lower leaves as the root system decays and the plant dies from the bottom up. These symptoms may be one-sided on the plant. Dead leaves remain on the plant, and a brownish-black discoloration can be seen in the sapwood. Wet rots cause a soft decay of the outer layers of roots, which can be easily stripped off between two fingers, leaving the firm, white stele intact (Figure 6).
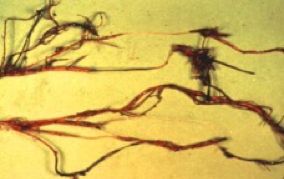
Credit: Juanita Popenoe, UF/IFAS
Contributing Factors
The disease is triggered by periods of excessive soil moisture and warm to hot temperatures. Conditions that favor disease development include planting too deep, poor drainage, shallow rooting, and poor water management.
Management Recommendations
Manage plants to keep them out of surface water by putting them on raised beds, ground cloth, or in well-drained soil. Reduce irrigation during rain periods. Fungicides can be used preventatively at potting, but are not much use after symptoms are noticed, because the root system will be significantly rotted before leaf symptoms are seen. Check roots of nursery-grown plants before planting them into the landscape. Provide adequate drainage and reduce irrigation.
Aphids (Most Common: Podocarpus)
Recognition
Often the first symptoms noticed of podocarpus aphids are the stunting and curling of the new terminal growth and the sooty mold. The podocarpus aphid adults are 1/16 of an inch long and dark reddish purple. The cornicles are very small and broader than long. Other aphids may lead to sooty mold but do not cause leaf distortion (Figures 6 and 7).

Credit: Lyle J. Buss, UF/IFAS
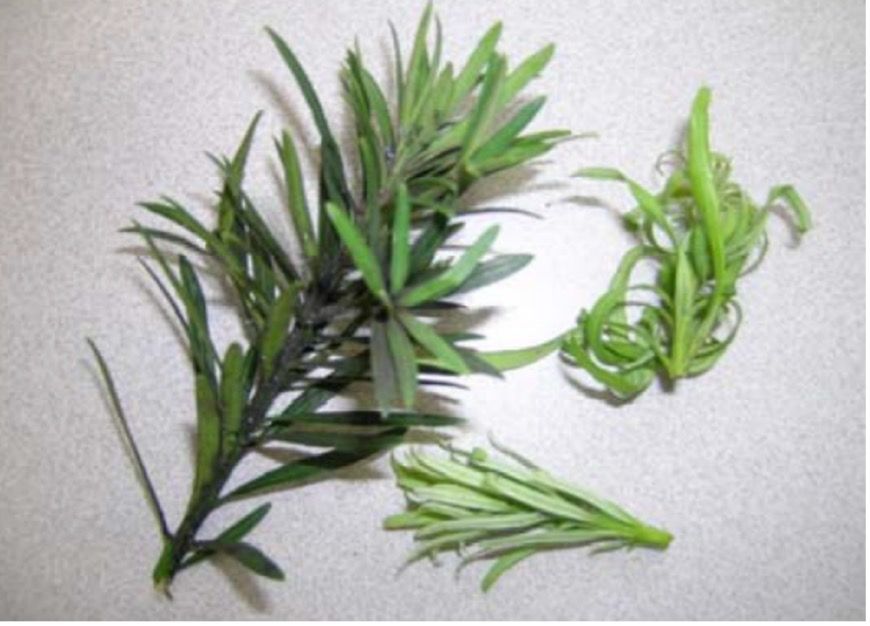

Credit: Juanita Popenoe, UF/IFAS
Contributing Factors
Aphid populations are at their largest in the spring when they feed on the new flush of growth and predator populations are low. High nitrogen levels lead to rapid flushes of new growth that are attractive to aphids.
Management Recommendations
Predators such as several species of lady beetles, lacewing larvae, and syrphid fly larvae will help to control populations. Insecticidal soaps and oils provide effective control and are less toxic than conventional insecticides.
Eriophyid Mite (Paracalacarus podocarpi)
Recognition
The mite (Figure 9) feeds on the terminal growth and causes stunting of new leaves; it also causes dark brown scarring of the terminal twigs and midrib of maturing leaves. The mite is light yellow and about the size of the citrus rust mite, although it is not related.
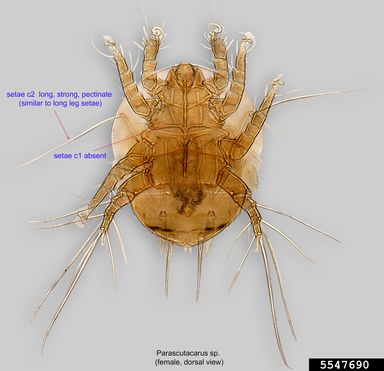
Credit: Pavel Klimov, Bee Mite ID, USDA APHIS PPQ, Bugwood.org
Contributing Factors
This mite has been found only in Florida and is specific to podocarpus.
Management Recommendations
Prune out and destroy affected growth.
Scale (Most Common: Asiatic Red, Cottony Cushion, and Indian Wax)
Recognition
Scale insects may be found on stems or leaves. Soft scales support the growth of sooty mold on the leaves beneath and may first be noticed because of the sooty mold (Figure 9). Scale feeding damage may result in chlorotic spots on the leaves and possible leaf drop. Eight species of scale are hosted on Podocarpus macrophyllus with Asiatic red, cottony cushion, and Indian wax being the most common. You may find the UF/IFAS publication “A Guide to Scale Insect Identification” useful in identifying specific species of scale.

Credit: Paul N. Choate, UF/IFAS
Contributing Factors
Most scale may be present year-round. Crawlers hatch in spring and should be monitored throughout the warm season.
Management Recommendations
If scale populations build to objectionable levels, oils or other approved insecticides may be used. The crawlers are the easiest stage to control.
Commonly Mistaken for Pests
Root Nodules (Mycorrhizal association)
Recognition
“Beaded root,” as it is often called, is not a disease or nematode but a beneficial mycorrhizal association (Figure 10). However, the nodules that line the roots may easily be confused with a nematode problem.

Credit: Juanita Popenoe, UF/IFAS
Contributing Factors
Mycorrhizae in soil.
Management Recommendations
None required.
References
Futch, S. H., C. W. McCoy, and C. C. Childers. 2018. A Guide to Scale Insect Identification. HS-817. Gainesville: University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/CH195
Gilman, E. F., D. G. Watson, R. W. Klein, A. K. Koeser, D. R. Hilbert, and D. C. McLean. 2019. Podocarpus macrophyllus: Podocarpus. ENH654. University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/ST495
Roberts, P. D., N. Dufault, R. Hochmuth, G. Vallad, and M. Paret. 2019. Fusarium wilt (Fusarium oxysporum F. SP. Niveum) of Watermelon. PP352. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/PP352