Introduction
This low growing plant can be used on dry sites. The main ornamental trait is the three-inch yellow flowers that contrast with the dark green foliage. The plant can grow a foot tall and can spread 1 ½ feet. There may be some top kill in winter in cold climate.

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS
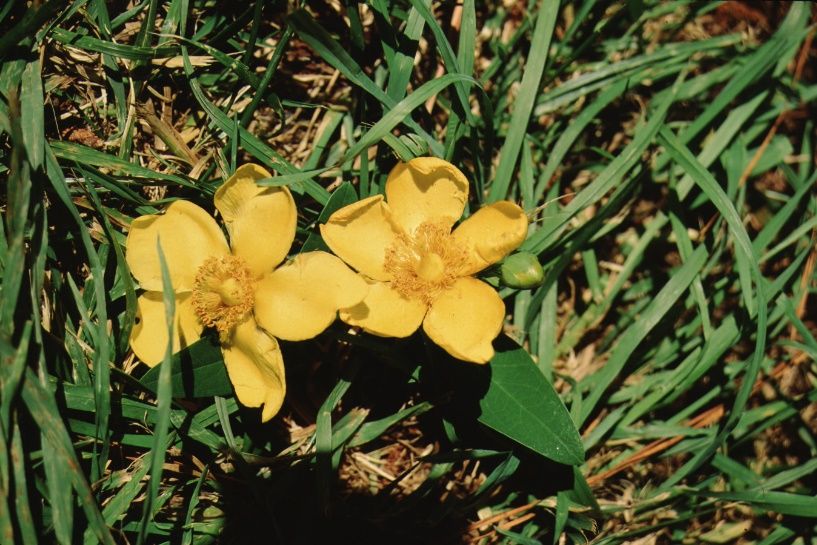

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS
General Information
Scientific name: Hypericum spp.
Pronunciation: hye-PAIR-rick-um species
Common name(s): St. John's wort
Family: Clusiaceae
Plant type: ground cover
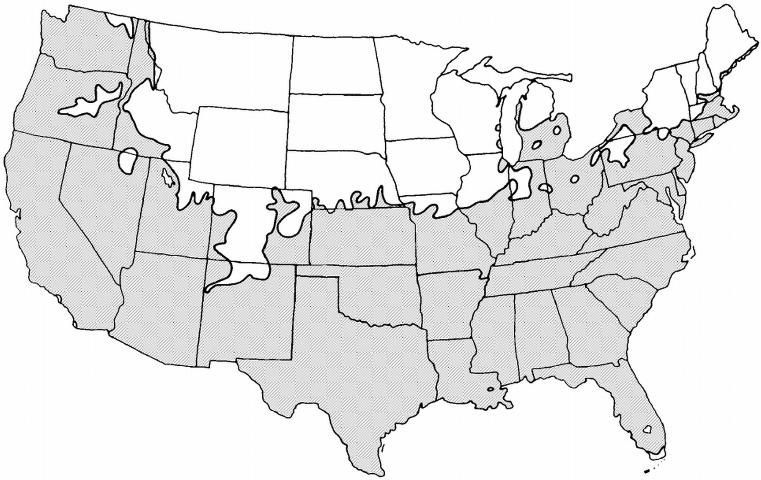
USDA hardiness zones: 5B through 10A (Figure 3)
Planting month for zone 7: year-round
Planting month for zone 8: year-round
Planting month for zone 9: year-round
Planting month for zone 10 and 11: year-round
Origin: native to Florida
Invasive potential: not known to be invasive
Uses: foundation; border; mass planting; edging
Availability: somewhat available, may have to go out of the region to find the plant
Credit:
Description
Height: 1 to 4 feet
Spread: 1 to 2 feet
Plant habit: spreading
Plant density: moderate
Growth rate: moderate
Texture: medium
Foliage
Leaf arrangement: opposite/subopposite
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: entire
Leaf shape: oblanceolate
Leaf venation: pinnate
Leaf type and persistence: deciduous
Leaf blade length: less than 2 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: no fall color change
Fall characteristic: not showy
Flower
Flower color: yellow
Flower characteristic: summer flowering
Fruit
Fruit shape: irregular
Fruit length: less than 0.5 inch
Fruit cover: dry or hard
Fruit color: brown
Fruit characteristic: showy
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: not particularly showy; typically, multitrunked or clumping stems
Current year stem/twig color: brown
Current year stem/twig thickness: very thick
Culture
Light requirement: plant grows in part shade/part sun
Soil tolerances: sand; occasionally wet; acidic; slightly alkaline; loam; clay
Drought tolerance: moderate
Soil salt tolerances: poor
Plant spacing: 24 to 36 inches
Other
Roots: not applicable
Winter interest: no special winter interest
Outstanding plant: plant has outstanding ornamental features and could be planted more
Pest resistance: long-term health usually not affected by pests