Linnaeus is commonly called the 'milkweed assassin bug,' as it closely resembles the milkweed bug, (Dallas). It is also known as the 'longlegged assassin bug' and the 'Zelus assassin bug' (Bug Guide). Members of the genus belong to the subfamily Harpactorinae and are diurnal in nature. They are generalist predators feeding on a wide range of soft-bodied prey in garden and fields such as mosquitoes, flies, earthworms, cucumber beetles, and caterpillars (fall armyworm, rootworm etc.).
Introduction
Zelus longipes Linnaeus is commonly called the 'milkweed assassin bug,' as it closely resembles the milkweed bug, Oncopeltus fasciatus (Dallas). It is also known as the 'longlegged assassin bug' and the 'Zelus assassin bug' (Bug Guide). Members of the genus Zelus belong to the subfamily Harpactorinae and are diurnal in nature. They are generalist predators feeding on a wide range of soft-bodied prey in garden and fields such as mosquitoes, flies, earthworms, cucumber beetles and caterpillars (fall armyworm, rootworm etc.).
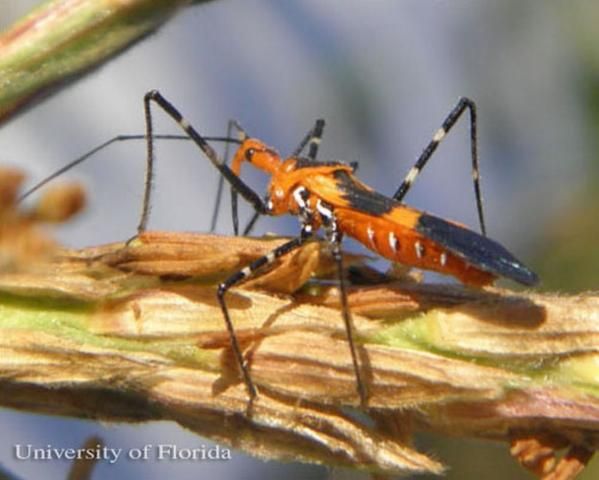

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida
Distribution
Zelus longipes is widely distributed in southern North America (Gulf Coast and South Atlantic states; southern California and southwestern Arizona in United States), Central America, South America (except Chile) through central Argentina, and the West Indies (Hart 1986; Melo 2005; Wolf & Reid 2001; Cogni et al. 2000).
Description and Life Cycle
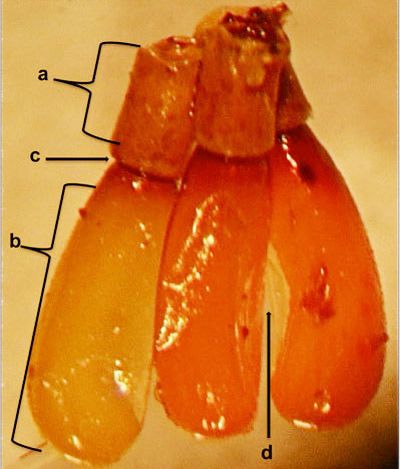
This species exhibits great variation in size and color, which resulted in confusion in correct species identification in the past. The greatest color variation is observed in West Indies populations where individuals may be orange-brown, brownish-black and even entirely black (Hart 1986). The United States populations are distinctively orange and black in color. Adults and nymphs have a pear-shaped head, constricted neck and long hairy legs. Their piercing and sucking mouthparts have a three-segmented beak which, when at rest, is bent and held under the thorax in a groove.
Adults: Males are smaller than females. In California and Arizona populations, males averaged 16.1 mm and females 18.4 mm in length, while in Gulf Coast populations, males and females averaged 16.8 mm and 18.2 mm, respectively. In females, the terminal abdominal segment is platelike or flattened, while in males it is cuplike or rounded (Hart 1986). Adults are known to overwinter.
Adult Zelus longipes can be differentiated from other Zelus species based on the following morphological characteristics:
-
In the pronotum, humeral angles are unarmed and rounded,
-
Dorsal surface of insect ranges from brownish-red to brownish-black in color,
-
Parameres (or lateral lobes of male genital organ) are cylindrical and long, surpassing 1/4 the length of median lobes.

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida
Eggs: The eggs are cylindrical and elongate in shape, non-ornamented, brown in color, with a light brown, cap-like structure (called the operculum) which has a central pore with a funnel-shaped opening. The egg can be divided into two parts: the operculum (which is attached to the anterior pole of the egg) and main eggshell or chorion (Wolf and Reid 2000). Each egg measures 2.0–2.3 mm in overall length while the appendage is 0.5 mm long (known to be longest among all bugs). The rest of the main eggshell measures 1.5 mm in length. The main eggshell is widest at the posterior pole (0.53 mm) and narrows near the anterior pole (0.32 mm). The anterior pole is flat and is attached to the anterior appendage at a distinct waist-shaped junction. Viewed sideways, the eggshell appears to be laterally flattened with a slight curvature inwards (Wolf and Reid 2000).
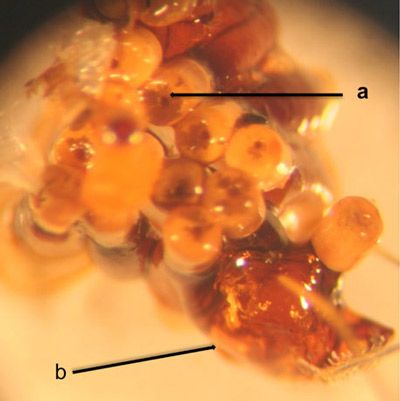

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida
Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida
The main eggshell has a smooth surface. The anterior appendage exhibits a highly diversified architecture internally when viewed under SEM (Scanning electronic microscope). The cylindrical outer layer of the anterior appendage is called a veil, which is continuous with the main eggshell and roughly equal in diameter. The veil folds inwards at the anterior pole forming a double layer and within this are many honeycomb-like structures. The function of the veil is to regulate humidity for the developing embryo. Partially removing the veil exposes a topographical arrangement of the important components of the anterior appendage which are micropyles (present at the base of veil) and operculum. The micropyles help in gaseous exchange while the operculum is a plate-like structure attached to the anterior part of egg that is lifted during hatching. Eggs are laid in a cluster of 15 or more, cemented at the base and covered with viscous material (except for the anterior appendage as its function is to protect the aeropyles from clogging) (Wolf and Reid 2000).

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida
Nymphs: Zelus longipes passes through five nymphal instars before developing into adults.
First instar: The body is elongated with a differentiated neck and is light brown in color, measuring 2.61 mm in length. The head is pyriform in shape, measuring 0.80 mm in length and 0.50 mm wide with sparse setae. The prominent reddish-brown eyes are 0.22 mm wide (ocelli are absent). The antennae are filiform, setose and 3.98 mm long. The legs are dark brown in color, except for the coxa which is light brown. The abdomen is dark brown to orange in color, and appears round in form with a few setae on the last segments. This stage lacks wing pads (Melo et al. 2005).

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida
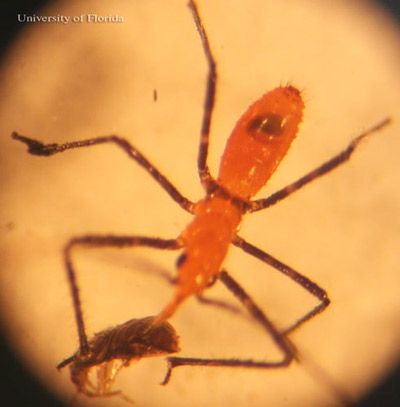

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida
Second instar: The body now is more elongated measuring 4.26 mm in length with pale brown color and orange tinge (Melo et al. 2005). The head is also more elongated, 1.08 mm long and 0.67 mm wide, compared to the previous instar. The legs are black with lightly colored coxa. And the abdomen is rounded and setose with faintly visible sweat glands. Wing pads are now present, and are dark brown to black in color and 0.35 mm long.
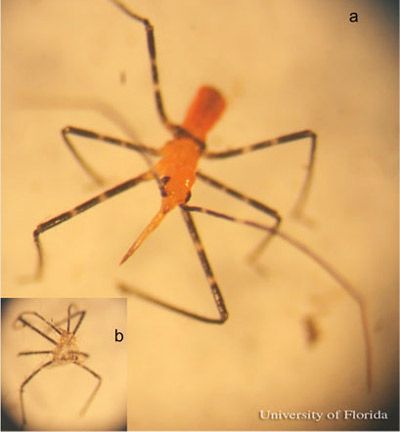

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida
Third instar: The body is elongated and 5.73 mm long ( Melo et al. 2005). The head is 1.56 mm long and 0.78 mm wide. It is uniformly orange with setae. The antennae are 7.5 mm long, with color and banding similar to the previous instar. Legs and wing pad color are same as the previous instar. The length of the wing pad now averages 0.84 mm. The abdomen is rounded, with setae and visible scent gland openings.
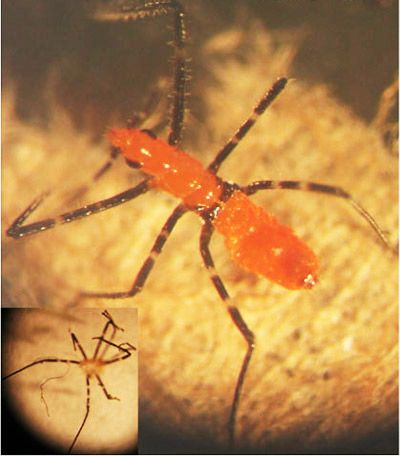

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida
Fourth instar: The total body length is 7.14 mm (Melo et al. 2005). The head width and length is 0.97 mm and 2.05 mm, respectively. Antennal length is now 10.23 mm,while the antennae are black and have two distal pale bands (light brown) on the first segment. The second and third antennal segments are setose. Legs are black with three pale bands, one on the forefemur and two on the median and hind femora. The wing pads are black, setose and 1.37 mm in length. The abdomen is more elongated and setose as compare to previous instars, and measures 2.67 mm in length and 0.65 mm in width. The posterior portion is yellow in color with prominent black dorsal spots present on the VI and VII sternites.
Fifth instar: The orange body is elongated, measuring 11.29 mm (Melo et al. 2005). Head length and width is 2.77 mm and 1.26 mm, respectively. Eyes are conspicuously black. Antennae, measuring 14.56 mm in length, are similar to previous instars in regard to color, band patterns and setae. The second segment of the antenna has five trichobothria (elongated, non-tapered setae) while the remaining three segments have abundant setae. The wing pads are 3.54 mm in length, setaceous and black. The abdomen is orange, setaceous and is 4.97 mm long and 1.77 mm wide. Lateral edges of the abdomen show thin whitish-yellow stripes.
Economic Importance
While a generalist predator, Z. longipes is also important as a predator of important economic pests such as the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (Cogni et al. 2000), the Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hall 2008), and the genista broom moth, Uresiphita reversalis Guenée (Carrel 2001).
While not a threat to humans, if not handled properly, a Z. longipes 'bite' can cause a burning sensation with swelling that may last for several days.
Feeding Behavior
The strategy Z. longipes uses to catch its prey is known as the "sticky trap strategy." Like many ambush bugs, Z. longipes attacks prey after hiding inside foliage with its forelegs raised in the air. The forelegs of Z. longipes are covered with a viscous material which acts as a glue, trapping the prey. Zelus longipes then rapidly paralyzes its prey by inserting its stylets into the host body and and prepares to feed through extra-oral digestion. Extra-oral digestion is a mode of digestion where a predator releases enzymes into its prey to dissolve the host's tissue, and later sucks up the dissolved liquid using its stylet as a straw (Wolf and Reid 2001). Zelus longipes can feed on prey that may be up to six times their own size. But with increasing prey size the handling and feeding time for Z. longipes also increases, allowing them to become vulnerable to other predators (Cogni et al. 2000).

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida

Credit: Megha Kalsi, University of Florida
Selected References
BugGuide. (October 2009). Species Zelus longipes - Milkweed Assassin Bug. BugGuide.net. http://bugguide.net/node/view/4832 (August 2018).
Carrel JE. 2001. "Response of predaceous arthropods to chemically defended larvae of the pyralid moth Uresiphita reversalis (Guenée) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae)." Journal of the Kansas Entomological Society 74: 128–135.
Cogni R, Freitas AVL, Filho FA. 2000. "Influence of prey size on predation success by Zelus longipes L. (Het., Reduviidae)." Journal of Applied Entomology 126: 74–78.
Hall DG. (2008). Biological control of Diaphorina citri. Concitver. https://www.ars.usda.gov/ARSUserFiles/35403/Hallpsyllidbiocontrol2008.pdf (February 2022).
Hart ER. 1986. "Genus Zelus Fabricius in the United States, Canada, and Northern Mexico (Hemiptera: Reduviidae)." Annals of the Entomological Society of America 79: 535–548.
Melo MC, Coscaron MC, Filho BA. 2005. "Immature stages of Zelus longipes (Heteroptera: Reduviidae, Harpactorinae)." Transactions of the American Entomological Society 31: 101–110.
Ralston JS. 1977. "Egg guarding by male assassin bug of the genus Zelus (Hemiptera: Reduviidae)." Psyche 84: 103–107.
Wolf KW, Reid W. 2000. "The architecture of the anterior appendage in the egg of the assassin bug, Zelus longipes (Hemiptera: Reduviidae)." Arthropod Structure and Development 29: 333–341.
Wolf KW, Reid W. 2001. "Surface morphology of legs in the assassin bug Zelus longipes (Hemiptera: Reduviidae): A scanning electron microscopy study with an emphasis on hairs and pores." Annals of the Entomological Society of America 94: 457–461.