Introduction
This large evergreen shrub or small tree is capable of reaching 15 to 20 feet in height and width but is most often seen at 10 to 12 feet high with an 8-foot-spread. Older plants grow as wide as tall and develop a vase shape with several main trunks typically originating close to the ground. The lustrous, dark-green leaves have paler undersides and are joined in the fall by a multitude of barely-noticeable, but extremely fragrant, white blossoms. They perfume a large area of the landscape.
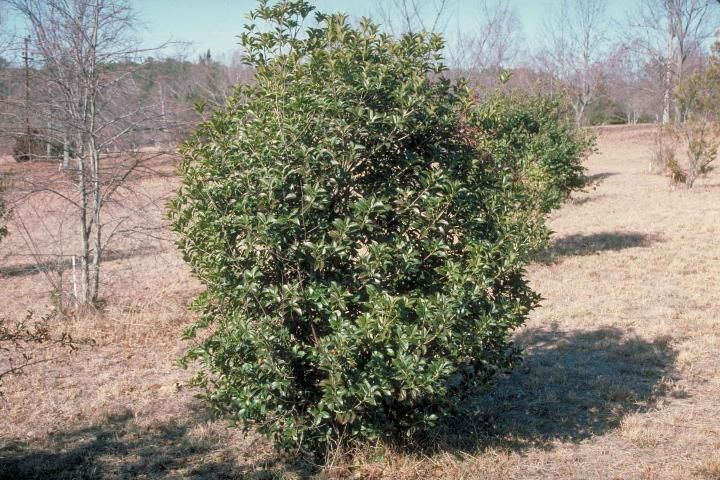

Credit: Ed Gilman
General Information
Scientific name: Osmanthus x fortunei
Pronunciation: oz-MANTH-us x for-TOO-nee-eye
Common name(s): Fortunes Osmanthus
Family: Oleaceae
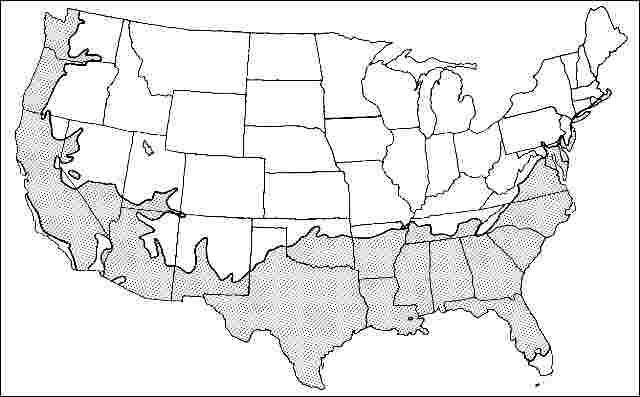
USDA hardiness zones: 7A through 9B (Fig. 2)
Origin: not native to North America
Invasive potential: has been evaluated using the IFAS Assessment of the Status of Non-Native Plants in Florida's Natural Areas (Fox et al. 2005). This species is not documented in any undisturbed natural areas in Florida. Thus, it is not considered a problem species and may be used in Florida.
Uses: hedge; screen; specimen; container or planter
Availability: not native to North America
Description
Height: 15 to 20 feet
Spread: 6 to 10 feet
Crown uniformity: symmetrical
Crown shape: oval
Crown density: dense
Growth rate: slow
Texture: medium
Foliage
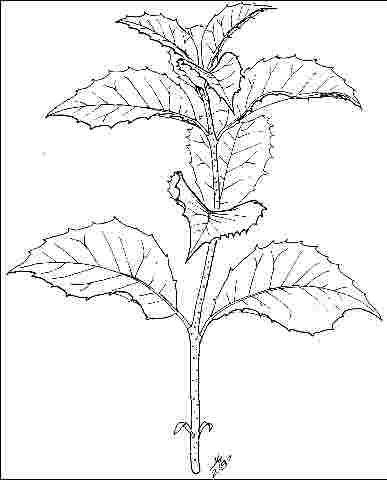
Leaf arrangement: opposite/subopposite (Fig. 3)
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: spiny, serrate, pectinate
Leaf shape: ovate, elliptic (oval)
Leaf venation: pinnate, brachidodrome
Leaf type and persistence: evergreen
Leaf blade length: 2 to 4 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: no color change
Fall characteristic: not showy
Flower
Flower color: white/cream/gray
Flower characteristics: not showy
Fruit
Fruit shape: round
Fruit length: less than .5 inch
Fruit covering: fleshy
Fruit color: black
Fruit characteristics: does not attract wildlife; not showy; fruit/leaves not a litter problem
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: branches don't droop; not showy; typically multi-trunked; thorns
Pruning requirement: little required
Breakage: resistant
Current year twig color: gray
Current year twig thickness: thin, medium
Wood specific gravity: unknown
Culture
Light requirement: full sun, partial sun or partial shade
Soil tolerances: clay; sand; loam; acidic; well-drained
Drought tolerance: high
Aerosol salt tolerance: unknown
Other
Roots: not a problem
Winter interest: no
Outstanding tree: no
Ozone sensitivity: unknown
Verticillium wilt susceptibility: unknown
Pest resistance: resistant to pests/diseases
Use and Management
With its upright oval to columnar growth habit in youth, Osmanthus is ideal for use as an unclipped hedge or trained as a small tree, and should be placed where its fragrance can be enjoyed. It is often planted as a hedge or foundation plant, and makes a very effect screen. Its spiny foliage makes it well-suited for planting as a barrier to help keep people from walking through an area. Since the flowers are not particularly showy, people will wonder where the delightful fragrance is coming from. This is a subtle plant which should be used more often in Southern landscapes.
Plants thin somewhat in full shade, but form a dense crown in a sunny or partially shaded location. Planted on 4 to 6 foot centers, Osmanthus can form a wall of fragrance during the fall and should be planted more often. They will not grow as fast as Leyland Cypress, but think of this Osmanthus as a substitute for use in a sunny or partially shaded spot. Plants can be clipped to form a denser canopy, but flowers form on old growth and removing branches will reduce the flower display. With time, older plants can be trained into a small, multi-trunked tree.
Osmanthus should be grown in sun or shade in well-drained soil. Plants are drought-tolerant once established. This is one of the most cold tolerant Osmanthus.
Propagation is by cuttings.
Pests and Diseases
No pests or diseases are of major concern. Scales and nematodes may present a problem, and mushroom root rot is troublesome when the soil is kept too wet.
Literature Cited
University of Florida, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences. 2018. "Assessment of Non-native Plants in Florida's Natural Areas" (https://assessment.ifas.ufl.edu, 4/29/2019) Gainesville, FL, 32611-4000, USA.
