The Featured Creatures collection provides in-depth profiles of insects, nematodes, arachnids, and other organisms relevant to Florida. These profiles are intended for the use of interested laypersons with some knowledge of biology as well as academic audiences.
Introduction
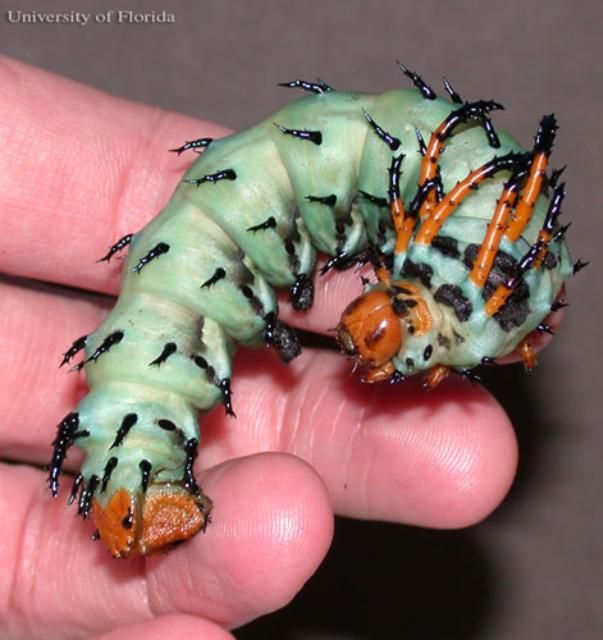
The regal or royal walnut moth, Citheronia regalis (Fabricius), is one of our largest and most spectacular moths. Like most other moths, it is nocturnal but is sometimes observed at lights. The imposing larva, known as the hickory horned devil, is most often observed when it is full grown and comes down from the trees to wander in search of a site for pupation.
The regal moth is a beautiful and fascinating member of our native fauna, and its larvae should not be killed. If a larva is found crawling on pavement or in an area of thick turf grass where it would have difficulty burrowing, it should be moved to an area of soft soil or a mulched area where it can burrow for pupation.

Credit: Lyle J. Buss, UF/IFAS
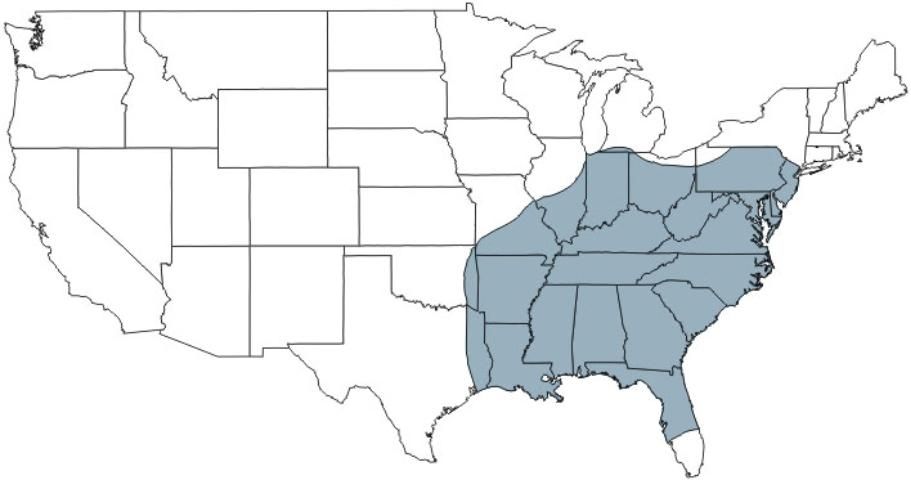
Distribution
The regal moth is found throughout the deciduous forest areas of the eastern United States from New Jersey to Missouri and southward to eastern Texas and central Florida (Wagner 2005). It is more common in the southern part of its distribution. Historically, it was found north to Massachusetts and seems to be declining in numbers in other parts of its range (Wagner 2005).
Description
Adult
The regal moth has a wingspan of 9.5 to 15.5 cm (3 ¾–6 1/8 in) (Covell 2005). Females are larger than males. The forewings are gray to gray-green with orange veins and a row of seven to nine yellow spots near the distal margin. There also are single yellow discal and basal spots. The hind wing is mostly orange with a basal yellow spot and yellow patches (or spots) on the costal and anal margins. The hind wing may also have one to two rows of gray-green spots. The body is orange with narrow yellow banding.

Credit: Donald W. Hall, UF/IFAS
Larva
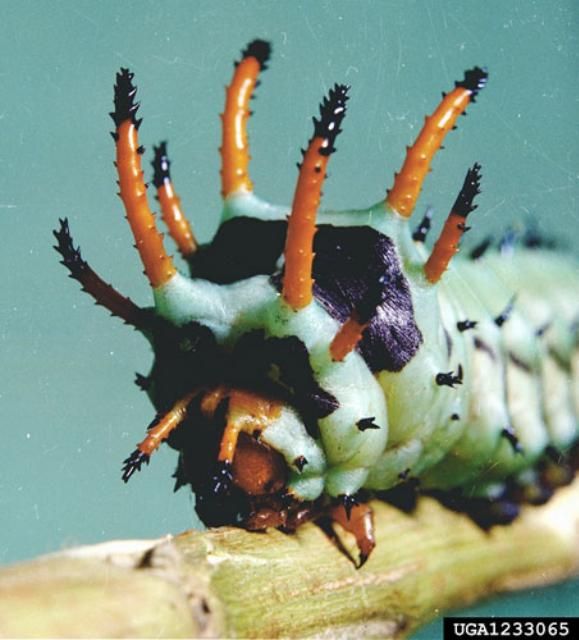
The hickory horned devil is among the largest of our native saturniid caterpillars. It is 12.5 to 14 cm (5–5 ½ in) in length—about the size of a large hot dog. The caterpillars vary slightly in color but are commonly blue-green. The second and third thoracic segments each bear two long and two shorter orange, black-tipped scoli (tubercles in the form of spinose projections of the body wall). The abdominal segments each have four short, black scoli, and segments 2 through 8 have a pale, oblique lateral stripe. Although the larva has a fierce appearance, it is harmless.

Credit: Lyle J. Buss, UF/IFAS

Credit: Clemson University, www.insectimages.org

Credit: Lyle J. Buss, UF/IFAS
For additional photographs of the regal moth and its life stages, see the North American Moth Photographers website.
Life Cycle
The regal moth typically has only a single generation per year, although a few late collection records suggest the possibility of a small second brood in the deep south. In Florida, adults have been collected in May, but are more common during the summer. Adults have vestigial mouthparts. Adults mate during the second evening after emergence and begin oviposition at dusk of the third evening. Eggs hatch in six to 10 days, and the duration of the larval stage is about 35 days. In central Florida, larvae are usually found from late July to mid-August while they are wandering on the ground searching for a suitable location to burrow into the soil for pupation. The pupa is the overwintering stage.
Worth (1979) reported that a small number of regal moth pupae diapaused through two winters. Locality (or latitude) where the parent moths were collected was not given, but the author's address was listed as New Jersey.

Credit: Lyle J. Buss, UF/IFAS
Hosts
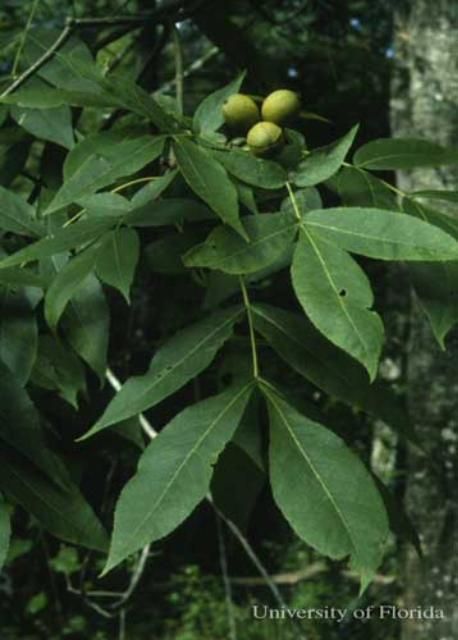
Larvae have been reported from a variety of host tree species. They are commonly found on species of the family (Juglandaceae) including walnut (Juglans nigra), butternut or white walnut (Juglans cinerea), and a variety of hickories (Carya spp.) including pecan. Other hosts commonly listed are persimmon (Diospyros virginiana), sweetgum (Liquidambar styraciflua), and sumacs (Rhus spp.). Of these latter three host plants, Worth et al. (1979 & 1982) reported that larvae grew faster and larger on persimmon. For detailed host lists, see Heppner (2003) and Robinson et al. (undated).

Credit: Donald W. Hall, UF/IFAS

Credit: Donald W. Hall, UF/IFAS

Credit: Donald W. Hall, UF/IFAS

Credit: Donald W. Hall, UF/IFAS
Natural Enemies
At least six species of tachinid flies (Diptera: Tachinidae) (Arnaud 1978; Peigler 1994), one species of sarcophagid fly (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) (Peigler 1994), and one species of braconid wasp (Krombein & Hurd 1979) have been reported from Citheronia regalis.
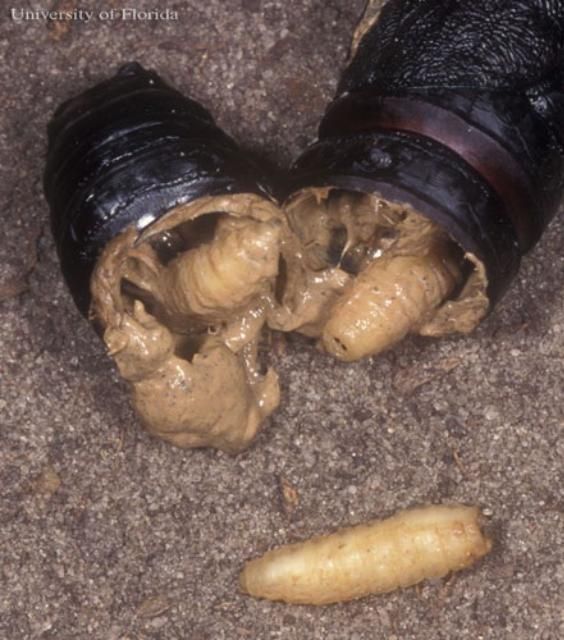

Credit: Lyle J. Buss, UF/IFAS
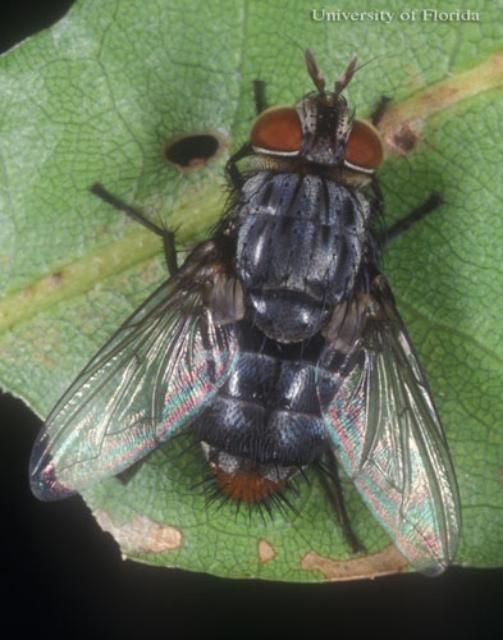

Credit: Lyle J. Buss, UF/IFAS
Selected References
Arnaud PH. 1978. A Host-Parasite Catalog of North American Tachinidae (Diptera). United States Department of Agriculture Miscellaneous Publication 1319. Washington, D.C.
Arnett RH Jr. 1985. American Insects. Van Nostrand Reinold Company, Inc. New York. p. 587.
Covell CV. 2005. A Field Guide to the Moths of Eastern North America. Virginia Museum of Natural History. Special Publication Number 12. Martinsville, VA. 496 pp. Ferguson DC. 1971. The Moths of North America. E.W. Classey Ltd. Middlesex, England. pp. 32–33.
Heppner JB. 2003. Lepidoptera of Florida. Part 1. Introduction and Catalog. Volume 17 of Arthropods of Florida and Neighboring Land Areas. Division of Plant Industry. Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services. Gainesville, Florida. 670 pp.
Krombein KV, Hurd Jr. PD, Smith DR, Burks BD. 1979. Catalog of Hymenoptera in America North of Mexico. Volume 1. Symphyta and Apocrita (Parasitica). Smithsonian Institution Press. Washington, D.C. 1198 pp.
North American Moth Photographers Group. http://mothphotographersgroup.msstate.edu/species.php?hodges=7706
Peigler RS. 1994. Catalog of parasitoids of Saturniidae of the world. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 33: 1–121.
Robinson GS, Ackery PR, Kitching IJ, Beccaloni GW, Hernández LM. HOSTS - a Database of the World's Lepidopteran Hostplants.
Stehr FW. 1987. Immature Insects. Vol. 1. Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company. Dubuque, IA. p. 515.
Tuskes PM, Tuttle JP, Collins MM. 1996. The Wild Silk Moths of North America. Cornell University Press. Ithaca, NY. 250 pp.
Wagner DL. 2005. Caterpillars of Eastern North America. Princeton University Press. Princeton, New Jersey. 512 pp.
Worth CB. 1979. Doubly overwintering Citheronia regalis Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society. 33(3): 166.
Worth CB, Williams TF, Platt AP, Bradley BP. 1979. Differential growth among larvae of Citheronia regalis (Saturniidae) on three genera of foodplants. Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 33(3): 162–166.
Worth CB, Platt AP, Williams TF. 1982. Differential growth and utilization of three food plants by first instar larvae of Citheronia regalis (Saturniidae). Journal of the Lepidoptera Society 36: 76–82.