Introduction
This publication is one in a series of pictorial guides that is designed to assist in the identification of common freshwater fish parasites.
The information provided in this guide is not intended to be a complete, detailed description of each parasite or parasite group and its characteristics but rather is intended to assist in the visual identification of some of the most common species or groups of parasites seen in freshwater fish. For further information on each parasite, refer to publications in the "Recommended Reading" and "Reference" sections below.
Guide Information
- Target Tissue: provides the location on/in the fish where the parasite is most commonly found.
- Characteristic: provides a brief description about the appearance of the parasite.
- Size: provides the size or size range of the parasite. (1 µm = 0.001 mm = 0.0001 cm) (µm = micron or micrometer; mm = millimeter; cm = centimeter)
- Movement: provides the type of movement, if any, of the parasite.
- Note: provides a brief comment of interest about the parasite.
Dinoflagellates, Coccidia, Microsporidians, and Myxozoans
Dinoflagellate: Piscinoodinium
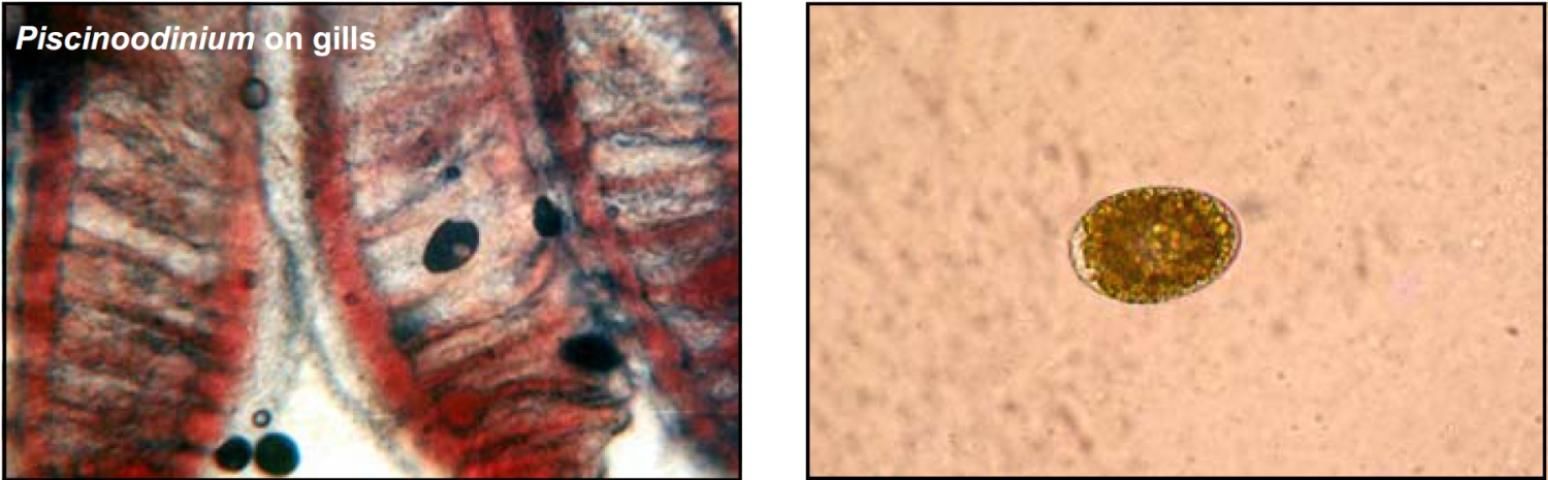
Target Tissues: Skin, fin, gills
Appearance: Oval shape with amber color, "granular" interior; may see clear area near middle and one end of oval
Size: Trophont approx. 12 μm x 96 μm
Movement: Not free-moving
Note: Most pathogenic to young fish; complex life cycle with stages on and off fish
Coccidia
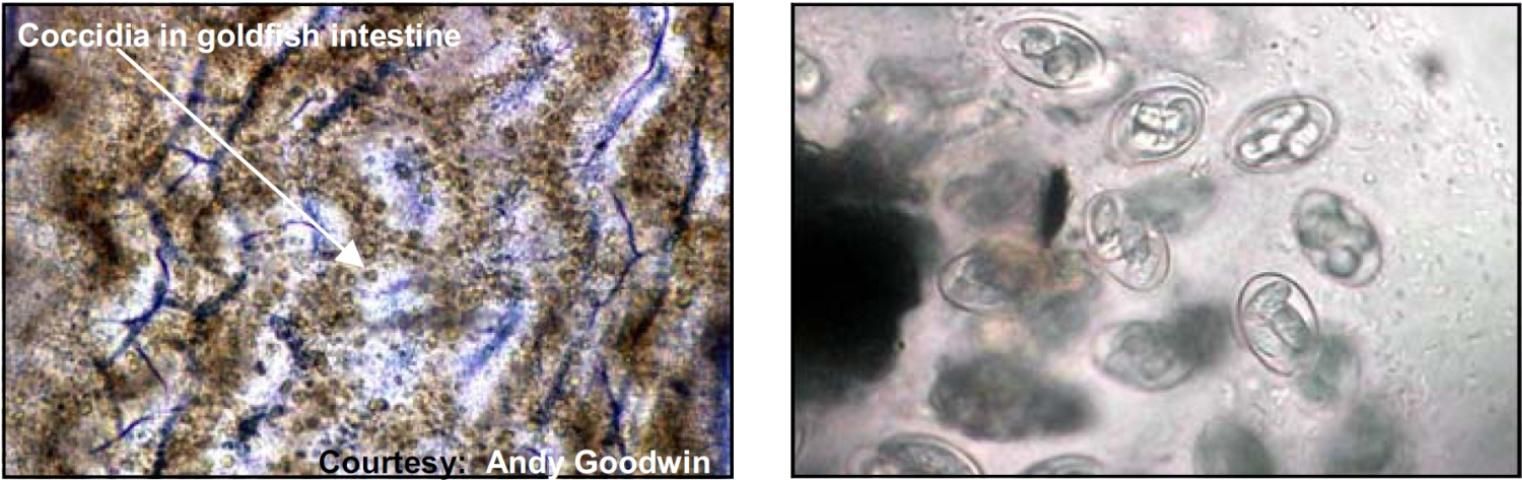
Target Tissues: Intestinal tract (most common); may be present in other organs
Appearance: Egg-shaped, clear oocyst; typically contains four sporocysts
Size: Approx. 25 μm in diameter
Movement: Not free-moving
Note: May or may not cause significant disease
Microsporidians
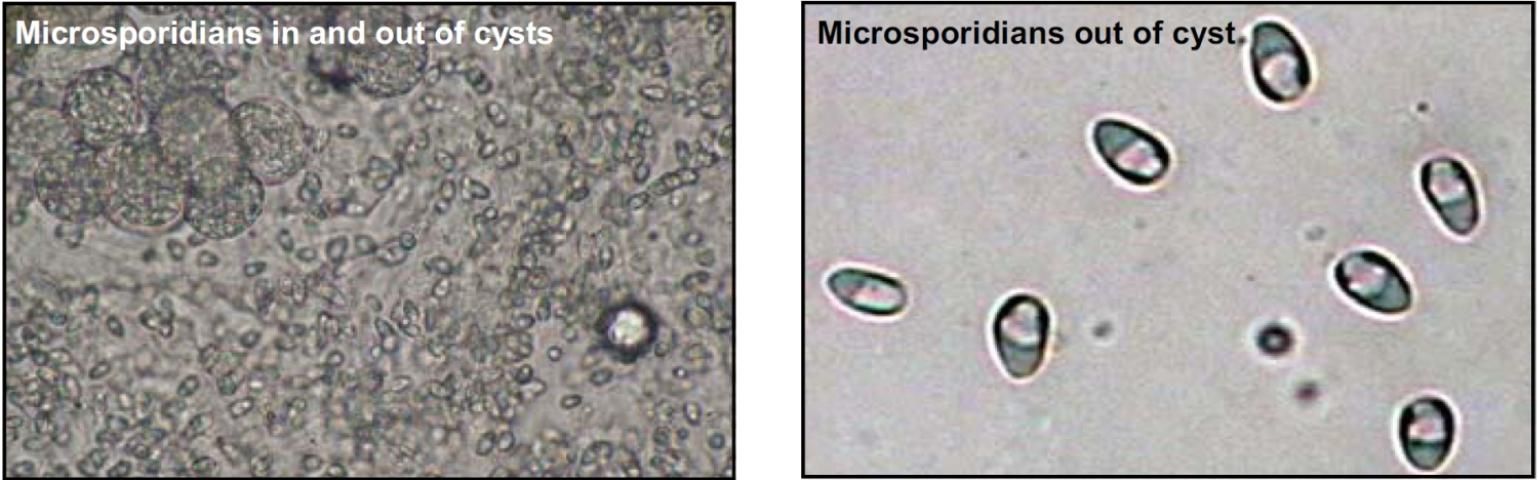
Credit: Courtesy of Andy Goodwin (left)
Target Tissues: Any; common in muscle for some fish
Appearance: Often see grainy-looking cysts first (parasites inside cyst); individual parasite shaped like egg or Dutch "wooden shoe"
Size: Spores approx. 3–10 μm; largest stage up to 50 μm
Movement: Not free-moving
Note: Burst cyst to "free" individual spores for identification; direct fish to fish transmission in species studied
Myxozoans
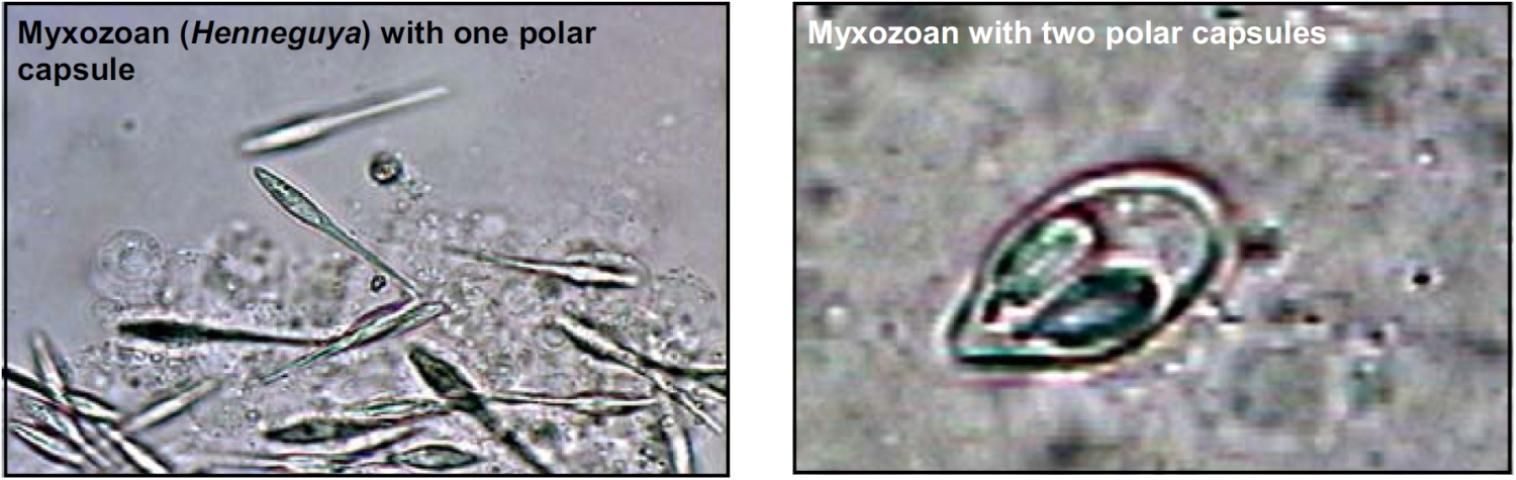
Target Tissues: Any
Appearance: Spores of different species vary greatly in shape and size; often see cysts first (parasites inside cyst); all spores have one to six polar capsules
Size: Spores approx. 8–20 μm
Movement: Not free-moving
Note: Burst cyst to "free" individual spores for identification; in species studied, indirect life cycle involving oligochaete worm
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Andy Goodwin for the photograph he contributed to this publication.
Recommended Reading
SRAC Publication No. 410 Calculating Treatments for Ponds and Tanks. Southern Regional Aquaculture Center. https://fisheries.tamu.edu/files/2013/09/SRAC-Publication-No.-0410-Calculating-Treatments-for-Ponds-and-Tanks.pdf
SRAC Publication No. 475 Proliferative Gill Disease (Hamburger Gill Disease). Southern Regional Aquaculture Center. https://fisheries.tamu.edu/files/2019/01/SRAC_0475.pdf
SRAC Publication No. 4701 Protozoan Parasites. Southern Regional Aquaculture Center. https://fisheries.tamu.edu/files/2013/09/SRAC-Publication-No.-4701-Protozoan-Parasites.pdf
UF/IFAS Circular 91 Nematode (Roundworm) Infections in Fish. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA091
UF/IFAS Circular 120 Fish Health Management Considerations in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems - Part 1: Introduction and General Principles. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA099
UF/IFAS Circular 121 Fish Health Management Considerations in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems - Part 2: Pathogens. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA100
UF/IFAS Circular 122 Fish Health Management Considerations in Recirculating Aquaculture Systems - Part 3: General Recommendations and Problem Solving Approaches. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA101
UF/IFAS Circular 716 Introduction to Freshwater Fish Parasites. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA041
UF/IFAS Circular 919 Stress--It's Role in Fish Disease. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA005
UF/IFAS Circular 920 Ichthyophthirius multifiliis (White Spot) Infections in Fish. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA006
UF/IFAS Circular 921 Introduction to Fish Health Management. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA004
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-13 Use of Copper in Freshwater Aquaculture and Farm Ponds. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA008
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-23 The Use of Potassium Permanganate in Fish Ponds. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA032
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-28 Monogenean Parasites of Fish. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA033
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-37 Use of Potassium Permanganate to Control External Infections of Ornamental Fish. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA027
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-55 Submission of Fish for Diagnostic Evaluation. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA055
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-90 Pentastomid Infections in Fish. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA090
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-107 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Sessile Ciliates. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA107
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-108 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Motile Ciliates. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA108
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-109 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Flagellates. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA109
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-111 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Monogeneans. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA111
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-112 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Digenean Trematodes. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA112
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-113 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Nematodes. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA113
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-114 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Acanthocephalans, Cestodes, Leeches, and Pentastomes. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA114
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet FA-115 Common Freshwater Fish Parasites Pictorial Guide: Crustaceans. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/FA115
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet VM-67 Management of Hexamita in Ornamental Cichlids. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/VM053
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet VM-77 Use of Formalin to Control Fish Parasites. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/VM061
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet VM-78 Bath Treatment for Sick Fish. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/VM037
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet VM-85 "Red Sore Disease" in Game Fish. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/VM059
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet VM-86 Use of Salt in Aquaculture. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/VM007
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet VM-87 Sanitation Practices for Aquaculture Facilities. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/AE081
UF/IFAS Fact Sheet VM-104 Cryptobia iubilans in Cichlids. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/VM077
References
Hoffman, G. L. 1999. Parasites of North American Freshwater Fishes. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press. https://doi.org/10.7591/9781501735059
Longshaw, M., and S. W. Feist. 2001. Parasitic Diseases. Pages 167–183 in W.H. Wildgoose, editor. BSAVA manual of ornamental fish, second edition. British Small Animal Veterinary Association, Gloucester, England. https://doi.org/10.22233/9781910443538.21
Noga, E. J. 1996. Fish Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment. St. Louis, MO: Mosby-Yearbook, Inc.
Stoskopf, M. K. 1993. Fish medicine. Philadelphia, PA: W. B. Saunders Company.
Woo, P. T. K., editor. 1995. Fish Diseases and Disorders, volume 1: protozoan and metazoan infections. CAB International, Wallingford, United Kingdom.