Introduction
Tetrazygia is a marvelous large shrub or small tree that is native to south Florida. The attractive, evergreen leaves of this 10- to 30-foot-tall plant are lanceolate in shape and have 3 conspicuous veins that run lengthwise. These leaves are dark green with silvery underside and attain a length of 3 to 6 inches. White or pinkish blooms with bright yellow stamens appear in the spring and summer. These showy flowers occur in terminal clusters that are 4 to 5 inches long. Purple or black berries ripen in the late summer and fall and are persistent on the plant. The fruits are edible, some say delicious, and the birds are very fond of them.

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS
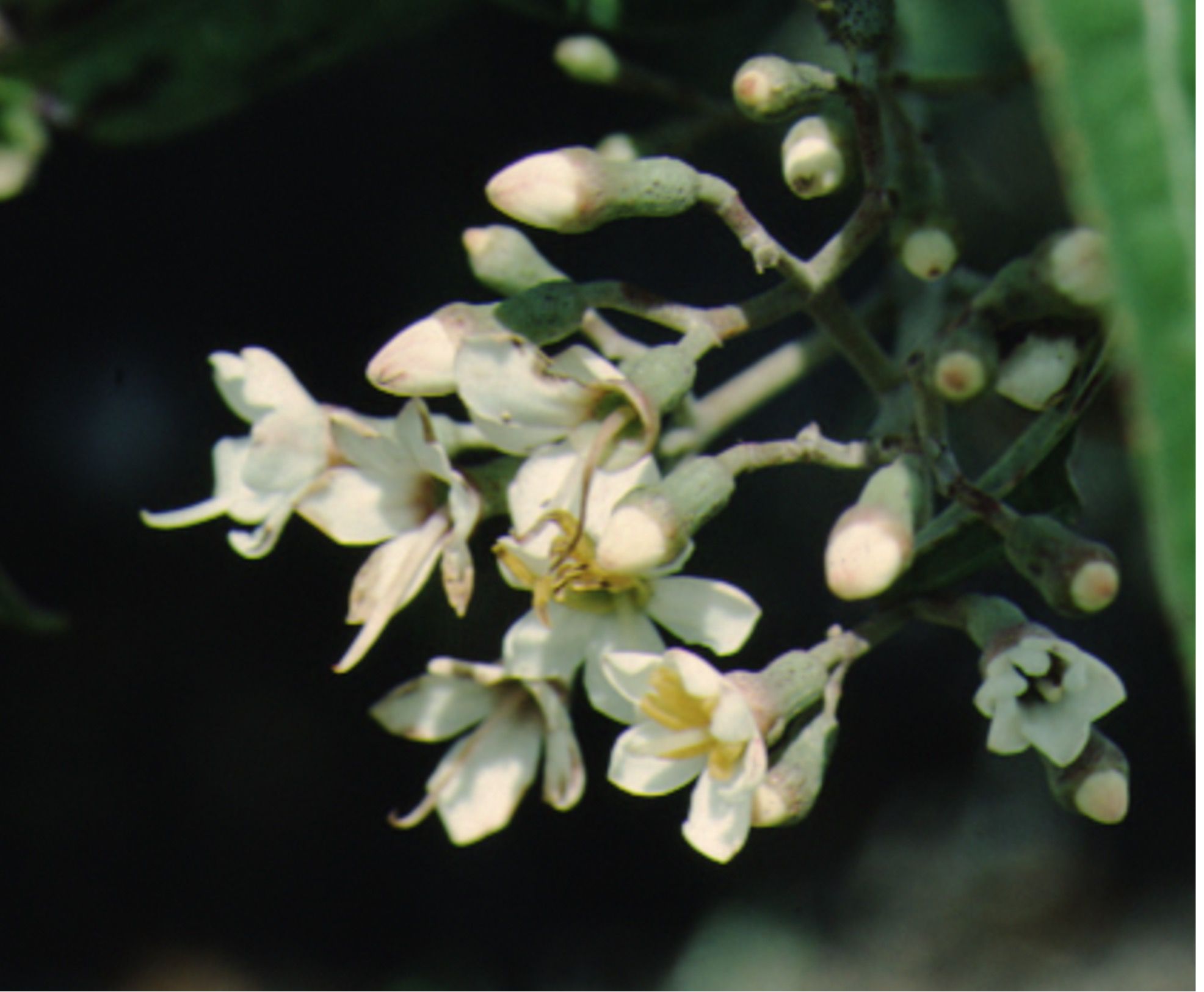

Credit: Edward F. Gilman, UF/IFAS
General Information
Scientific name: Tetrazygia bicolor
Pronunciation: tet-truh-ZIG-ee-uh BI-cull-ler
Common name(s): Florida tetrazygia, West Indian lilac, Florida clover ash, tetrazygia
Family: Melastomataceae
Plant type: shrub
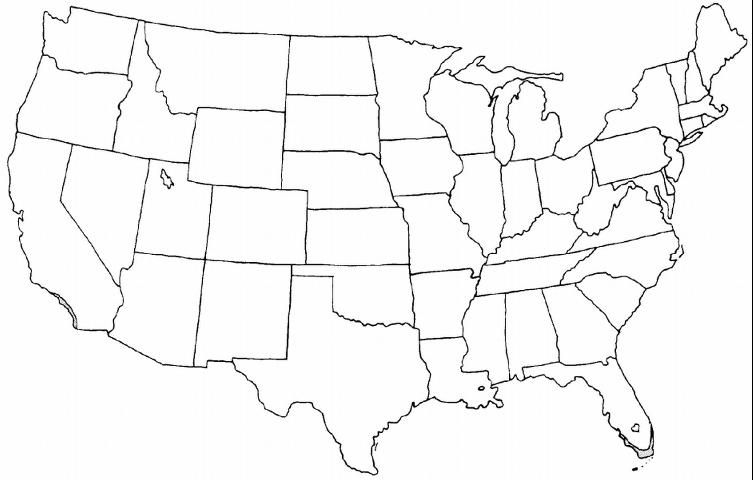
USDA hardiness zones: 10B through 11 (Figure 4)
Planting month for zone 10 and 11: year-round
Origin: native to Florida
Invasive potential: not known to be invasive
Uses: specimen; reclamation plant; trained as a standard; screen; foundation; border
Availability: grown in small quantities by a small number of nurseries
Credit:
Description
Height: 10 to 30 feet
Spread: 4 to 10 feet
Plant habit: oval
Plant density: open
Growth rate: moderate
Texture: medium
Foliage
Leaf arrangement: opposite/subopposite
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: entire
Leaf shape: lanceolate
Leaf venation: parallel
Leaf type and persistence: evergreen
Leaf blade length: 4 to 8 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: no fall color change
Fall characteristic: not showy
Flower
Flower color: white; pink
Flower characteristic: spring flowering; summer flowering
Fruit
Fruit shape: oval
Fruit length: less than 0.5 inch
Fruit cover: fleshy
Fruit color: brown
Fruit characteristic: suited for human consumption; persists on the plant; attracts birds
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: typically multi-trunked or clumping stems; can be trained to grow with a short, single trunk; not particularly showy
Current year stem/twig color: green; reddish
Current year stem/twig thickness: medium
Culture
Light requirement: plant grows in part shade/part sun
Soil tolerances: acidic; alkaline; sand; loam; clay
Drought tolerance: high
Soil salt tolerances: poor
Plant spacing: 36 to 60 inches
Other
Roots: usually not a problem
Winter interest: no special winter interest
Outstanding plant: plant has outstanding ornamental features and could be planted more
Pest resistance: no serious pests are normally seen on the plant
Use and Management
Tetrazygia can be used in the landscape as a specimen or tall hedge or screen. It is best to use a hand pruner instead of a hedge pruner to clip the plant because leaves are large. Large leaves look best if they are not cut during the clipping process, and it is hard to avoid cutting leaves in half with a hedge pruner. Some consider this plant to be one of the best landscape plants for central and south Florida. Unfortunately, it is seldom grown or used. The foliage presents a beautiful, drooping display of coarse texture that will fit into any landscape site, provided there is ample room for its large size.
Tetrazygia bicolor will survive in full sun but prefers partial shade. It will tolerate drought and grows well on most well-drained soils.
Tetrazygia can be propagated from seed.
Pests and Diseases
No pests or diseases are of major concern.