Introduction
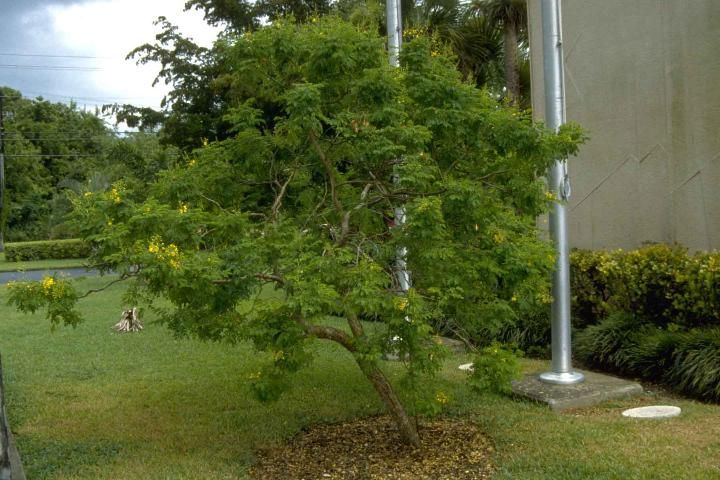
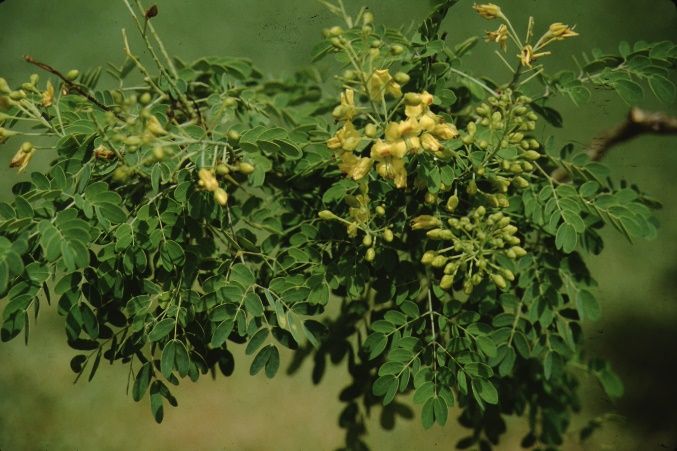
Fine textured foliage and bright yellow flowers borne on the new growth combine to make this a wonderful small tree or large shrub for any garden or landscape. Flowers cover the canopy for several months during the warm season. Soft flowers and pinnately compound foliage contrast with the small, inconspicuous thorns present along the stems. The pods are slightly curled and seeds germinate only locally in the landscape. They do not appear to spread to other landscapes.

Credit: Ed Gilman, UF/IFAS

Credit: Ed Gilman, UF/IFAS

Credit: Ed Gilman, UF/IFAS
General Information
Scientific name: Caesalpinia mexicana
Pronunciation: sez-al-PIN-ee-uh meck-sick-KAY-nuh
Common name(s): Mexican caesalpinia
Family: Leguminosae
Plant type: tree
USDA hardiness zones: 10B through 11 (Figure 4)
Planting month for zone 10 and 11: year round
Origin: not native to North America
Invasive potential: not known to be invasive
Uses: specimen; near a deck or patio; container or above ground planter; small parking lot islands (< 100 square feet in size); medium-sized parking lot islands (100-200 square feet in size); large parking lot islands (> 200 square feet in size)
Availability: somewhat available, may have to go out of the region to find the plant
Credit: undefined
Description
Height: 15 to 25 feet
Spread: 12 to 18 feet
Plant habit: round
Plant density: moderate
Growth rate: moderate
Texture: fine
Foliage
Leaf arrangement: opposite/subopposite
Leaf type: bipinnately compound
Leaf margin: entire
Leaf shape: elliptic (oval)
Leaf venation: pinnate
Leaf type and persistence: evergreen
Leaf blade length: less than 2 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: no fall color change
Fall characteristic: not showy
Flower
Flower color: yellow
Flower characteristic: summer flowering
Fruit
Fruit shape: pod or pod-like
Fruit length: 3 to 6 inches
Fruit cover: dry or hard
Fruit color: brown
Fruit characteristic: inconspicuous and not showy
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: can be trained to grow with a short, single trunk; not particularly showy; no thorns
Current year stem/twig color: brown
Current year stem/twig thickness: medium
Culture
Light requirement: plant grows in part shade/part sun
Soil tolerances: clay; acidic; well-drained; sand; loam; alkaline
Drought tolerance:
Soil salt tolerances: unknown
Plant spacing: not applicable
Other
Roots: usually not a problem
Winter interest: no special winter interest
Outstanding plant: not particularly outstanding
Pest resistance: long-term health usually not affected by pests
Use and Management
Locate Mexican caesalpinia in full sun in any spot in the landscape including near a patio or deck, or in a shrub border to add color and texture. Train the plant into a small tree by removing lower foliage and branches, or let the rounded form develop with branches drooping to the ground if there is enough room for it to spread. The outstanding flower display and small size makes it well suited for planting in a container, even in a hot, dry location. Good drought tolerance makes it well adapted for planting in parking lot buffer strips and in other tough sites.
Pest and Diseases
Leaf chewing insects occasionally eat some foliage. The plant has not been widely grown so its pest problems are not well known.