Whole Grains vs. Refined Grains
Grain products include foods such as bread, pasta, breakfast cereals, and crackers. Any food made with wheat, oats, rice, corn, barley, or other cereal is considered a grain product (USDA n.d.).
Whole grains contain the entire grain kernel. Whole-grain foods may be minimally or highly processed.
Refined grains have been processed so that the germ and the bran have been removed (Figure 1). This removes much of the fiber from the grain. B vitamins, removed in the refining process, must be added back through enrichment.
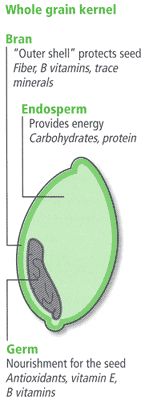
Credit: USDA
How many grains do we need?
Recommendations for servings of grains depend on your age, gender, and energy needs. The US Department of Agriculture (USDA) recommends that people of all ages get at least half their grain servings from whole-grain sources (USDHHS and USDA 2020). An ounce equivalent is comparable to a slice of bread, a cup of breakfast cereal, or a half cup of cooked rice or pasta. Table 1 lists the recommended daily grain intake for individuals with moderate physical activity (USDA Choose MyPlate 2022).
Shopping for Whole Grains
One of the best ways of identifying foods containing whole grains is to look for a "Whole Grain Stamp" (Figure 2). A "Whole Grain Stamp" on a food package identifies foods approved by the Whole Grains Council.
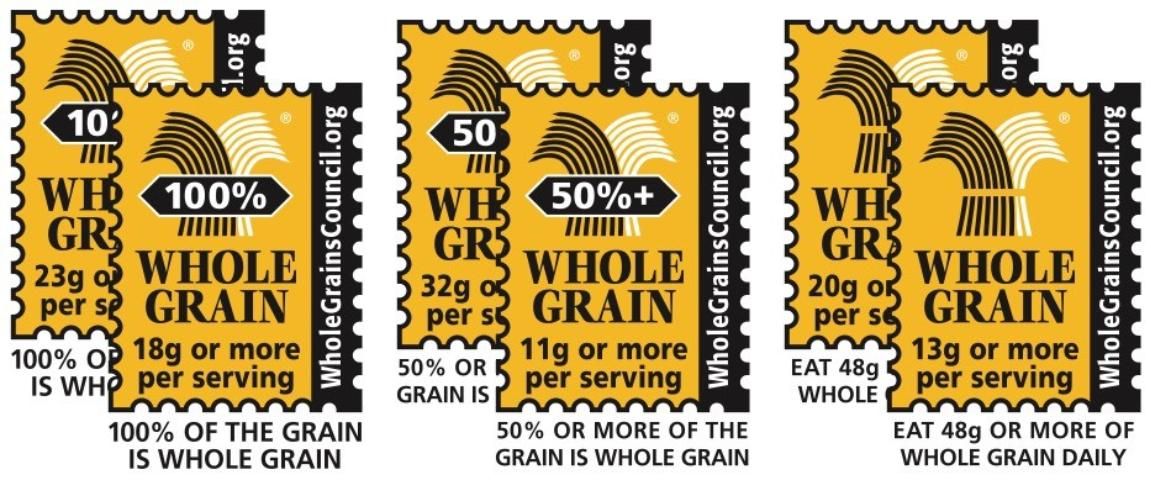
Credit: Whole Grains Council
The ingredient list on the label of food products is also helpful in identifying whole grains. If whole grains are listed as the first ingredient of the product, it is probably a good source of whole grains. Examples of whole grains include whole wheat, whole oats/oatmeal, whole-grain corn, popcorn, brown rice, whole rye, and whole-grain barley.
An example of a whole-grain product ingredient list is shown below.
Shopping for Snacks
Many whole-grain snack foods are available. Whole grains often have more fiber than refined-grain snacks, which may help to satisfy your appetite!
Several brands of crackers and other snack foods offer varieties made with whole grains. Listed below are some snacks that carry the "Whole Grain Stamp." When shopping for snacks, read labels carefully, as brands often carry similar varieties that may not have the same quantity of whole grains.
Shopping for Meals
Whole grains can easily be incorporated into any meal. Choose 100% whole-wheat breads, flatbreads, and whole-grain tortillas. When choosing pasta, look for 100% whole wheat on the front panel or 100% whole durum wheat semolina as the first or only ingredient on the ingredient list. Choose brown rice over the many white rice products. Shopping for ready-to-eat meals that contain whole grains may seem challenging, but there are several frozen entrées and side dishes that incorporate whole grains. Check the ingredient list. Also, remember when selecting pizzas to choose a whole wheat crust.

Credit: ~Photo by Bryan Ochalla, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.0 License.
Shopping for Breakfast Cereal
Getting enough whole grains is easy if you like breakfast cereals. Many breakfast cereals are made with whole-grain ingredients (e.g., General Mills®, Kashi®, Cascadian Farm™), so check the labels of your favorites. Some carry the "Whole Grain Stamp."

Credit: Kendalia, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 2.0 License.
Be an informed shopper!
Substituting whole-grain products for refined ones may help with weight management and decrease your risk of chronic diseases (USDHHS and USDA 2020). When shopping, read food labels and look for the "Whole Grain Stamp"!
Here are tips to help you incorporate whole grains into your day:
- Choose whole-grain bread or cereals for breakfast.
- Snack on whole-wheat pita triangles and hummus.
- Snack on whole-grain ready-to-eat cereals.
- Serve brown rice instead of white rice.
- Substitute whole-wheat flour for all-purpose flour in baking.
References
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). n.d. "Choose MyPlate." Accessed February 15, 2022. https://www.myplate.gov/eat-healthy/grains
Whole Grains Council. n.d. "Whole Grain Stamp." Accessed March 17, 2020. http://wholegrainscouncil.org/whole-grain-stamp
U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025. 9th Edition. December 2020. Available at DietaryGuidelines.gov.