Introduction
This North American native reaches 50 feet in height with a broad, spreading canopy and grayish-brown bark which may be either smooth or scaly. The 2-to 5-inch-diameter, lustrous, dark green, lobed leaves which have a pale underside are noted for their striking brilliance in fall, when they change into beautiful shades of red, orange, and yellow before dropping. The insignificant, hairy, yellow flowers appear among the leaves in late spring and are followed by the production of 1-inch-long, winged seeds.
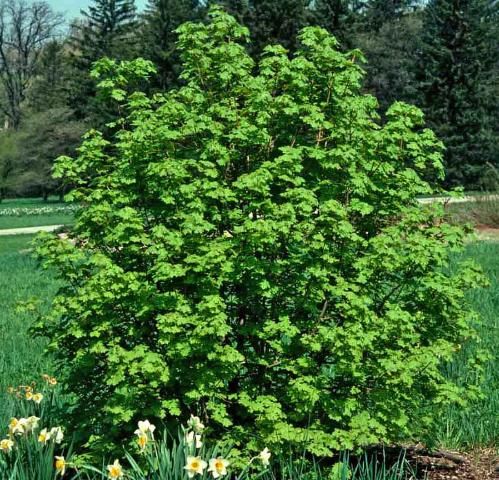

Credit: Ed Gilman
General Information
Scientific name: Acer grandidentatum
Pronunciation: AY-ser gran-dih-den-TAY-tum
Common name(s): Bigtooth maple, Rocky Mountain sugar maple, canyon maple
Family: Aceraceae
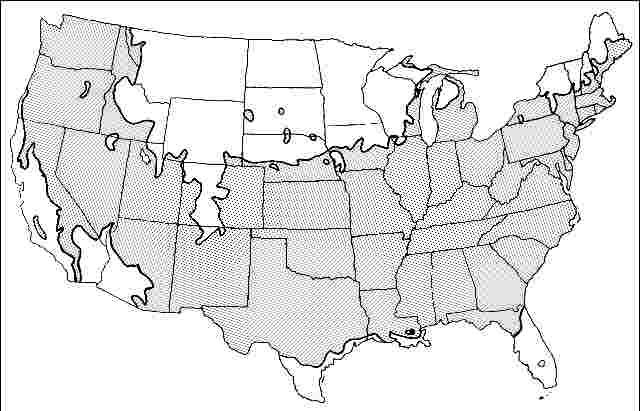
USDA hardiness zones: 5A through 8B (Fig. 2)
Origin: native to North America
Invasive potential: little invasive potential
Uses: specimen; reclamation; street without sidewalk; shade; parking lot island 100-200 sq. ft.; parking lot island > 200 sq. ft.; tree lawn 4-6 feet wide; tree lawn > 6 ft. wide
Availability: not native to North America
Description
Height: 40 to 50 feet
Spread: 25 to 35 feet
Crown uniformity: irregular
Crown shape: round
Crown density: moderate
Growth rate: moderate
Texture: medium
Foliage
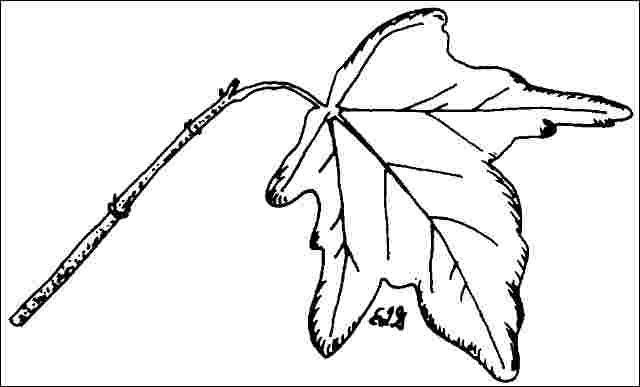
Leaf arrangement: opposite/subopposite (Fig. 3)
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: lobed, dentate
Leaf shape: star-shaped
Leaf venation: palmate
Leaf type and persistence: deciduous
Leaf blade length: 2 to 4 inches, 4 to 8 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: yellow, red, orange
Fall characteristic: showy
Flower
Flower color: yellow
Flower characteristics: not showy
Fruit
Fruit shape: elongated
Fruit length: .5 to 1 inch
Fruit covering: dry or hard
Fruit color: green
Fruit characteristics: attracts birds; not showy; fruit/leaves not a litter problem
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: branches droop; not showy; typically one trunk; thorns
Pruning requirement: needed for strong structure
Breakage: resistant
Current year twig color: reddish, brown
Current year twig thickness: thin, medium
Wood specific gravity: unknown
Culture
Light requirement: full sun, partial sun or partial shade
Soil tolerances: clay; sand; loam; acidic; alkaline; well-drained
Drought tolerance: moderate
Aerosol salt tolerance: none
Other
Roots: not a problem
Winter interest: no
Outstanding tree: yes
Ozone sensitivity: tolerant
Verticillium wilt susceptibility: susceptible
Pest Resistance: resistant to pests/diseases
Use and Management
This maple may need some training to develop a dominant central leader. Once selected, this leader should more or less stay dominant. This can make bigtooth maple a good candidate for planting along streets in an area with plenty of soil space for root expansion.
Bigtooth maple will grow in full sun or partial shade and is found most often in its natural habitat in moist, well-drained soils. It tolerates limestone soils well. Plants in the wild grown in open areas have withstood long periods of drought.
Pests
No pests are of major concern.
Diseases
No diseases are of major concern.