Prunus maackii: Amur Chokecherry1
Introduction
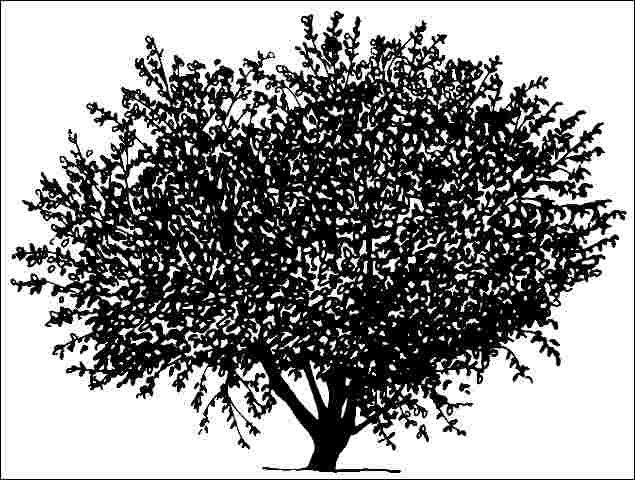
Amur Chokecherry is pyramidal when young but ultimately forms a 30 to 40-foot-tall tree with a dense, rounded canopy which provides light shade below. The deciduous leaves are three inches long and are joined in early to mid-May by an explosion of white, fragrant flowers in two to three-inch-long racemes. The multitude of tiny black fruits which follow ripen in August and are quite attractive to birds. The bark is occasionally handsome cinnamon brown peeling off in shaggy masses on the trunk, but more often is an attractive brown with minimum exfoliation. This tree has one of the most attractive bark features of any tree in North America.

General Information
Scientific name: Prunus maackii
Pronunciation: PROO-nus MACK-ee-eye
Common name(s): Amur Chokecherry, Manchurian Cherry
Family: Rosaceae
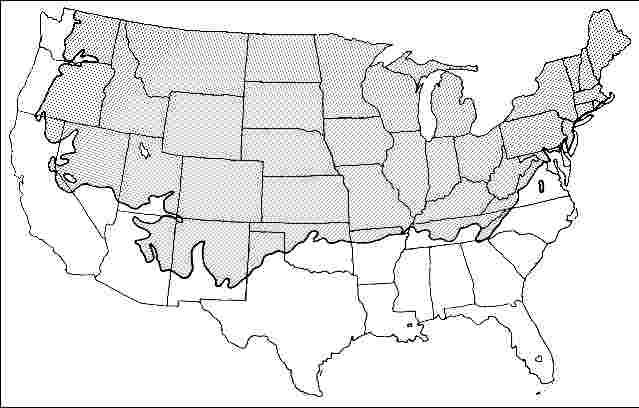
USDA hardiness zones: 2B through 6B (Fig. 2)
Origin: not native to North America
Invasive potential: little invasive potential
Uses: specimen; deck or patio; container or planter; street without sidewalk; highway median; Bonsai
Availability: somewhat available, may have to go out of the region to find the tree
Description
Height: 30 to 40 feet
Spread: 25 to 35 feet
Crown uniformity: symmetrical
Crown shape: round
Crown density: moderate
Growth rate: moderate
Texture: medium
Foliage
Leaf arrangement: alternate (Fig. 3)
Leaf type: simple
Leaf margin: serrate
Leaf shape: ovate, elliptic (oval)
Leaf venation: pinnate, brachidodrome
Leaf type and persistence: deciduous
Leaf blade length: 2 to 4 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: yellow
Fall characteristic: showy
Flower
Flower color: white/cream/gray
Flower characteristics: showy
Fruit
Fruit shape: round
Fruit length: less than .5 inch
Fruit covering: fleshy
Fruit color: black
Fruit characteristics: attracts birds; not showy; fruit/leaves a litter problem
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: branches don't droop; very showy; typically multi-trunked; thorns
Pruning requirement: little required
Breakage: resistant
Current year twig color: reddish, brown
Current year twig thickness: thin
Wood specific gravity: unknown
Culture
Light requirement: full sun, partial sun or partial shade
Soil tolerances: clay; sand; loam; slightly alkaline; acidic; well-drained
Drought tolerance: high
Aerosol salt tolerance: moderate
Other
Roots: not a problem
Winter interest: yes
Outstanding tree: yes
Ozone sensitivity: sensitive
Verticillium wilt susceptibility: susceptible
Pest resistance: resistant to pests/diseases
Use and Management
Prune to open up the canopy to develop more of a tree-form, otherwise it looks like a large shrub. Remove interior branches and space main branches along the trunk. A more upright shape can be created by removing lateral branches, a more spreading shape can be promoted by removing upright branches.
Use the tree along an entrance road to a commercial development planted on 20 to 25-foot centers or along side the patio or deck in the back yard.
Amur Chokecherry should be grown in full sun on well-drained soil, and performs well only in the north. The trees should be located where the roots can remain moist, but not wet, as drought tolerance is not characteristic.
Propagation is by softwood cuttings from June to July, or by seed.
Pests
Some of its pests are borers in warm climates, aphids, scale.
Diseases
This tree is susceptible to infection by leaf spot.


