Introduction
Small, white flowers arranged in dense, showy, eight-inch-diameter clusters at branch tips and large, shiny, dark green leaves combine to make Chinese photinia an attractive evergreen. It is suited for multiple landscape applications provided it is kept in the full sun to reduce leaf spot disease. In some areas of the country, it is an under-used landscape tree with very showy flowers and bright red fruit. This variety has reddish young stems, more serrate leaves than the species, and reaches about 10 feet in height. Often kept trimmed into a hedge shape, multitrunked Chinese photinia creates an ideal small tree with the proper training, and when the lower branches are removed, the natural rounded canopy adds to its attractive silhouette. New growth is tinged pink, though not as much as Photinia glabra, and young twigs are red to reddish-brown. The serrate-margined leaves can reach eight inches in length and are two inches wide. The springtime flower clusters are followed by small, red berry-like fruit clusters which persist through the winter.
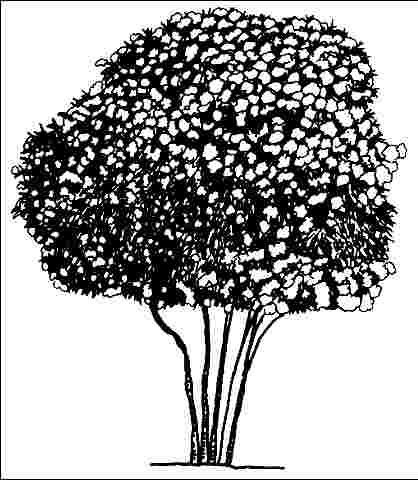

Credit: UF/IFAS
General Information
Scientific name: Photinia serratifolia var. aculeata
Pronunciation: foe-TIN-nee-uh ser-RAY-ti-fol-ee-uh
Common name(s): 'Aculeata' Chinese photinia
Family: Rosaceae
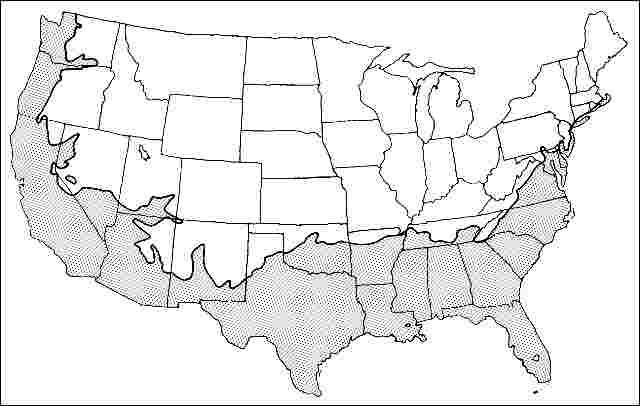
USDA hardiness zones: 6A through 11 (Figure 2)
Origin: not native to North America
Invasive potential: not considered a problem species at this time, may be recommended (North, Central, South)
Uses: street without sidewalk; deck or patio; screen; hedge; parking lot island < 100 sq ft; parking lot island 100–200 sq ft; parking lot island > 200 sq ft; sidewalk cutout (tree pit); tree lawn 3–4 feet wide; tree lawn 4–6 feet wide; tree lawn > 6 ft wide; urban tolerant; highway median; container or planter; specimen
Credit: UF/IFAS
Description
Height: 10 to 12 feet
Spread: 6 to 10 feet
Crown uniformity: symmetrical
Crown shape: round, vase
Crown density: dense
Growth rate: moderate
Texture: medium
Foliage
Leaf arrangement: alternate (Figure 3)
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: serrate
Leaf shape: elliptic (oval), oblong
Leaf venation: pinnate
Leaf type and persistence: evergreen, broadleaf evergreen
Leaf blade length: 4 to 8 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: no color change
Fall characteristic: not showy
Credit: UF/IFAS
Flower
Flower color: white/cream/gray
Flower characteristics: very showy
Fruit
Fruit shape: round
Fruit length: less than .5 inch
Fruit covering: fleshy
Fruit color: red
Fruit characteristics: does not attract wildlife; showy; fruit/leaves not a litter problem
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: branches don't droop; not showy; typically multi-trunked; thorns
Pruning requirement: little required
Breakage: resistant
Current year twig color: green, brown
Current year twig thickness: thick
Wood specific gravity: unknown
Culture
Light requirement: full sun
Soil tolerances: sand; loam; clay; acidic; alkaline; well-drained
Drought tolerance: high
Aerosol salt tolerance: none
Other
Roots: not a problem
Winter interest: no
Outstanding tree: yes
Ozone sensitivity: unknown
Verticillium wilt susceptibility: susceptible
Pest resistance: resistant to pests/diseases
Use and Management
Nurseries could produce trees with a single leader and market them as street trees. They stay fairly small, grow fast when young but slow down later as the crown broadens. Great for beneath powerlines.
Chinese photinia needs well-drained soil and a full sun location. Leaves often become infected with leaf spot fungi when grown in shade or when the leaves remain too moist. Plants grow at a moderate rate and tolerate pruning very well, although the bottom of the plant often thins when clipped into a hedge. There are much better plants for hedges, although photinia makes a good tall screen plant. Well-adapted to sand or clay (well-drained), acid or alkaline soil, photinia likes to be kept on the dry side and is very drought-tolerant. It is popular in all of USDA hardiness zones 7 and 8 as a highway median plant and could be used more as a multi-stemmed specimen, street or patio tree.
'Nova' reaches 10 feet in height with a seven- to eight-foot spread. There is a hybrid between red-leaved Photinia (Photinia glabra) and Chinese Photinia (Photinia serratifolia) which perhaps displays the best characteristics of both parents, called Photinia x fraseri. It is very popular in the nursery trade and is often used as a hedge or foundation plant, a usage which is quite inappropriate due to its large size and rapid growth rate.
Propagation is by cuttings.
Pests
It is usually pest-free but caterpillars, mites, scales, and European fruit-tip moth are sometimes a problem.
Diseases
Chinese photinia is usually disease-free, except for leaf spot which can be devastating. Fire blight and mildew in shady locations can also be troublesome.