Introduction
Blackeyed Susan forms a clumping, 2 foot tall mound of foliage topped with a bright display of red/orange flowers bordered with yellow. Distribution of color in the flower varies depending on the cultivar and seed source. Flowering is more profuse when the faded blossoms are regularly removed. The flowers are useful for cutting. Space plants 18 to 24 inches apart in a mass planting to create a carpet of color. Plants can become weeds in the garden because seeds germinate readily in nearby beds. What a wonderful weed to have in the garden!

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS
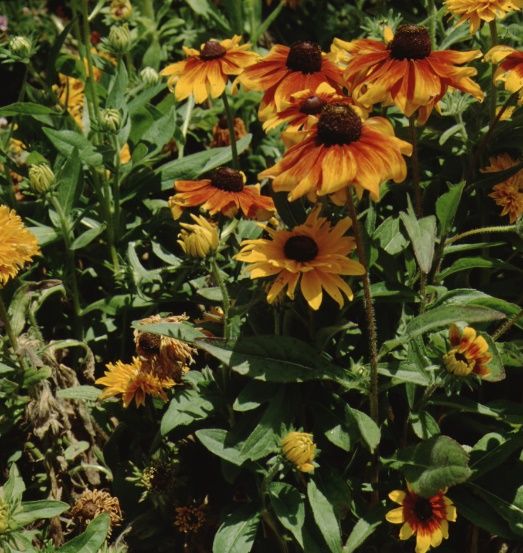

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS
General Information
Scientific name: Rudbeckia hirta
Pronunciation: rudd-BECK-kee-uh HER-tuh
Common name(s): blackeyed Susan, gloriosa daisy, coneflower
Family: Asteraceae
Plant type: annual; perennial; biennial; herbaceous
USDA hardiness zones: 2 through 11 (Figure 3)
Planting month for zone 7: Jun; Jul
Planting month for zone 8: May; Jun
Planting month for zone 9: Apr; May
Planting month for zone 10 and 11: Mar; Apr; Oct; Nov
Origin: native to North America
Invasive potential: may self-seed each year
Uses: mass planting; border; cut flowers
Availability: generally available in many areas within its hardiness range
Credit:
Description
Height: 2 to 3 feet
Spread: 2 to 3 feet
Plant habit: spreading; round
Plant density: open
Growth rate: moderate
Texture: medium
Foliage
Leaf arrangement: alternate
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: entire
Leaf shape: ovate
Leaf venation: none, or difficult to see
Leaf type and persistence: deciduous
Leaf blade length: 4 to 8 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: not applicable
Fall characteristic: not applicable
Flower
Flower color: orange-red; yellow
Flower characteristic: summer flowering; fall flowering
Fruit
Fruit shape: no fruit
Fruit length: no fruit
Fruit cover: no fruit
Fruit color: not applicable
Fruit characteristic: inconspicuous and not showy
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: not applicable
Current year stem/twig color: green
Current year stem/twig thickness: medium
Culture
Light requirement: plant grows in full sun
Soil tolerances: clay; sand; acidic; loam
Drought tolerance: high
Soil salt tolerances: good
Plant spacing: 12 to 18 inches
Other
Roots: not applicable
Winter interest: not applicable
Outstanding plant: not particularly outstanding
Pest resistance: long-term health usually not affected by pests
Use and Management
The many Rudbeckia species tolerate most well-drained soils if given full sun. Provide excellent drainage for best growth. High salt tolerance makes Rudbeckia well-suited for planting close to the beach.
Various flower color combinations of red, orange, and yellow are available in the five or more available cultivars. Rudbeckia hirta 'Indian Summer' is a sturdy selection with large, yellow flowers that develop 10 to 14 weeks after seeds are sown. Unlike many other blackeyed Susans, this one does not require staking. It is also relatively free of disease and insect problems.
Rudbeckia seed may be planted directly into the garden. The seed germinates in 5 to 10 days at temperatures between 70°F to 75°F. Seed started indoors germinates more quickly. Barely cover the seed. The plants wilt for one or two days after transplanting. Propagate perennial types by division. Rudbeckia is generally propagated in the garden by division or cuttings in the spring or fall season.
Pests and Diseases
Aphids suck sap from the plants and coat the leaves with sticky honeydew.
Goldenglow sawfly may completely defoliate plants. The larvae are gray with dark stripes.
Four-lined plant bug causes round, brown, sunken spots on the leaves. The injury is often mistaken for a disease.
Downy mildew causes seedlings to wilt and die. On older plants the foliage is mottled light yellow.
Several leaf spots may be found but are not serious. Remove and destroy infected leaves.
Powdery mildew may cause a white, powdery growth on the leaves in late summer.
White smut causes light spots on the leaves. Destroy plant residues in the fall and get rid of infected plants as you notice them.
Verticillium wilt may kill Rudbeckia spp.