Climate and Carbon Extension Educators (C2E2)
Available Languages:
English
Climate change may be one of the biggest issues facing Florida agriculture. Most countries are trying to slow global warming by reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, including through climate-smart agriculture (CSA). Climatesmart agriculture is an integrated approach to managing landscapes, including cropland, livestock, and forests, which addresses the interlinked challenges of food security and climate change.
For example, certain management practices can increase the amount of carbon stored, or sequestered, in the soil. Carbon credits, which can be traded, are a way to reward these management activities. But how can Florida agriculture contribute to carbon sequestration? How can a producer generate carbon credits? And how can they participate in carbon markets?To help answer these UF/IFAS Extension has formed a team of specialists: the Climate and Carbon Extension Educators (C2E2).
Understanding the science, mechanisms, and policy behind the carbon cycle and trading will help Florida’s agriculture better prepare for the carbon economy.
Narrower Topics
Carbon markets
An arena for carbon dioxide emissions trading, i.e. the buying and selling of emission allowances (credits or shares) and emission reductions for metric tons of carbon dioxide, or its equivalent in other greenhouse gases emitted into the atmosphere.
Carbon Sequestration
The uptake and storage of carbon in a carbon sink, such as the oceans, or a terrestrial sink such as forests or soils, in order to keep the carbon out of the atmosphere.
Climate Change
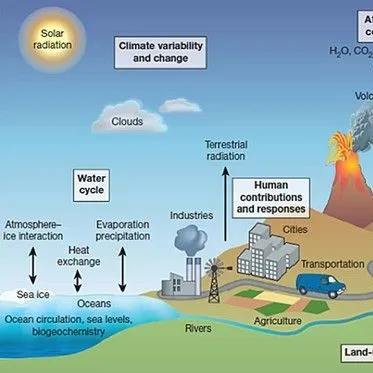
Climate change refers to a change in the state of the climate that can be identified (e.g., by using statistical tests) by changes in the mean and/or the variability of its properties and that persists for an extended period, typically decades or longer. Climate change may be due to natural internal processes or external forcings such as modulations of the solar cycles, volcanic eruptions and persistent anthropogenic changes in the composition of the atmosphere or in land use.
Climate-Smart Agriculture
Climate-smart agriculture (CSA) is agriculture that sustainably increases productivity, resilience (adaptation), reduces/removes green house gases (mitigation), and enhances achievement of national fool security and development goals.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The discharge of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and various halogenated hydrocarbons, into the atmosphere. Combustion of fossil fuels, agricultural activities and industrial processes contribute to the emissions of greenhouse gases.