Introduction
Chastetree can be grown as a large, deciduous, multistemmed shrub or small, 10 to 15 feet tall tree, and is noteworthy for its showy, summer display (late springtime in the deep South) of fragrant, upwardly-pointing, terminal panicles of lavender blooms which are quite attractive to butterflies and bees. The tree is often planted where honey is marketed to promote excellent honey production. The trunk is gray and blocky and somewhat ornamental. The sage-scented leaves of Chastetree are shaped liked a hand, or palmate, and were once believed to have sedative effects. Vitex has the common name "Chastetree" since Athenian women used the leaves in their beds to keep themselves chaste during the feasts of Ceres. Vitex seeds itself into landscaped beds and can become somewhat weedy.
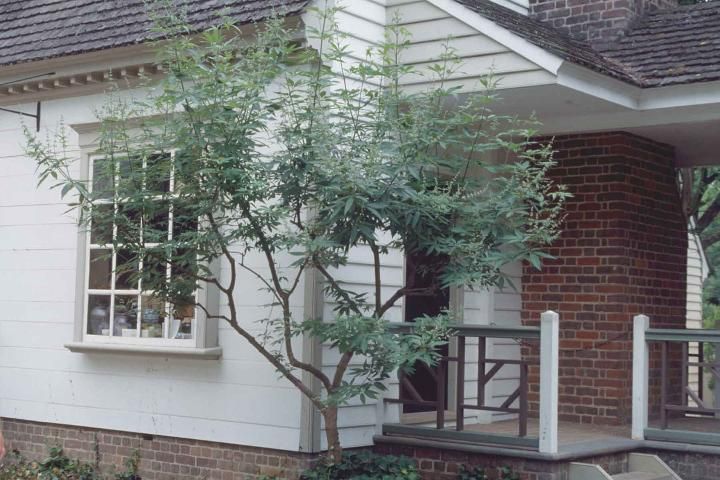

Credit: Ed Gilman
General Information
Scientific name: Vitex agnus-castus
Pronunciation: VYE-tecks AG-nus-KASE-tus
Common name(s): Chastetree, Vitex
Family: Verbenaceae
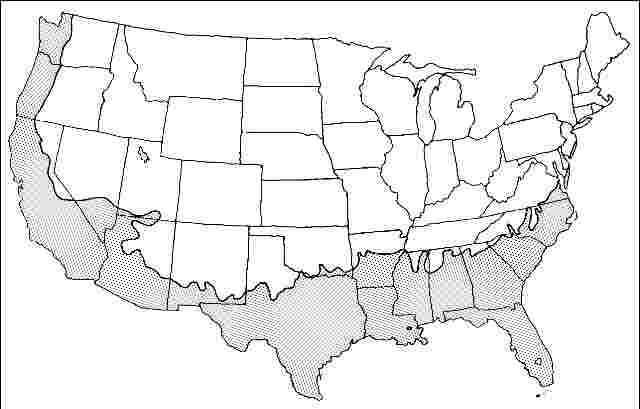
USDA hardiness zones: 7B through 11 (Fig. 2)
Origin: not native to North America
Invasive potential: invasive non-native
Uses: specimen; container or planter; trained as a standard; deck or patio; highway median
Availability: somewhat available, may have to go out of the region to find the tree
Description
Height: 10 to 15 feet
Spread: 15 to 20 feet
Crown uniformity: irregular
Crown shape: vase, round
Crown density: moderate
Growth rate: fast
Texture: fine
Foliage
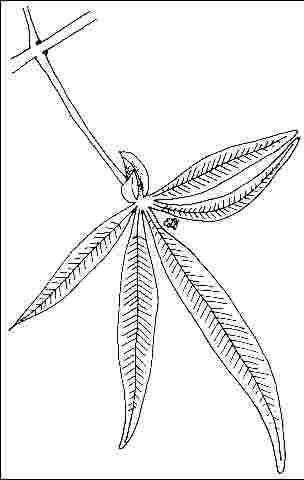
Leaf arrangement: opposite/subopposite (Fig. 3)
Leaf type: palmately compound
Leaf margin: entire
Leaf shape: lanceolate
Leaf venation: pinnate
Leaf type and persistence: deciduous, fragrant
Leaf blade length: 2 to 4 inches, 4 to 8 inches
Leaf color: green, blue or blue-green
Fall color: no color change
Fall characteristic: not showy
Flower
Flower color: lavender
Flower characteristics: very showy
Fruit
Fruit shape: unknown
Fruit length: unknown
Fruit covering: fleshy
Fruit color: black
Fruit characteristics: does not attract wildlife; not showy; fruit/leaves not a litter problem
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: branches droop; showy; typically multi-trunked; thorns
Pruning requirement: needed for strong structure
Breakage: resistant
Current year twig color: green
Current year twig thickness: thin, medium
Wood specific gravity: unknown
Culture
Light requirement: full sun, partial sun or partial shade
Soil tolerances: sand; loam; clay; acidic; alkaline; well-drained
Drought tolerance: high
Aerosol salt tolerance: moderate
Other
Roots: not a problem
Winter interest: no
Outstanding tree: yes
Ozone sensitivity: unknown
Verticillium wilt susceptibility: unknown
Pest resistance: resistant to pests/diseases
Use and Management
Chastetree is used effectively in the mixed shrubbery border or as a specimen. It is usually seen with a multiple trunk but can be trained in the nursery into a tree with one or several trunks, if so desired. Occasionally used as a street or median tree since it will not grow up and into powerlines, but branches tend to droop toward the ground and would hinder traffic visibility if planted too close to the street. Median planting would be fine if there is adequate horizontal space for the crown to develop and spread. Since the flowers attract bees, locate it accordingly.
Chastetree prefers a loose, well-drained soil that is moist or on the dry side, not wet, but will tolerate drained clay or sandy soils. The tree often suffers from dieback in organic, mucky, or other soil which is kept too moist, such as in the New Orleans or Dallas areas. Chastetree should be planted in full sun or light shade, and will tolerate hot weather extremely well, moderate salt air exposure and alkaline soil.
In the colder regions (USDA hardiness zones 6b and 7), Chastetree can be killed to the ground by severe winters and is more often seen as a multistemmed shrub. Chastetree is a fast-grower and can easily recover its size when cold weather prunes it. Very similar to Vitex negundo, which also is called Chastetree, Vitex agnus-castus is not as cold hardy as Vitex negundo (grows in USDA hardiness zone 6a). Vitex agnus-castus may survive in USDA hardiness zone 6a if protected from winter winds.
Several cultivars are available which offer flower color variety. `Silver Spire' and `Alba' have white flowers, and `Rosea' has pink flowers.
Propagate by softwood cuttings in early summer or by seeds.
Pests
No pests are of major concern.
Diseases
Leaf spot can almost defoliate the tree. Root rot can cause decline in soils which are kept too moist.