The Featured Creatures collection provides in-depth profiles of insects, nematodes, arachnids and other organisms relevant to Florida. These profiles are intended for the use of interested laypersons with some knowledge of biology as well as academic audiences.
Distribution
Diadegma insulare is found in the United States and South America: New Hampshire west to southern British Columbia, south to Florida, Texas, and California; Hawaii, West Indies, and Mexico south to Venezuela.
These wasps are found in cruciferous crops, overwintering as a cocoon. The number of generations per year corresponds to the number of generations of its hosts: Hellula undalis (F.), Plutella armoracia Bsk., and P. xylostella (L.), the diamondback moth.
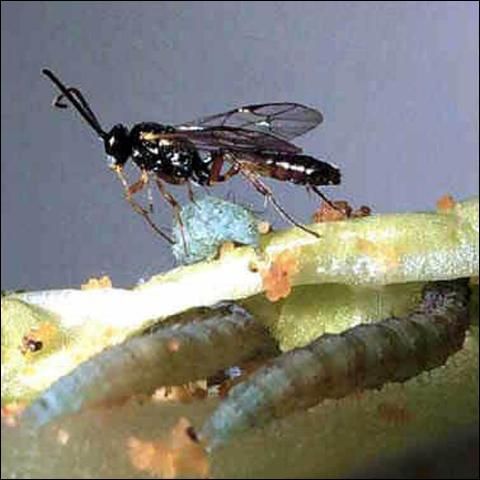

Credit: Andrei Sourakov, Florida Museum of Natural History
Description
Egg
The egg is clear and is hard to distinguish from the host's fat body when it is dissected. Unlike Cotesia plutella, another parasitoid of the diamondback moth, the egg is rounded rather than pointed and lacks a projection.
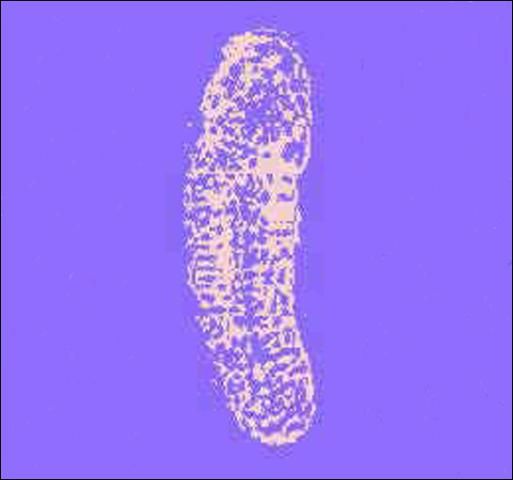
Credit: Guangye Hu, USDA
Larva
The larva of Diadegma insulare is white and can be noticed more easily in a dissected host due to its extensive movements. It looks strongly segmented and bears a short (1/4 of the total length of the larva) narrow "tail".
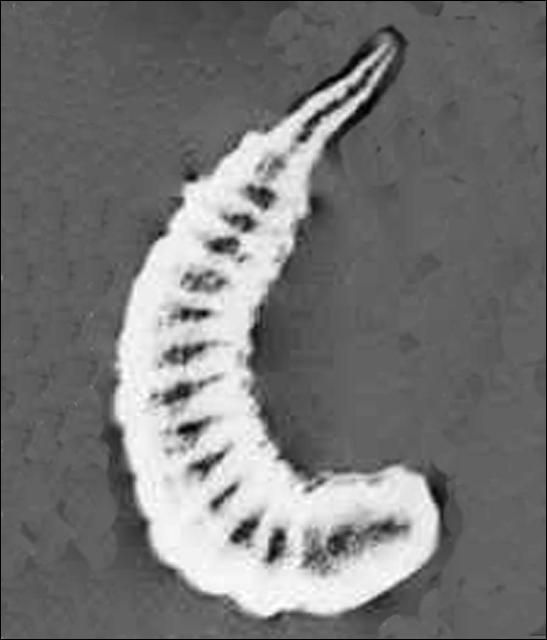
Credit: Guangye Hu, USDA
Pupa
The larva of Diadegma insulare stays inside the diamondback moth larva until the latter spins a cocoon and is ready to pupate. Once emerged, Diadegma insulare's larva spins its own cocoon inside the cocoon of the moth.
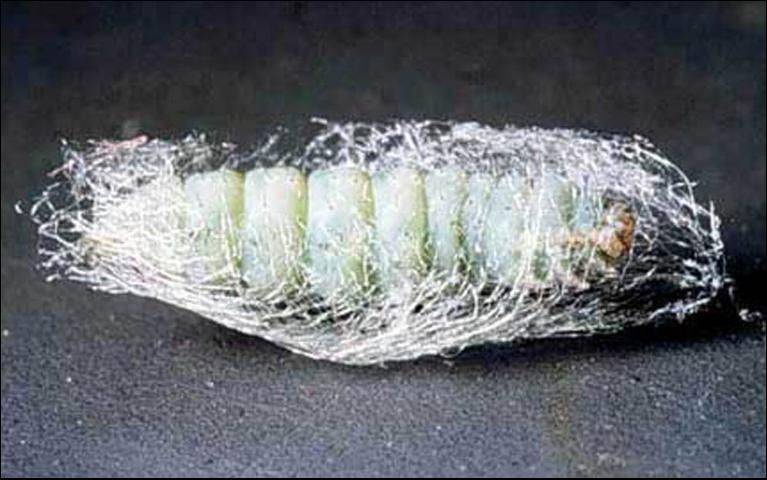

Credit: Andrei Sourakov, Florida Museum of Natural History
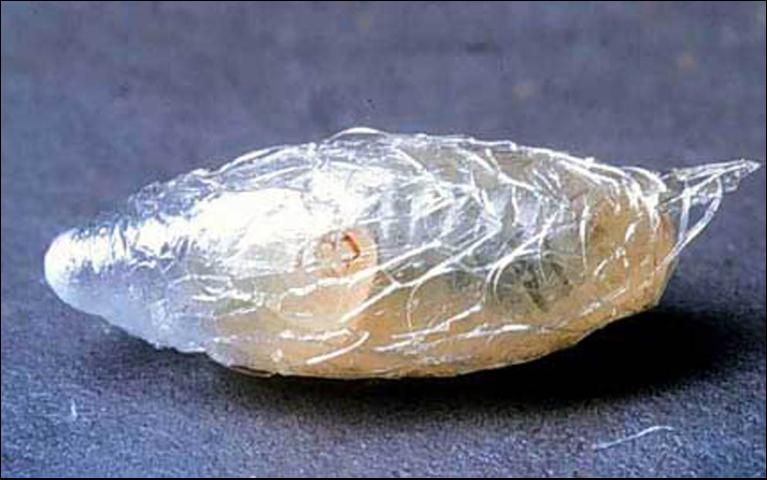

Credit: Andrei Sourakov, Florida Museum of Natural History
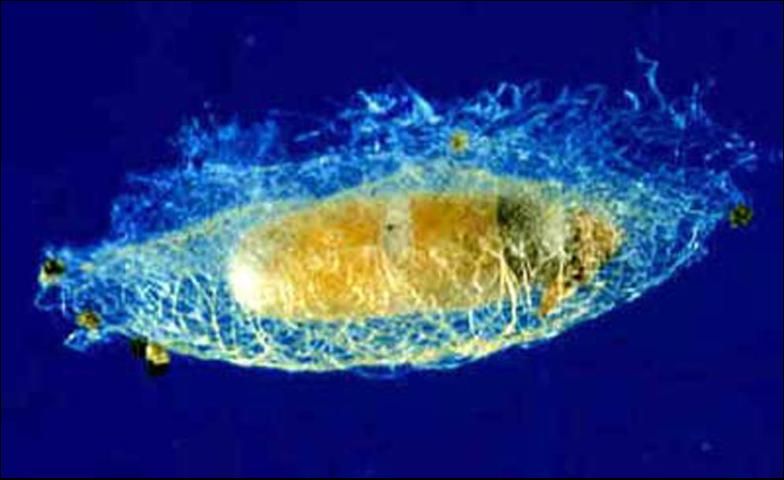
Credit: Guangye Hu, USDA
Adult
The length of this wasp does not exceed 6 mm (1/4 in). The female has a well defined ovipositor.
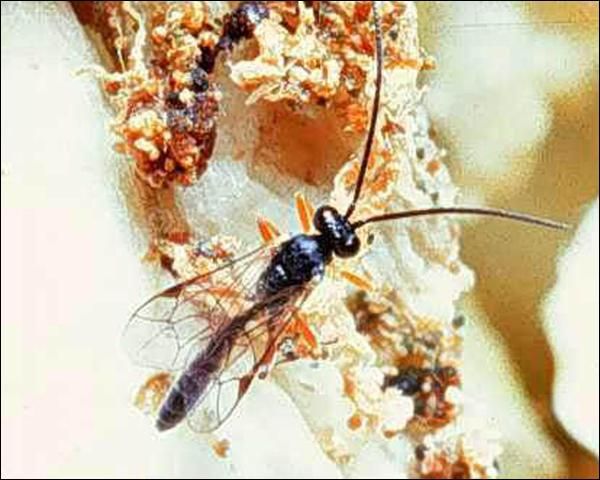

Credit: Andrei Sourakov, Florida Museum of Natural History
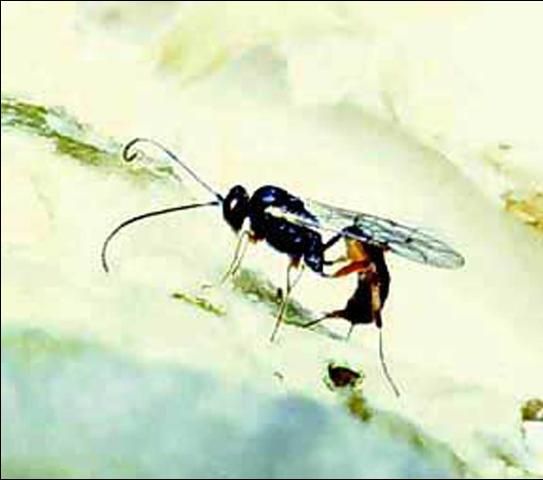

Credit: Andrei Sourakov, Florida Museum of Natural History
Importance
Diadegma insulare is the most important naturally occurring enemy of the diamondback moth as it can parasitize up to 90% of its larvae. Not only the parasitized larvae die, but they also do less damage, consuming 80% less food than the non-parasitized individuals. Diadegma insulare can be reared in captivity, but mass rearing presents many challenges. For instance, the wasps rarely parasitize larvae that are reared on artificial diet. Hence, the larvae have to be presented to the wasps while feeding on a cruciferous plant (e. g., cabbage).
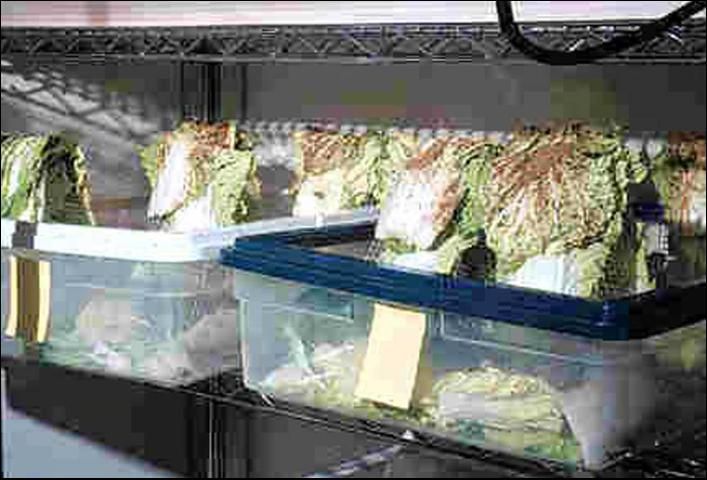

Credit: Andrei Sourakov, Florida Museum of Natural History
Conservation
Diadegma insulare is highly susceptible to pesticides, which kill adult wasps through direct contact. The larvae inside the host also die when pesticides kill their hosts. Thus, major outbreaks of the diamondback moth are more likely in fields that are sprayed heavily, and to avoid such outbreaks one needs to conserve the Diadegma populations by planting its nectar sources and limiting the use of pesticides.
Selected References
Harcourt, D.G. 1960. Biology of the Diamondback Moth, Plutella maculipennis (Curt.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae), in Eastern Ontario. III. Natural Enemies. The Canadian Entomologist, 92: 419–428.
Harcourt, D.G. 1963. Major mortality factors in population dynamics of the diamondback moth, Pluttella maculipennis (Cur.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Memoirs of the Entomological Society of Canada 32: 55–56.
Hoffmann, M.P. and Frodsham, A.C. 1993. Natural Enemies of Vegetable Insect Pests. Cooperative Extension, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY. 63 pp.
Idris, A. B. and E. Grafius. 1993. Field studies on the impact of pesticides on the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) and parasitism by Diadegma insulare (Cresson) (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae). Journal of Economic Entomology 86: 1196–1220.
Lasota, J. A., Kok L. T. 1986. Diadegma insulare (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) parasitism of the diamondback moth (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) in southwest Virginia. Journal of Entomological Science 21: 237–242.
Mitchell, E. R., G. Y. Hu, and J. S. Okine. 1997. Diamondback moth (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) infestation and parasitism by Diadegma insulare (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) in collards and adjacent fields. Florida Entomologist 80: 54–62.
Mitchell, E. R. et al. (February 2000). Stage by stage comparison of parasitoids important in biocontrol of cabbage pests. USDA. http://www.usda.ufl.edu/biocontrol/guide.htm (March 2000).