Introduction
This cultivar of Redcedar is an evergreen growing 25 to 35 feet tall in an open, pyramidal form and spreads 8 to 15 feet when given a sunny location. 'Ketlerii' is commonly available in the mid-west and is more open with spaces between branches at the top of the tree. It develops a brownish tint in winter in the north. The fruit is a blue berry on female trees and is ornamental when produced in quantity. Birds devour the fruit and 'plant' it along farm fences and in old abandoned fields. Some botanists do not separate Juniperus virginiana from Juniperus silicicola.

Credit: Ed Gilman, UF/IFAS
General Information
Scientific name: Juniperus virginiana
Pronunciation: joo-NIP-er-us ver-jin-ee-AY-nuh
Common name(s): 'Keteleeri' Eastern Redcedar
Family: Cupressaceae
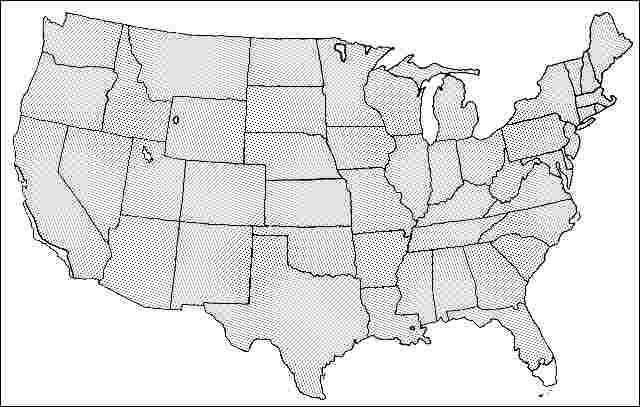
USDA hardiness zones: 3A through 9B (Fig. 2)
Origin: native to North America
Invasive potential: little invasive potential
Uses: urban tolerant; screen; street without sidewalk; reclamation; tree lawn 3-4 feet wide; tree lawn 4-6 feet wide; tree lawn > 6 ft wide; highway median; specimen; bonsai
Availability: somewhat available, may have to go out of the region to find the tree
Description
Height: 25 to 35 feet
Spread: 8 to 15 feet
Crown uniformity: symmetrical
Crown shape: pyramidal
Crown density: moderate
Growth rate: fast
Texture: fine
Foliage
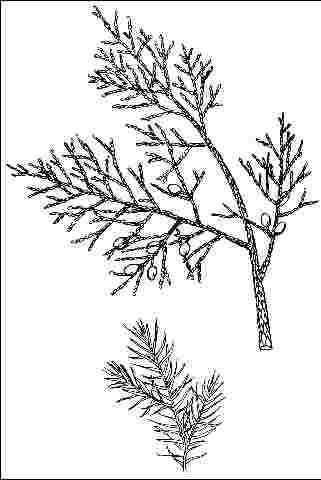
Leaf arrangement: whorled (Fig. 3)
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: entire, terminal spine
Leaf shape: awl-like, scale-like
Leaf venation: none, or difficult to see
Leaf type and persistence: evergreen
Leaf blade length: less than 2 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: no color change
Fall characteristic: not showy
Flower
Flower color: yellow, green
Flower characteristics: not showy
Fruit
Fruit shape: cone, round
Fruit length: less than .5 inch
Fruit covering: fleshy
Fruit color: blue, purple
Fruit characteristics: attracts birds; showy; fruit/leaves not a litter problem
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: branches don't droop; showy; typically one trunk; thorns
Pruning requirement: little required
Breakage: susceptible to breakage
Current year twig color: brown, green
Current year twig thickness: thin
Wood specific gravity: 0.47
Culture
Light requirement: full sun, partial sun, or partial shade
Soil tolerances: sand; loam; clay; acidic; alkaline; well-drained
Drought tolerance: high
Aerosol salt tolerance: high
Other
Roots: not a problem
Winter interest: no
Outstanding tree: yes
Ozone sensitivity: unknown
Verticillium wilt susceptibility: resistant
Pest resistance: free of serious pests and diseases
Use and Management
The dense growth and attractive foliage make Eastern Redcedar a favorite for windbreaks, screens, and wildlife-cover for large-scale landscapes. The open habit makes it more suited for a specimen planting than the species. Its high salt-tolerance makes it ideal for seaside locations. Redcedar can make a nice Christmas tree, and the fragrant wood is popular for repelling insects.
Planted in full sun or partial shade, Eastern Redcedar will easily grow on a variety of soils, including clay, but will not do well on soils kept continually moist. Growth will be poor in landscapes which are over-irrigated. Plants are difficult to transplant due to a coarse root system, except when quite small. Many nurseries offer Redcedar in containers. Water until well-established and then forget about the tree. It performs admirably with no care, even on alkaline soil and along the coast. Usually insects and diseases are not a problem if grown in the full sun. There may be local restrictions on planting this tree near apple orchards because it is the alternate host for cedar-apple rust.
Some nurseries carry a cultivar or two of Redcedar.
Cultivars include: 'Burkii' - pyramidal, blue foliage, 15 to 25 feet tall; 'Canaertii' - compact, pyramidal, good fruit production, fairly common in Texas; 'Hillspire' - (cupressifolia) - good green color; 'Elegantissima' - Goldtip Redcedar - branchlets with yellow tips, less than 20 feet tall; 'Filifera' - pyramidal, branchlets divided, foliage gray green; 'Glauca' - Silver Redcedar - narrow, columnar, 15 to 20 feet tall, silvery blue foliage especially in spring; 'Ketlerii' is commonly available in the mid-west, is more open with spaces between branches at the top of the tree, pyramidal; 'Manhattan Blue' - compact, 20 feet tall, pyramidal, foliage bluish green; 'Pendula' - Weeping Redcedar - branchlets pendulous, to 40 feet tall; 'Pyramidalis Dundee' - pyramidal, purplish green in winter; 'Skyrocket' - silver-blue foliage, narrow columnar form.
Pests
Usually none are serious.
Bagworm caterpillars occasionally web foliage and debris together to make bags up to 2 inches long. The insects live in the bags and emerge to feed on the foliage. Use sprays of Bacillus thuringiensis. The insects can also be picked off the plants by hand.
Juniper scale causes yellowed needles, and infected branches fail to produce new growth. The scale is round and at first white, later turning gray or black.
The Juniper webworm webs twigs and needles together, causing them to brown and die. The larva is 1/2-inch-long and is brown with darker stripes. The larvae are often in the densest part of the plant and can go unnoticed.
Mites cause stippled and bronzed foliage.
Diseases
Twig blights cause death and browning of twigs tips. The diseases may progress down the stem killing the whole branch. Small lesions may be seen at the base of dead tissue. Prune out dead branch tips. Dieback from Kabatina blight appears in early spring, from Phomopsis in summer.
Three rust diseases seen most often are cedar-apple rust, hawthorn rust, and quince rust. The most common is cedar-apple rust. On Juniper the first two diseases form galls and orange jelly-like horns in spring. The horns are most likely to form following periods of rainy, warm weather. Spores formed in the horns infect the alternate host. The diseases are more serious on the alternate host than Juniper. There may be local restrictions on planting this tree near apple orchards because it is the alternate host for cedar-apple rust. A separation of a few hundred yards may help avoid the disease. Prune out the spore horns when seen in the spring. Do not plant near hawthorns, apples, or crabapples.
Junipers are not tolerant of ice coatings. Expect dieback when Junipers are covered with ice for several days. Removing the ice is impractical.