Introduction
The wild plantain is an herbaceous perennial with leathery, dark green leaves which are borne on long petioles arising directly from the ground (Figure 1). The wild plantain has no trunk or stems but manages to grow 10 to 15 feet tall due to the enormous leaves. The attractive petioles are usually 4 to 5 feet long, and the leaf blade is equally as long. The flowers are held in showy clusters that emerge from second year stalks. They are enclosed by scarlet or yellow colored bracts that are 6 to 8 inches long. This unique plant is used as a specimen for tropical gardens. The inflorescence may be cut for indoor decoration where they last for several weeks.
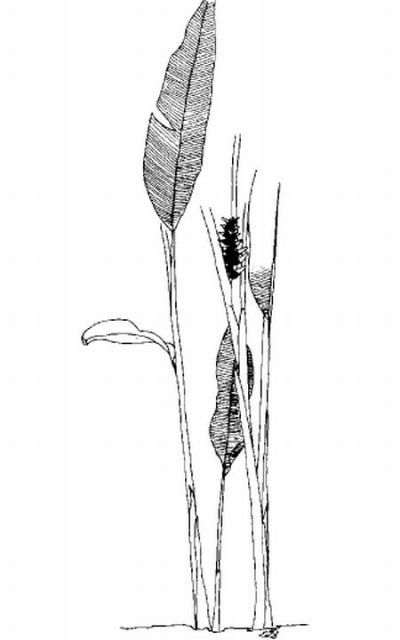
General Information
Scientific name: Heliconia caribaea
Pronunciation: hel-lick-KOE-nee-uh kuh-RIB-ee-uh
Common name(s): Caribbean heliconia, wild plantain
Family: Heliconiaceae
Plant type: herbaceous
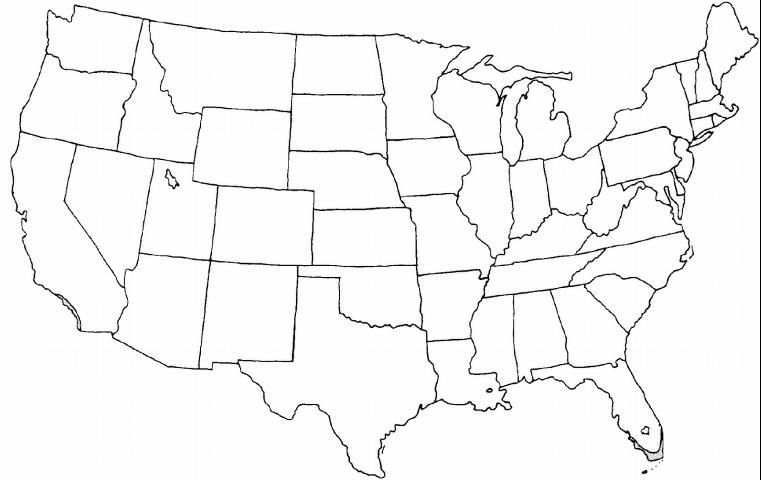
USDA hardiness zones: 10B through 11 (Figure 2)
Planting month for zone 10 and 11: year round
Origin: not native to North America
Uses: cut flowers; suitable for growing indoors
Availablity: somewhat available, may have to go out of the region to find the plant
Description
Height: 10 to 15 feet
Spread: 3 to 6 feet
Plant habit: upright
Plant density: open
Growth rate: fast
Texture: coarse
Foliage
Leaf arrangement: alternate
Leaf type: simpley multi-trunked or clumping
Leaf margin: entire
Leaf shape: ovate
Leaf venation: pinnate
Leaf type and persistence: evergreen
Leaf blade length: more than 36 inches
Leaf color: green
Fall color: no fall color change
Fall characteristic: not showy
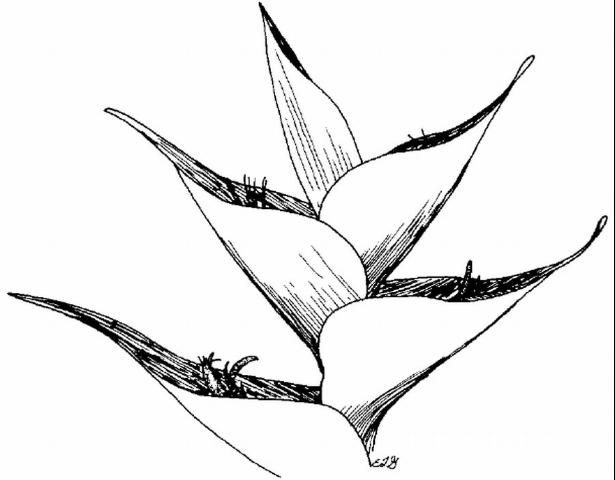
Flower
Flower color: red; yellow
Flower characteristic: spring flowering; summer flowering
Fruit
Fruit shape: unknown
Fruit length: unknown
Fruit cover: unknown
Fruit color: blue
Fruit characteristic: inconspicuous and not showy
Trunk and Branches
Trunk/bark/branches: typically multi-trunked or clumping stems
Current year stem/twig color: green
Current year stem/twig thickness: very thick
Culture
Light requirement: plant grows in part shade/part sun
Soil tolerances: acidic; alkaline; sand; loam; clay
Drought tolerance: moderate
Soil salt tolerances: moderate
Plant spacing: 36 to 60 inches
Other
Roots: not applicable
Winter interest: no special winter interest
Outstanding plant: plant has outstanding ornamental features and could be planted more
Invasive potential: not known to be invasive
Pest resistance: very sensitive to one or more pests or diseases which can affect plant health or aesthetics
Use and Management
Wild plantain will prosper in locations that receive full or partial sun. It grows and flowers best in fertile, moist soil. Fertilize this plant regularly during the growing season.
Propagate wild plantain by division of the matted clumps.
Pests and Diseases
This plant is bothered by Cercospora and Helminthosporum leaf spots. Scales and nematodes may also cause problems.