Introduction
Because of its attractive, long-lasting flowers, Anthurium is popular as both an exotic cut-flower crop and as a flowering potted-plant crop. Growers most often report two bacterial diseases and three fungal diseases in their commercial greenhouse environments. This article provides guidelines to identify and treat diseases that may be encountered during commercial greenhouse production of Anthurium.
Anthurium
Commonly known as flamingo flower, Hawaiian love plant, cresta de gallo, or tongue of fire, Anthurium has nearly 1,000 species, making it the largest genus in the plant family Araceae. Anthurium is native to tropical America, Mexico, Costa Rica, Cuba, and Brazil. Growth habits vary depending on species; some are terrestrial, others are epiphytic (Chen et al. 2003).
Most cut-flower Anthurium cultivars are selections of Anthurium andraeanum, an epiphytic-growing plant native to Columbia and Ecuador. The large red flowers produced by Anthurium andraeanum cultivars are very recognizable to consumers (Figure 1). Breeding has introduced such flower colors as pink, orange, white, green, purple, and combinations of these colors.
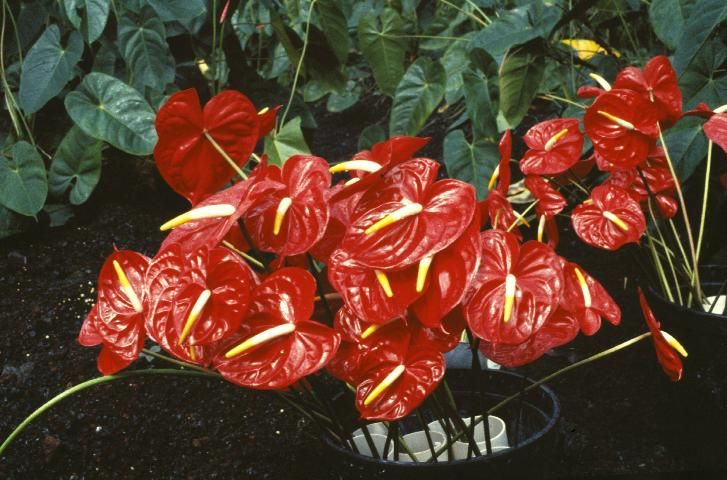

Credit: D. Norman, UF/IFAS
Florida is now leading the nation in flowering potted Anthurium production. Cultivars for potted plant production have been derived from crosses of A. andraeanum with dwarf species, such as A. amnicola and A. antioquiense. Compact, hybrid varieties of potted Anthurium released by the University of Florida Plant Breeding Program include 'Red Hot' (Henny, Chen, and Mellich 2008a), 'Orange Hot' (Figure 2) (Henny, Chen, and Mellich 2008b), and 'Southern Blush' (Henny, Poole, and Conover 1988).
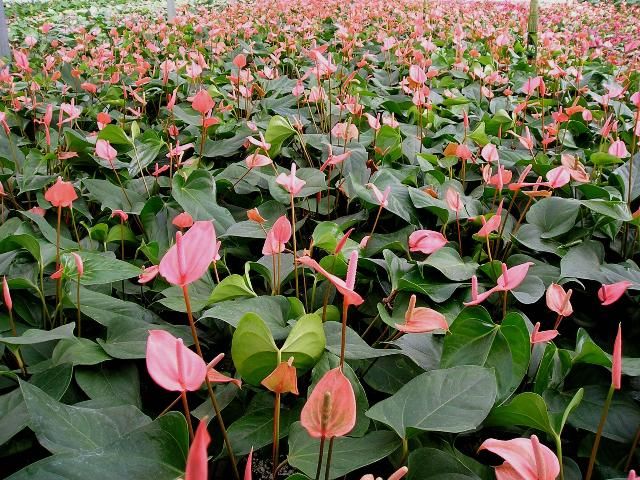

Credit: R. J. Henny, UF/IFAS
Anthurium is very susceptible to bacterial and fungal diseases that can seriously limit commercial production. Bacterial blight caused by Xanthomonas is probably the most serious. Root rots caused by Rhizoctonia, Pythium, and Phytophthora also occur in Anthurium production. It is therefore important to be able to identify and eliminate these diseases.
Bacterial Diseases of Anthurium
Bacterial Blight
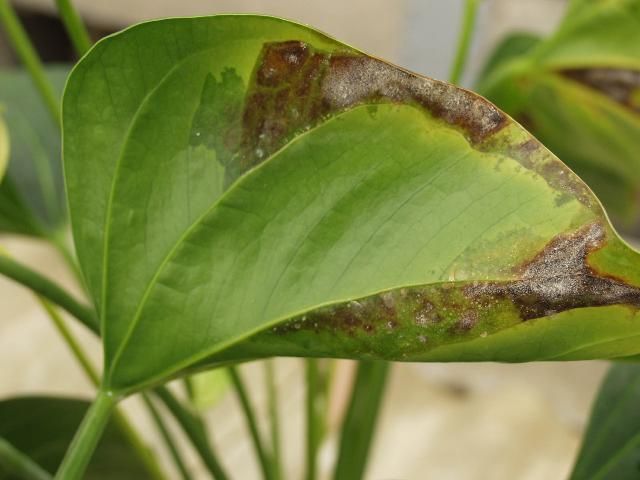

Credit: D. Norman, UF/IFAS
Symptoms: The first visible symptoms are yellowed (chlorotic), water-soaked lesions along the leaf margins that grow rapidly to form dead (necrotic) V-shaped lesions characteristic of this disease (Figure 3).
The bacteria infect Anthurium plants by entering pores (hydathodes) along the leaf margins (Figure 4). Bacteria may also enter if leaf tissues become torn through pruning, or if leaf tissues are punctured by insects. When flowers are harvested, bacteria can enter via wounds.
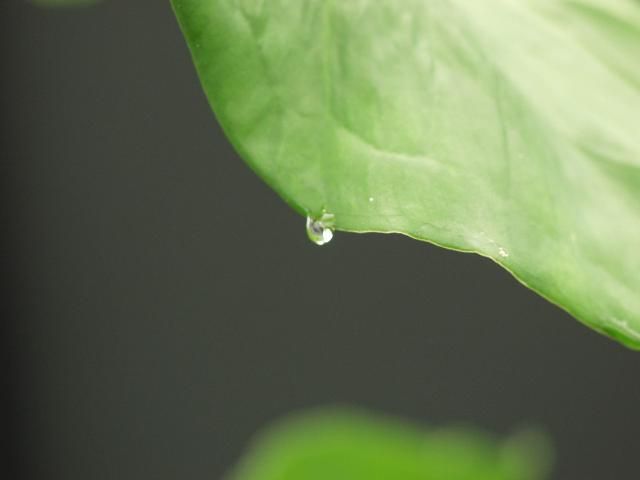

Credit: D. Norman, UF/IFAS

Credit: D. Norman, UF/IFAS
Guttation droplets form at night when humidity is high and potting soil is warm and wet. Amino acids found in this guttation fluid are a source of food for the invading bacteria. Some infected plants are asymptomatic (do not show any disease symptoms) for months as the bacteria multiply. Bacteria in the guttation fluid from these asymptomatic infected plants can infect adjacent plants.
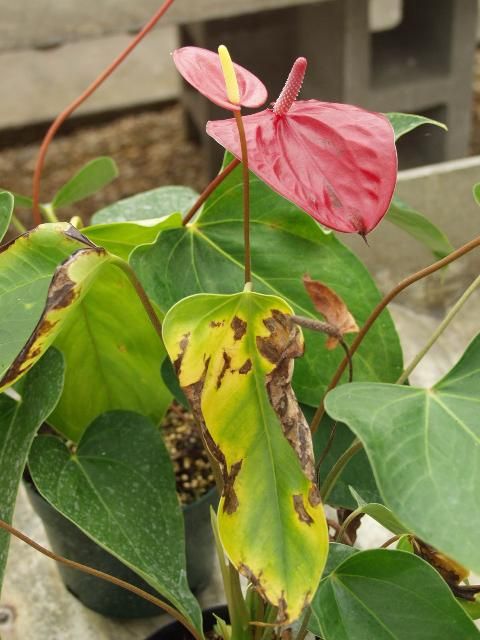
Invading bacteria quickly spread throughout the plant (Figure 5). Leaves of systemically infected plants may exhibit a bronzed appearance. Floral quality may be reduced and/or flowers may become unmarketable (Figure 6). Eventually, plants wilt and die.

Credit: D. Norman, UF/IFAS
Causal Agent: Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. dieffenbachiae
The species of Xanthomonas that infects Anthurium has a very broad host range and is able to infect most aroid species; therefore, Anthurium plants may get blight when grown in close proximity to other aroids, such as Dieffenbachia, Aglaonema, and Spathiphyllum.
Factors Favoring the Disease: Bacteria can swim across wet surfaces; therefore, it is very important to keep the foliage dry. The most effective way of accomplishing this is through drip irrigation.
Control and Treatment: Lower greenhouse humidity and temperature by increasing air circulation and venting the production facility. Allow space between the plants on the bench. Warm temperatures, high humidity, and saturated soils contribute to the formation of guttation droplets.
Only clean, tissue-cultured plantlets should be used when establishing new plantings. Because Xanthomonas bacteria can enter the plant through any wound or tear in the stem or foliage, the disease is easily spread if propagation is done via cuttings or division.
The disease can be spread when harvesting flowers or removing old foliage. Sterilize knives and clippers by dipping cutting tools in a disinfectant between plants. The most effective disinfectants are the quaternary ammonium compounds. It is also good practice to have two knives or shears in a dip bucket so they can be alternated, thus extending time in disinfectant and allowing for better coverage of the cutting surface.
When infected plants are found, they should be discarded immediately.
Products containing copper (Kocide® 3000 O, Phyton 27®, Camelot), mancozeb (Protect T/O™, Dithane®), and Bacillus subtilis (Cease®) are effective against Xanthomonas.
Bacterial Wilt

Credit: D. Norman, UF/IFAS
Symptoms: Leaf yellowing (chlorosis) is usually the first symptom observed. The disease spreads rapidly throughout the vascular system of the plant, turning veins in the leaves and stems a brown, bronze color (Figure 8). Bacterial ooze (brown slime) will be present if cuts are made into the stems of highly infected plants. Plants will exhibit wilt symptoms even though adequate soil moisture is available.
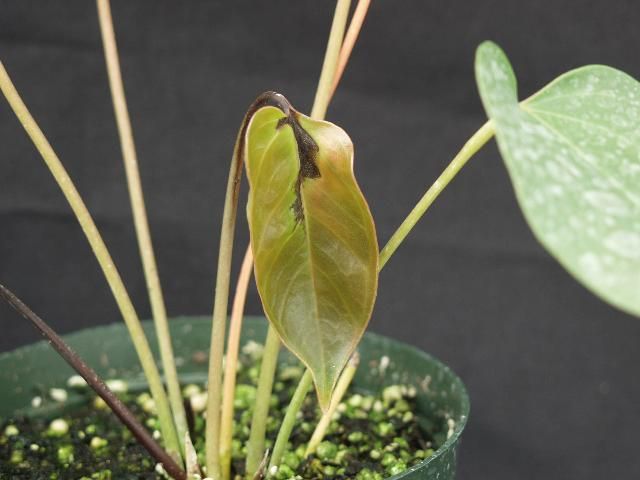

Credit: D. Norman, UF/IFAS
Causal Agent: Ralstonia solanacearum
Ralstonia is known to infect several hundred plant genera. This bacterial disease is an opportunistic pathogen that colonizes soil and can remain viable for years without a host plant.
Factors Favoring the Disease: Cool greenhouse temperatures may temporarily mask symptoms and give bacteria time to spread. Symptoms appear rapidly during hot weather.
Control and Treatment: A strict sanitation program is the most successful way to stop the spread of this pathogen and eventually eradicate it from a production facility. Fungicides that contain phosphorous acid have also been shown to be effective in preventing infection; however, they do not cure systemically infected plants (Norman et al. 2006).
Bacterial wilt is spread via contaminated soil, water, tools, or worker contact. Use disease-free propagation material. The bacterial wilt pathogen is easily spread via infected cuttings. Because the bacteria survive well in soil, both contaminated plant material and the supporting soil should be discarded. If pots and trays from contaminated infected plants are to be reused, they should be scrubbed free of adhering soil and then soaked in a disinfectant to kill the remaining bacteria. Knives and clippers should be sterilized between plants with a disinfectant containing a quaternary ammonium compound (Physan 20™, Green-Shield®) or diluted solution of bleach to prohibit spread.
Fungal Diseases of Anthurium
Rhizoctonia Root Rot
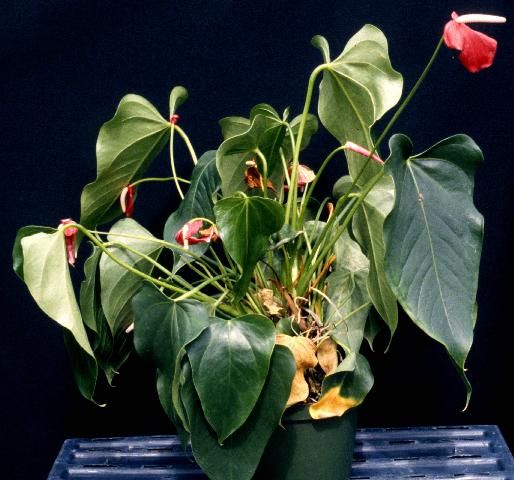

Credit: D. Norman, UF/IFAS
Symptoms: The term "damping-off" is used to describe these classical symptoms. Young, tender stems are girdled, become water soaked, and are unable to support the weight of the plant (Figure 9). Rhizoctonia attacks the roots and lower stems of plants (Figure 10), but under wet conditions it can also attack and spread in the upper leaf canopy.
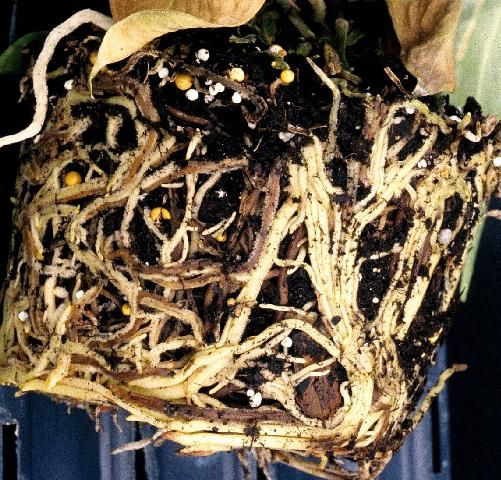

Credit: D. Norman, UF/IFAS
Causal Agent: Rhizoctonia solani
Rhizoctonia can survive within soil for years without a host plant. The fungus produces small mats of tightly woven mycelia called sclerotia. Sclerotia are irregular in shape, brown in color, and resemble particles of soil. Sclerotia provide a seedlike mechanism for the fungus to survive unfavorable conditions, such as drought or cold weather. These small sclerotia stick to trays and pot surfaces and are one of the ways the fungus spreads through nurseries.
Factors Favoring the Disease: Water-saturated soils are conducive to disease development.
Control and Treatment: Never incorporate native soils into media mixes without steam sterilizing. Use well-drained soil mixes. Never store peat moss, sphagnum moss, chips, or potting media mixes directly on soil surfaces where they can be colonized by the fungus. Plants should be cultivated on raised benches to limit root contact with soil. Rhizoctonia frequently gains access to production facilities via infected propagation material.
Many fungicides are effective against outbreaks of Rhizoctonia. Examples include 3336®, OHP 6672®(thiophanate methyl), Medallion® (fludioxonil), and Prostar® (flutolanil).
Phytophthora/Pythium
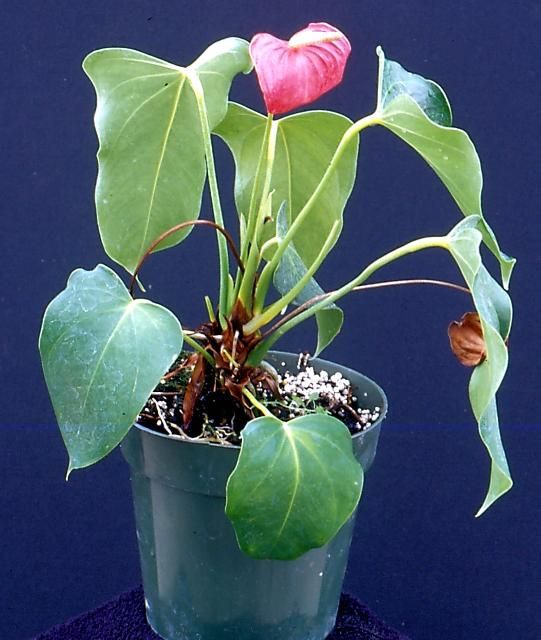

Credit: D. Norman, UF/IFAS
Both Phytophthora and Pythium are called "oomycetes," commonly known as water molds. The control, spread, and management recommendations for Phytophthora and Pythium infestations are the same. Plants infected with either of these pathogens exhibit wilting, leaf yellowing (chlorosis), and root dieback (Figure 11).
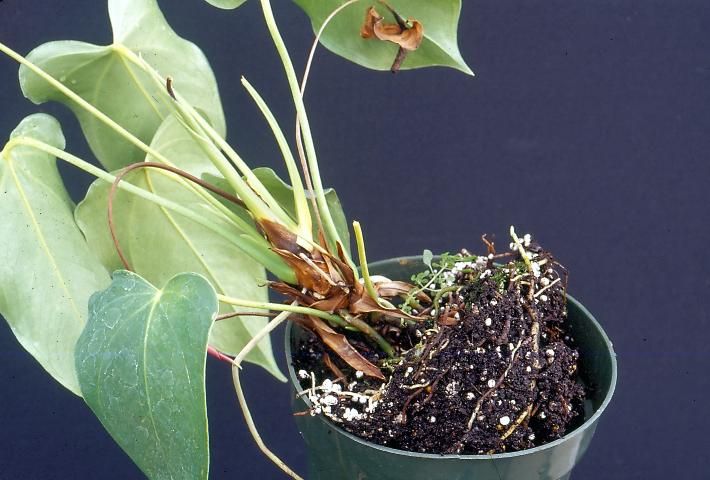

Credit: D. Norman, UF/IFAS
Symptoms: Phytophthora and Pythium infections primarily attack root systems. Plants will wilt even though adequate soil moisture is available. Root sloughing is the primary diagnostic tool (Figure 12). Under severe conditions, the foliage may exhibit black to brown leaf lesions.
These symptoms are similar to symptoms caused by Rhizoctonia; however, fungal strands (mycelial growth) are rarely observed with Phytophthora or Pythium infections.
Causal Agents: Phytophthora nicotianae var. parasitica and Pythium splendens
Phytophthora and Pythium species cause substantial damage to Anthurium and numerous tropical foliage crops.
Factors Favoring the Disease: Water-saturated soils are conducive to disease development. These diseases can usually be avoided by using light, well-drained soil mixes.
Control and Treatment: Use well-drained, synthetic soil mixes. Use disease-free stock plants. Plants with symptoms of disease should be discarded and the rest of the production facility should be treated with a fungicide drench. If potting containers are reused, they should be scrubbed and sterilized. Cutting shears, knives, and tools should be dipped in an appropriate disinfectant between plants.
Fungicides such as mefenoxam (Subdue® Maxx®) and aluminum tris/Fosetyl-al (Aliette® WDG), dimethomorph (Stature®), fluopicolide (Adorn™), and phosphorous acid (Alude™, K-Phite®) may be used to control Phytophthora and Pythium.
Black Nose Disease

Credit: D. Norman, UF/IFAS
Credit: D. Norman, UF/IFAS
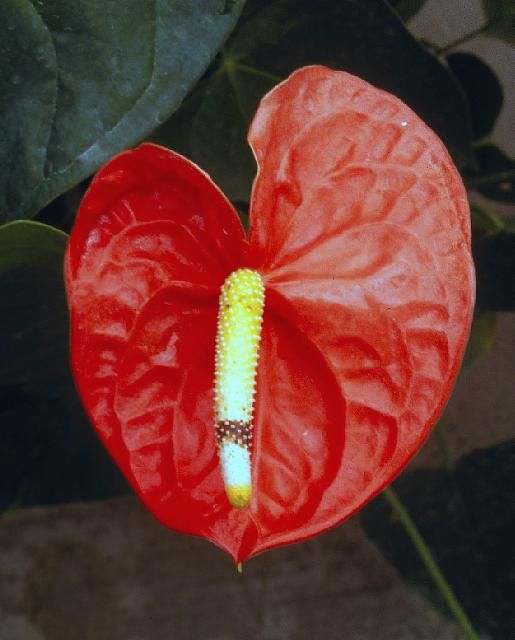
Symptoms: Black nose can cause havoc in cut-flower and potted-plant production. Flowers and flowering potted plants cannot be sold with this condition.
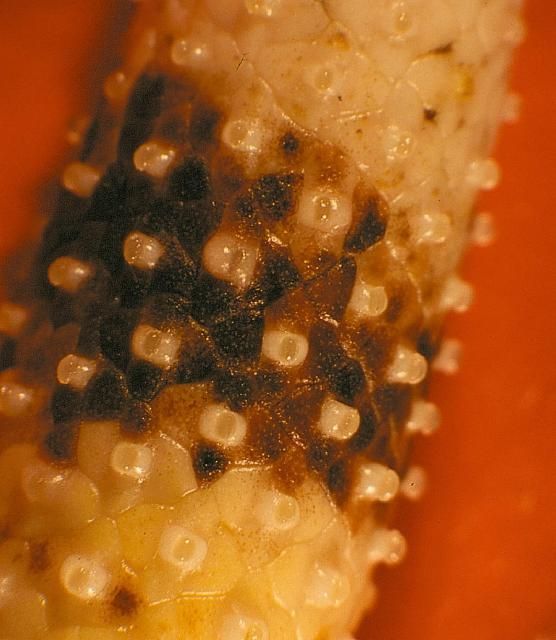
The first symptoms observed are small, brown to black flecks on the floral spadix (nose) (Figure 13). These spots rapidly enlarge, become watery, turn brown to black, and may totally encompass the spadix. The spadix may eventually fall off. Growers may also observe black, spore-containing structures (acervuli) on dead leaves and stems.
Causal Agent: Colletotrichum gloeosporioides
The fungus Colletotrichum gloeosporioides attacks many temperate and tropical crops and can cause damage to roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. However, in Anthurium the pathogen is highly specific, only attacking the spadix portion of the flower (the nose).
Factors Favoring the Disease: This disease is most severe during humid, warm conditions. Colletotrichum readily invades plant tissues previously damaged by pesticides, fertilizer, or bacterial blight (Xanthomonas).
Control and Treatment: The Colletotrichum fungus produces thousands of small hot-dog-shaped spores that can readily be moved by splashing water, air movement, and workers. A strict sanitation program is crucial to control the spread of this pathogen in a production facility.
Fungicides containing mancozeb (Protect T/O™, Dithane®) are effective. Fungicide applications are usually discouraged because chemical residues diminish the marketability of flowers and plants.
Anthurium plant breeding programs both in Hawaii and Florida have incorporated disease resistance into many of the current cultivars. Newer cultivars are highly resistant to this pathogen and rarely exhibit black nose.
References
Chen, J., D. B. McConnell, R. J. Henny, and K. C. Everitt. 2003. Cultural Guidelines for Commercial Production of Interiorscape Anthurium. ENH956. Gainesville: University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/EP159
Henny, R. J., J. Chen, and T. A. Mellich. 2008a. New Florida Foliage Plant Cultivar: 'Red Hot' Anthurium. ENH1009. Gainesville: University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/EP363
Henny, R. J., J. Chen, and T. A. Mellich. 2008b. New Florida Foliage Plant Cultivar: 'Orange Hot' Anthurium. ENH1100. Gainesville: University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/EP364
Henny, R. J., R. T. Poole, and C.A. Conover. 1988."'Southern Blush' Anthurium." HortScience 23(5): 922–923.
Norman, D. J., J. Chen, A. Mangravita-Nova, and J. M. F. Yuen. 2006. "Control of Bacterial Wilt of Geranium with Phosphorus Acid." Plant Dis. 90(6): 798–802.