The Featured Creatures collection provides in-depth profiles of insects, nematodes, arachnids and other organisms relevant to Florida. These profiles are intended for the use of interested laypersons with some knowledge of biology as well as academic audiences.
Introduction
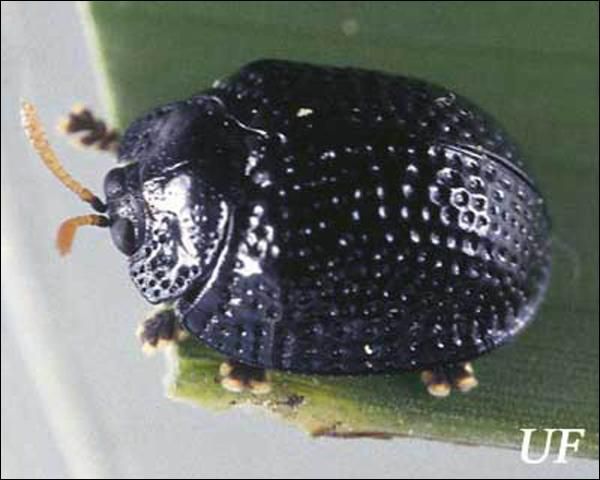
The Florida tortoise beetle, Hemisphaerota cyanea (Say), is a beautiful small beetle on a variety of native and exotic palms on which it occasionally inflicts damage by its feeding activities. It is our only tortoise beetle that feeds on palms.
Distribution
The Florida tortoise beetle is recorded from Florida, Georgia, Alabama, and Texas, and also probably occurs in Louisiana and Mississippi in areas where palms grow.
Description
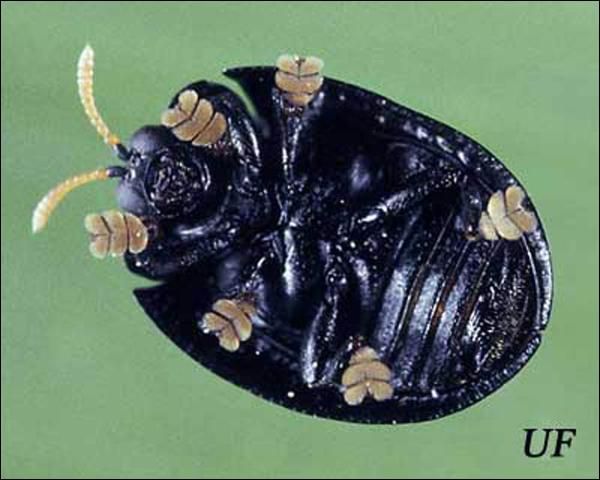
The adult beetle is dark blue to purple in color. It has alternating longitudinal rows of pits and ridges on the elytra. Its hemispherical shape is the basis for its genus name. The antennae are yellow except for the basal segment which is black. The tarsi are greatly enlarged and modified for grasping the substrate.
Each of the greatly enlarged tarsi is equipped with approximately 10,000 adhesive bristles. Each bristle has two terminal pads. When walking, only a few of the bristles touch the leaf surface. However, when attacked by a predator, the beetle puts all or nearly all of the bristles in contact with the surface and secretes oil onto the pads. With the adhesive force created by the oil between the leaf surface and tarsi, the beetle is able to clamp its hemispherical shell down tightly against the leaf and has been demonstrated to withstand pulling forces of approximately 60 times its own weight for up to two minutes. This time period is sufficient to thwart the efforts of predatory ants attempting to pry the beetle from the leaf. The oils used are similar to those of the cuticle of insects and are not believed to be unique for the defensive function. The wheel bug, Arilus cristatus (L.) (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) is able to overcome the defenses of the beetle—possibly by injecting toxic saliva to kill the beetle.

Credit: J. F. Butler, UF/IFAS

Credit: J. F. Butler, UF/IFAS
Life Cycle
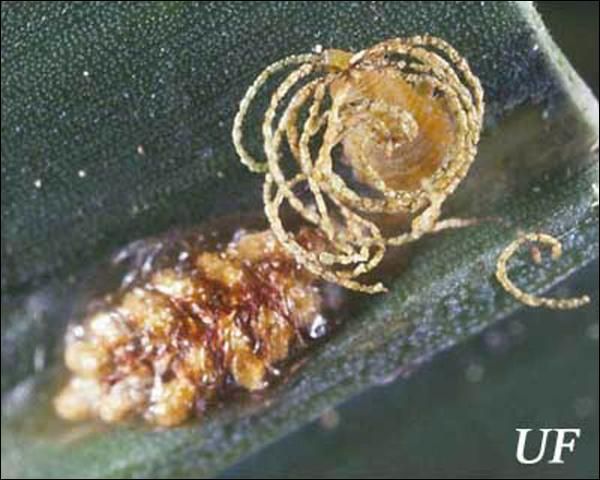
Eggs are yellow and elongated. They are cemented to host leaves and then covered with a double row of fecal pellets by the adult female. The fecal covering probably protects the eggs from predators and parasitoids. In Georgia, viable eggs were present from early March to mid-April.
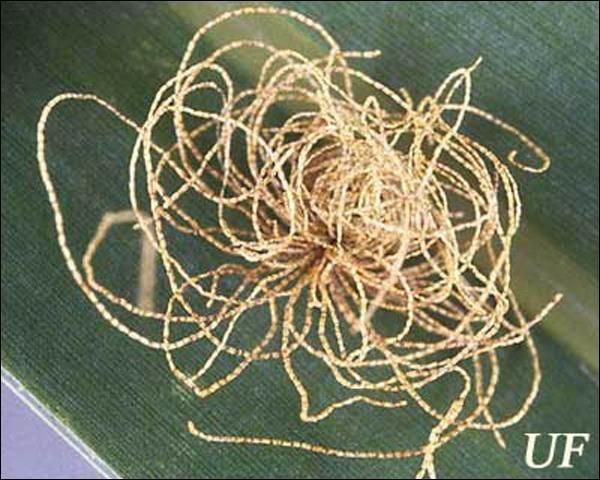
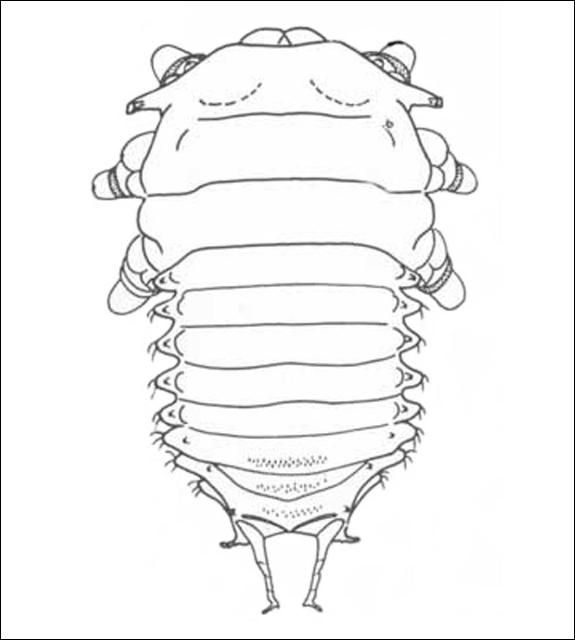
Upon hatching, the young larva begins to excrete strands of dry feces that curl up over its back and accumulate to form a dense thatch-like shield. Larvae have an anal fork to hold the fecal shield in place. The fecal shield has been shown to be an effective defense against a predacious larva of Cycloneda sanguinea (L.) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) and the predacious stink bug, Stiretrus anchorago (Fabricius) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). However, the carabid beetle, Calleida viridipennis (Say) (Coleoptera: Carabidae) is able to penetrate the larva's defense by chewing through the shield or by getting underneath it and prying it up.
The larvae cause trough-like feeding damage as they scarify the leaf epidermis, but rarely cause significant economic damage to trees.
Credit: J. F. Butler, UF/IFAS

Credit: J. F. Butler, UF/IFAS
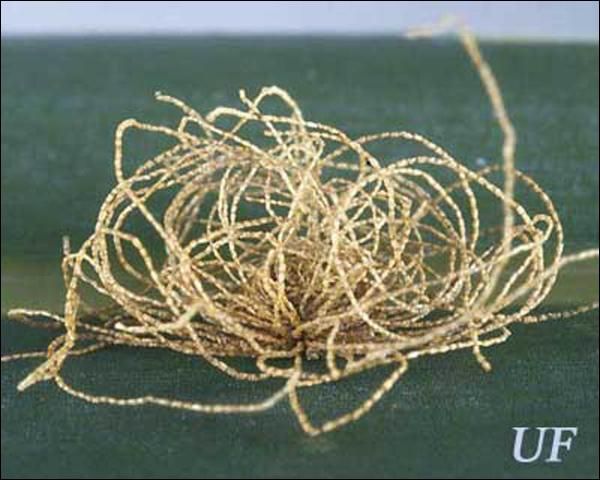

Credit: J. F. Butler, UF/IFAS
Credit: M. W. Sanderson, Illinois Natural History Survey
After reaching maturity, the larva clings to the leaf surface and pupates under the fecal thatch. Larvae and pupae are found throughout mid to late summer. Adults are found throughout the entire year.
The Florida tortoise beetle is found most commonly on native saw palmetto, Serenoa repens, but also feeds on cabbage palm, Sabal palmetto (W. Bartram) Small, dwarf palmetto, Sabal minor (Jacq.) Pers., scrub palmetto, Sable etonia Swingle ex Nash, and probably other native palms. It also has been reported from a variety of exotic palms in Florida.
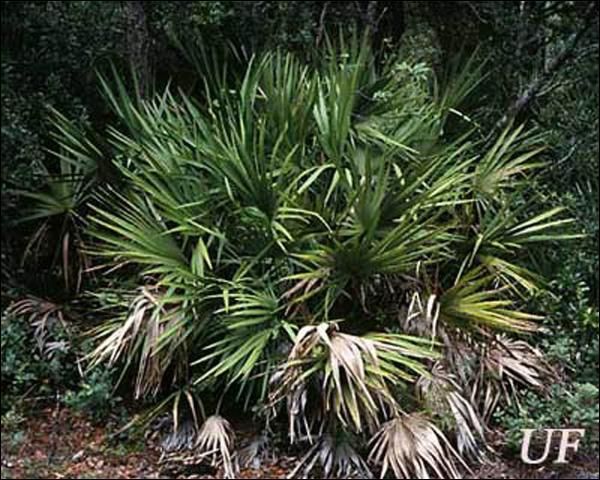

Credit: D. W. Hall, UF/IFAS
Selected References
Attygalle, A.B., D.J. Aneshansley, J. Meinwald, and T. Eisner. 2000. Defense by foot adhesion in a chrysomelid beetle (Hemisphaerota cyanea): Characterization of the adhesive oil. Zoology (Jena) 103: 1–6.
Beshear, R.J. 1969. Observations on the life history of Hemisphaerota cyanea in Georgia. Journal of the Entomological Society of Georgia 4: 168–170.
Eisner, T. and D.J. Aneshansley. 2000. Defense by foot adhesion in a beetle (Hemisphaerota cyanea). Proceedings of the National Academy of Science 97: 6568–6573.
Eisner, T. and M. Eisner. 2000. Defensive use of a fecal thatch by a beetle larva (Hemisphaerota cyanea) Proceedings of the National Academy of Science 97: 2632–2636.
Jackman, J.A. 1976. A tortoise beetle, Hemisphaerota cyanea, on palms in Texas. The Southwestern Entomologist 1: 181–183.
Woodruff, R.E. 1965. A tortoise beetle (Hemisphaerota cyanea (Say)) on palms in Florida (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Florida Department of Agriculture, Division of Plant Industry. Entomology Circular No. 35. Gainesville, FL.