Introduction
This cultivar of red maple is somewhat pyramidal, but is probably best described as broadly columnar in shape. It is a moderate grower, reaching a height of about 50 feet with a 25-foot spread. Young trees are dense and quite narrow, but they broaden with age. Trees are often shorter in the southern part of its range unless growing next to a stream or on a wet site. Unless irrigated or on a wet site, red maple is best used north of USDA hardiness zone 9. The newly emerging leaves and red flowers and fruits signal that spring has come. They appear in December and January in Florida, later in the northern part of its range. The seeds of red maple are quite popular with squirrels and birds. This tree if often confused with red-leaved cultivars of Norway maple. Fall color is not reliable, but ranges in any given year from red to orange to yellow. It can be spectacular in some years.
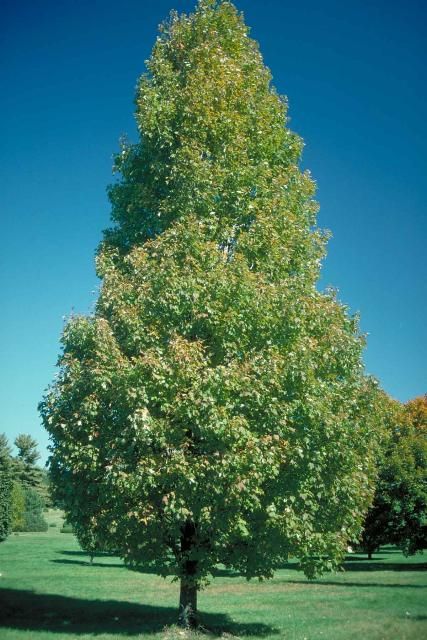

Credit: Ed Gilman
General Information
Scientific name: Acer rubrum
Pronunciation: AY-ser ROO-brum
Common name(s): 'Bowhall' red maple
Family: Aceraceae
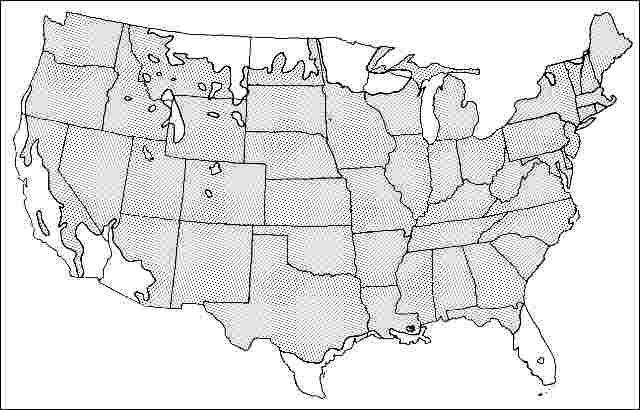
USDA hardiness zones: 4A through 8B (Fig. 2)
Origin: native to North America
Invasive potential: little invasive potential
Uses: reclamation; highway median; screen; street without sidewalk; tree lawn 3–4 feet wide; tree lawn 4–6 feet wide; tree lawn > 6 ft. wide; Bonsai
Availability: somewhat available, may have to go out of the region to find the tree
Description
Height: 45 to 50 feet
Spread: 18 to 25 feet
Crown uniformity: symmetrical
Crown shape: upright/erect
Crown density: dense
Growth rate: fast
Texture: medium
Foliage
Leaf arrangement: opposite/subopposite (Fig. 3)
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: incised, serrate, lobed
Leaf shape: ovate
Leaf venation: palmate
Leaf type and persistence: deciduous
Leaf blade length: 2 to 4 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: yellow, orange, red
Fall characteristic: showy
Flower
Flower color: red
Flower characteristics: showy
Fruit
Fruit shape: elongated
Fruit length: 1 to 3 inches
Fruit covering: dry or hard
Fruit color: red
Fruit characteristics: attracts squirrels/mammals; showy; fruit/leaves not a litter problem
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: branches don't droop; not showy; typically one trunk; thorns
Pruning requirement: needed for strong structure
Breakage: susceptible to breakage
Current year twig color: gray, reddish
Current year twig thickness: medium
Wood specific gravity: 0.54
Culture
Light requirement: full sun, partial sun or partial shade
Soil tolerances: sand; loam; clay; acidic; well-drained; extended flooding
Drought tolerance: moderate
Aerosol salt tolerance: low
Other
Roots: can form large surface roots
Winter interest: yes
Outstanding tree: no
Ozone sensitivity: unknown
Verticillium wilt susceptibility: susceptible
Pest resistance: resistant to pests/diseases
Use and Management
The tree makes the best growth in wet places and has no other particular soil preference, except chlorosis may develop on alkaline soil where it also grows poorly. It is well suited as a street tree in northern and mid-south climates in residential and other suburban areas, but the bark is thin and easily damaged by mowers. Irrigation is often needed to support street tree plantings in well-drained soil in the south. Roots can raise sidewalks as silver maples can, but they have a less aggressive root system and so they make a good street tree. Surface roots beneath the canopy can make mowing difficult.
Red maple is easily transplanted and usually develops surface roots in soil ranging from well-drained sand to clay. It is not especially drought-tolerant, particularly in the southern part of the range, but selected individual trees can be found growing on dry sites. This trait shows the wide range of genetic diversity in the species. Branches often grow upright through the crown, forming poor attachments to the trunk. These should be removed in the nursery or after planting in the landscape to help prevent branch failure in older trees during storms. Select branches with a wide angle from the trunk and prevent branches from growing larger than half the diameter of the trunk. Graft incompatibility on grafted trees can cause branch failure in wind storms. Preference should be given to trees produced on their own roots.
A number of other cultivars are listed. Due to graft-incompatibility problems that cause the tree to break apart, preference should be given to cultivars produced on their own roots. In the northern and southern end of the range, choose cultivars with regional adaptation. The cultivars are 'Armstrong'—upright growth habit, almost columnar, somewhat prone to splitting branches due to tight crotches, 50 feet tall; 'Autumn Flame'—45 feet tall, round, above average fall color; 'Gerling'—densely branched, broadly pyramidal, about 35 feet tall when mature; 'October Glory'—above average fall color, excellent tree, retains leaves late, 60 feet tall; 'Red Sunset'—above average orange to red fall color, does well in the south in USDA hardiness zone 8, probably the best cultivar for the deep south, oval, 50 feet tall; 'Scanlon'—upright growth habit; 'Schlesinger'—good fall color, rapid growth rate; 'Tilford'—globe-shaped crown. Variety drummondii suitable in USDA hardiness zone 8.
Pests
Leaf stalk borer and petiole borer cause the same type of injury. Both insects bore into the leaf stalk just below the leaf blade. The leaf stalk shrivels, turns black, and the leaf blade falls off. The leaf drop may appear heavy but serious injury to a healthy tree is rare.
Aphids infest maples, usually Norway maple, and may be numerous at times. High populations can cause leaf drop. Another sign of heavy aphid infestation is honey dew on lower leaves and objects beneath the tree. Aphids are controlled by spraying or they may be left alone. If not sprayed, predatory insects will bring the aphid population under control.
Scales are an occasional problem on maples. Perhaps the most common is cottony maple scale. The insect forms a cottony mass on the lower sides of branches. Scales are usually controlled with horticultural oil sprays. Scales may also be controlled with well-timed sprays to kill the crawlers.
If borers become a problem it is an indication the tree is not growing well. Controlling borers involves keeping trees healthy. Chemical controls of existing infestations are more difficult. Proper control involves identification of the borer infesting the tree then applying insecticides at the proper time.
Twig borers can cause die-back of the terminal 8 to 12 inches of small-diameter branches. This is usually not serious and does not require control measures, but it can be a problem on young trees in the nursery.
Diseases
Scorch may occur during periods of high temperatures accompanied by wind. Trees with diseased or inadequate root systems will also show scorching. When trees do not get enough water they scorch. Scorch symptoms are light brown or tan dead areas between leaf veins. The symptoms are on all parts of the tree or only on the side exposed to sun and wind. Scorching due to dry soil may be overcome by watering. If scorching is due to an inadequate or diseased root system, watering may have no effect.
Nutrient deficiency symptoms are yellow or yellowish-green leaves with darker green veins. The most commonly deficient nutrient on maple is manganese. Implanting capsules containing a manganese source in the trunk will alleviate the symptoms. Test soil samples to determine if the soil pH is too high for best manganese availability. Plants exposed to weed killers may also show similar symptoms.
Tar spot and a variety of leaf spots cause some concern among homeowners but are rarely serious enough for control.