Introduction
European birch is graceful and ornamental with wonderful yellow fall color but is susceptible to fatal attacks of bronze birch borer. The leaves are often browned by birch leaf miner. When grown, plan to provide the necessary insect control and provide the necessary cultural conditions for best growth. European birch grows rapidly, reaching a height of 35 to 75 feet. Lawn grasses grow well in its light shade. A moist soil and a regular fertilization program plus watering in dry weather are suggested. Although popular, the tree requires more care and spraying than other ornamental trees. Not a low maintenance tree. Maintaining a good mulch around the root zone is helpful.
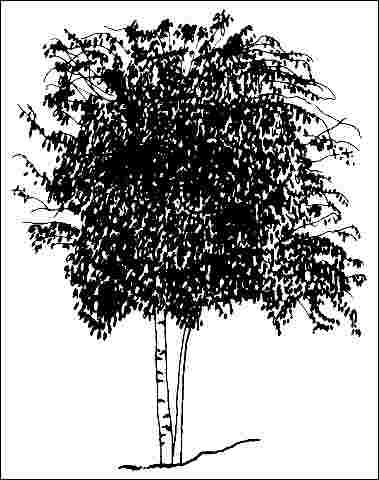
General Information
Scientific name: Betula pendula
Pronunciation: BET-yoo-luh PEND-yoo-luh
Common name(s): European birch
Family: Betulaceae
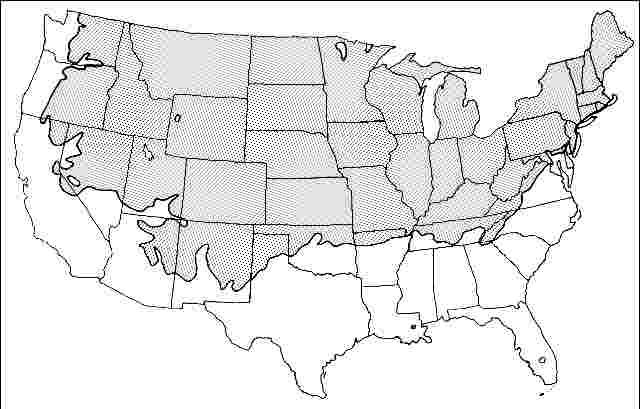
USDA hardiness zones: 3A through 6B (Fig. 2)
Origin: not native to North America
Invasive potential: little invasive potential
Uses: deck or patio; specimen; shade
Availability: not native to North America
Description
Height: 40 to 50 feet
Spread: 15 to 25 feet
Crown uniformity: irregular
Crown shape: oval, pyramidal, weeping
Crown density: open
Growth rate: moderate
Texture: fine
Foliage
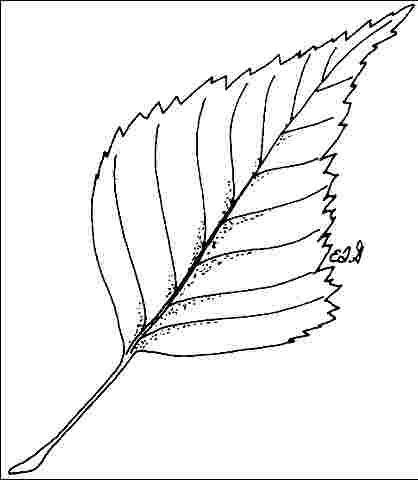
Leaf arrangement: alternate (Fig. 3)
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: double serrate
Leaf shape: rhomboid, ovate
Leaf venation: pinnate
Leaf type and persistence: deciduous
Leaf blade length: less than 2 inches, 2 to 4 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: yellow
Fall characteristic: showy
Flower
Flower color: brown
Flower characteristics: showy
Fruit
Fruit shape: elongated
Fruit length: .5 to 1 inch, 1 to 3 inches
Fruit covering: dry or hard
Fruit color: brown
Fruit characteristics: attracts birds; not showy; fruit/leaves not a litter problem
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: branches droop; very showy; typically one trunk; thorns
Pruning requirement: needed for strong structure
Breakage: resistant
Current year twig color: brown
Current year twig thickness: thin
Wood specific gravity: unknown
Culture
Light requirement: full sun
Soil tolerances: clay; sand; loam; acidic; well-drained
Drought tolerance: moderate
Aerosol salt tolerance: moderate
Other
Roots: not a problem
Winter interest: yes
Outstanding tree: yes
Ozone sensitivity: tolerant
Verticillium wilt susceptibility: resistant
Pest resistance: sensitive to pests/diseases
Use and Management
Several cultivars are available, but these too will have pest problems: 'Dalecarlica'—deeply lobed leaves on pendulous branches; 'Laciniata'—cut leaves; 'Fastigiata'—upright growth habit; 'Purple Splendor' (purpurea), 'Scarlet Glory'—purple leaves; 'Tristis'—weeping habit; 'Youngii'—weeping habit.
Pests
A light aphid infestation may not be serious, but heavy infestations cause distorted and stunted growth and produce large amounts of honeydew. The honeydew serves as a substrate for sooty mold.
Birch skeletonizer feeding causes leaf browning. The skeletonizer larva is yellowish-green and one quarter-inch long.
Birch leaf miner is a common insect pest of birch. A small white worm eats out the middle of the leaf, which turns brown. Severe attacks of birch leaf miner predispose trees to bronze birch borer infestation. The insect shows up in mid-May, but timing can vary from one year to the next and will vary according to your location in the country. The first of two generations per year is the most damaging.
The most serious pest of landscape birches is bronze birch borer. Stressed trees are most susceptible to borer attacks. The insect bores in the sapwood, beginning in the top third of the tree, causing death of the tree crown. The tunnels are slightly raised and faintly rust colored. Emergence holes in the trunk are shaped like capital Ds. Keep the trees healthy by controlling other insects, fertilizing, and watering as needed. Chemical control is applied to the trunk and main branches. Timing of the first spray will vary from year to year depending on weather conditions. A commercial sprayer may be needed to apply the spray adequately.
Diseases
Several fungi cause canker diseases on birch. These diseases infect and kill sapwood, causing sunken areas on the trunk and larger branches. There is no chemical control for canker diseases. Preventive measures include keeping the tree healthy and avoiding wounding. Regular fertilization will keep birches vigorous and more resistant to cankers. Water in dry weather to prevent water stress.
Dieback is characterized by a slow death of the branches. The tree crown accumulates dead branches. Injury caused by bronze birch borer is similar but far more prevalent. Prevent dieback by maintaining tree vigor with water and fertilizer. When the disease does occur, prune out dead branches and increase tree vigor.
Several fungi also cause leaf spots that, when severe, can cause defoliation.