Introduction
Glossy, dark green leaves, easy care, and a natural mounding shape make pittosporum a popular landscape shrub. However, rapid growth when young makes this a fairly high maintenance shrub, requiring frequent pruning, but growth does slow with age. Clusters of creamy white flowers with a fragrance similar to orange blossoms appear in spring, but they are rarely seen on shrubs because they are frequently pruned off with the regular trimming required to keep the plant in check. It is really better suited as a small tree with lower branches removed to reveal the multi-stemmed trunk, and branches should be left unpruned to allow the flowers to show in the spring. Prune after the flower display. Careful training and pruning can create an ornamental small tree form.

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS
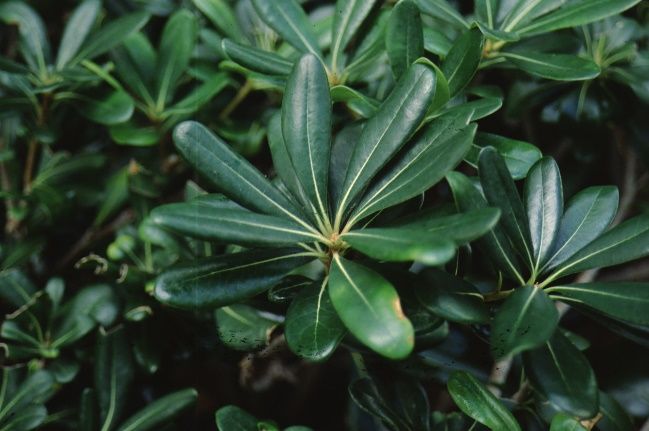

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS
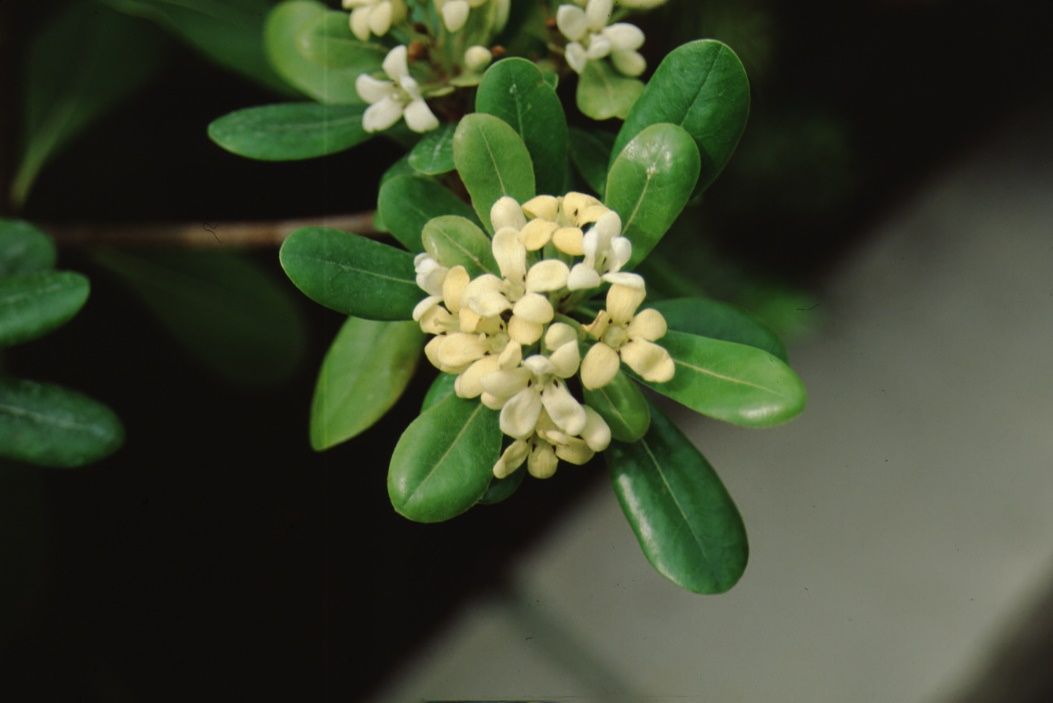

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS
General Information
Scientific name: Pittosporum tobira
Pronunciation: pit-tuss-SPOR-rum toe-BYE-ruh
Common name(s): Japanese pittosporum, Japanese cheesewood
Family: Pittosporaceae
Plant type: shrub; tree
USDA hardiness zones: 8 through 11 (Figure 4)
Planting month for zone 8: year-round
Planting month for zone 9: year-round
Planting month for zone 10 and 11: year-round
Origin: native to temperate Asia
Invasive potential: not considered a problem species at this time and may be recommended by UF/IFAS faculty (reassess in 10 years)
Uses: screen; hedge; border; mass planting; container or aboveground planter; trained as a standard; near a deck or patio
Availability: generally available in many areas within its hardiness range
Credit:
Description
Height: 8 to 12 feet
Spread: 12 to 18 feet
Plant habit: vase shape
Plant density: dense
Growth rate: moderate
Texture: medium
Foliage
Leaf arrangement: alternate
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: entire
Leaf shape: obovate
Leaf venation: pinnate
Leaf type and persistence: evergreen
Leaf blade length: 2 to 4 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: no fall color change
Fall characteristic: not showy
Flower
Flower color: white
Flower characteristic: spring flowering; pleasant fragrance
Fruit
Fruit shape: irregular
Fruit length: less than 0.5 inch
Fruit cover: dry or hard
Fruit color: red
Fruit characteristic: inconspicuous and not showy
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: not particularly showy; typically multi-trunked or clumping stems
Current year stem/twig color: gray/silver
Current year stem/twig thickness: medium
Culture
Light requirement: plant grows in part shade/part sun
Soil tolerances: alkaline; sand; acidic; loam
Drought tolerance: high
Soil salt tolerances: moderate
Plant spacing: 36 to 60 inches
Other
Roots: usually not a problem
Winter interest: no special winter interest
Outstanding plant: not particularly outstanding
Pest resistance: very sensitive to one or more pests or diseases which can affect plant health or aesthetics
Use and Management
Excellent when used as a specimen or informal shrubbery border, pittosporum can be maintained at any desired height by selective hand pruning. The stiff branches with dense foliage can be sheared if this is begun when they are young. Plant on 4 to 5 foot centers for mass planting.
Pittosporum is highly salt-tolerant and grows well on a variety of soils in full sun to partial shade. Growth rate is rapid on well-drained, acid soil of average fertility, although pittosporum can tolerate occasional drought. It does not tolerate poorly drained or wet soil since root rot quickly infects and kills the root system. This often occurs along foundations where drainage is poor or rain water accumulates from the roof or gutters.
The cultivar 'Wheeleri' has a more compact growth habit and is more suited to residential landscapes. 'Variegata' has creamy white variegated leaves and is quite susceptible to leaf spot diseases.
Propagation of the species is by cuttings or by seed.
Pests and Diseases
Problems include cottony cushion scale and aphids. Micronutrient deficiencies become obvious on soils with a high pH.
Leaf spot and root rot diseases can be problems for pittosporum.
Avoid planting in areas where water accumulates.