Introduction
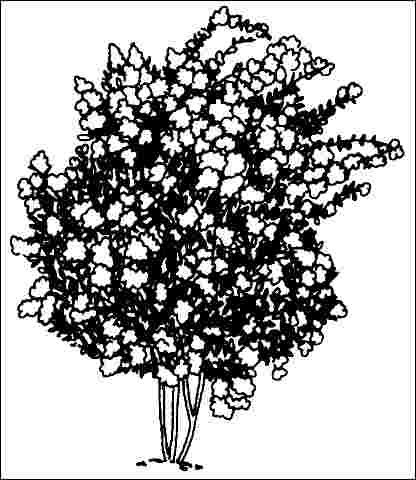
A long period of striking summer flower color, attractive fall foliage, and good drought-tolerance all combine to make this cultivar of crape myrtle a favorite very small tree or large shrub for either formal or informal landscapes. Most are seen seven to nine feet tall with a similar spread. It is highly recommended for planting in urban areas.

Credit: UF/IFAS
General Information
Scientific name: Lagerstroemia indica
Pronunciation: lay-ger-STREE-mee-uh in-dih-cah
Common name(s): 'Cherokee' crape myrtle
Family: Lythraceae
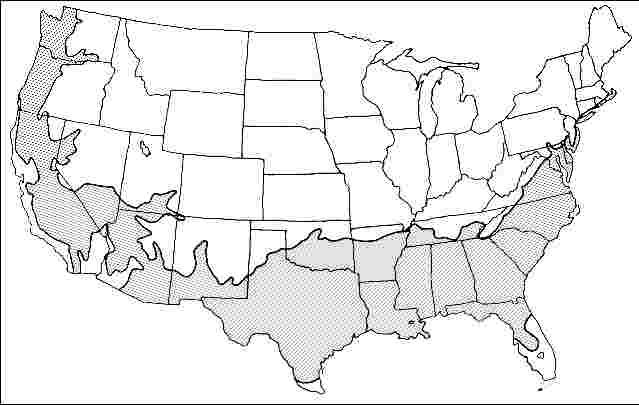
USDA hardiness zones: 7A through 9A (Figure 2)
Origin: not native to North America
Invasive potential: not considered a problem species at this time, may be recommended (North, Central, South)
Uses: tree lawn 3-4 feet wide; tree lawn 4-6 feet wide; tree lawn > 6 ft wide; street without sidewalk; parking lot island < 100 sq ft; parking lot island 100-200 sq ft; parking lot island > 200 sq ft; container or planter; trained as a standard; deck or patio; specimen; highway median
Description
Height: 10 to 15 feet
Spread: 6 to 10 feet
Crown uniformity: symmetrical
Crown shape: vase
Crown density: moderate
Growth rate: moderate
Texture: medium
Foliage
Leaf arrangement: opposite/subopposite (Figure 3)
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: entire
Leaf shape: oblong, elliptic (oval), obovate
Leaf venation: pinnate
Leaf type and persistence: deciduous
Leaf blade length: less than 2 inches, 2 to 4 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: orange, red, yellow
Fall characteristic: showy
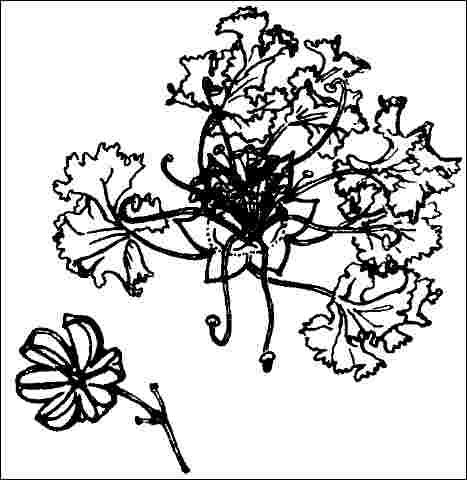
Flower
Flower color: red
Flower characteristics: very showy

Fruit
Fruit shape: oval, round
Fruit length: less than 0.5 inch
Fruit covering: dry or hard
Fruit color: brown
Fruit characteristics: does not attract wildlife; showy; fruit/leaves not a litter problem
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: branches droop; showy; typically multi-trunked; thorns
Pruning requirement: little required
Breakage: resistant
Current year twig color: brown, green
Current year twig thickness: thin
Wood specific gravity: unknown
Culture
Light requirement: full sun
Soil tolerances: sand; loam; clay; acidic; slightly alkaline; well-drained
Drought tolerance: high
Aerosol salt tolerance: moderate
Other
Roots: not a problem
Winter interest: yes
Outstanding tree: no
Ozone sensitivity: unknown
Verticillium wilt susceptibility: resistant
Pest resistance: resistant to pests/diseases
Use and Management
The 6- to 12-inch-long clustered bright red blooms appear on the tips of branches during late spring and summer in USDA hardiness zones 9 and 10 and summer in other areas. If flowers appear pink instead of red, then you have not purchased the true 'Cherokee' cultivar. The individual flowers are ruffled and crinkly as to appear made of crepe paper. The smooth, peeling bark and multi-branched, open habit make it ideal for specimen planting where its bright red to orange-colored fall leaves add further interest.
Pruning should be done in late winter or early in the spring before growth begins because it is easier to see which branches to prune. New growth can be pinched during the growing season to increase branchiness and flower number. It is not recommended to prune crape myrtle by topping or cutting it nearly to the ground each spring as these practices stress the tree, cause sprouting and will lead to its decline. It is better to remove dead wood and old flower stalks after blooming. Lower branches are often thinned to show off the trunk form and color. You can remove the spent flower heads to encourage a second flush of flowers and to prevent formation of the brown fruits. Since cultivars are now available in a wide range of growth heights, severe pruning should not be necessary to control size. Severe pruning can stimulate basal sprouting which can become a constant nuisance, requiring regular removal. Some crape myrtle trees sprout from the base of the trunk and roots even without severe heading.
Crape myrtle grows best in full sun with rich, moist soil but will tolerate less hospitable positions in the landscape just as well, once it becomes established. It grows well in limited soil spaces in urban areas such as along boulevards, in parking lots, and in small pavement cutouts if provided with some irrigation. They tolerate clay and alkaline soil well. However, the flowers of some selections may stain car paint. Insect pests are few (except for the crape myrtle aphid) and crape myrtle is susceptible to powdery mildew damage, especially when planted in some shade or when the leaves are kept moist. There are other new cultivars (many developed by the USDA) available which are resistant to powdery mildew.
Many other cultivars of crape myrtle are available: hybrid 'Acoma', 14 to 16 feet tall, white flowers, purple-red fall foliage, mildew resistant; hybrid 'Biloxi', 25 feet tall, pale pink blooms, orange-red fall foliage, hardy and mildew resistant; 'Powhatan', 14 to 20 feet, clear yellow fall foliage, medium purple flowers. The hybrid cultivars 'Natchez', 30 feet tall, pure white flowers, 'Muskogee', 24 feet tall, light lavender flowers, and 'Tuscarora', 16 feet tall, dark coral pink blooms, are hybrids between Lagerstroemia indica and Lagerstroemia fauriei and have greater resistance to mildew. The cultivar 'Crape Myrtlettes' have the same color range as the species but only grow to three to four feet high. The National Arboretum releases are generally superior because they have been selected for their disease resistance.
Propagation is by cuttings.
Pests
Aphids often infest the new growth causing an unsightly but harmless sooty mold to grow on the foliage. Heavy aphid infestations cause a heavy black sooty mold which detracts from the tree's appearance.
Diseases
Powdery mildew can severely affect crape myrtle. Select resistant cultivars and hybrids to avoid this disease. Leaf spots are only a minor concern and do not require treatment.