Infectious Diseases
Available Languages:
English
Narrower Topics
COVID-19 (Novel Coronavirus)
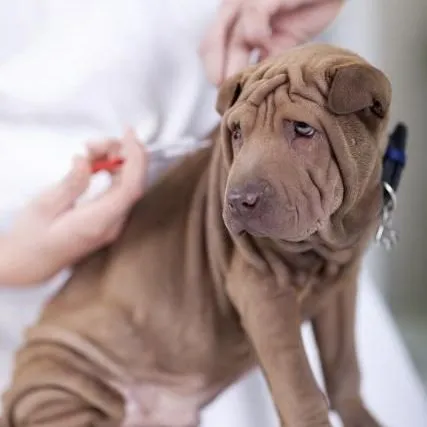
COVID-19, a highly infectitious respiratory disease in humans, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The virus probably emerged from an animal source in Wuhan (China) and spreaded globaly from person to person. Most people infected with COVID-19 have had mild to severe respiratory illness with symptoms of cough, fever, and shortness of breath. In some cases, patients had pneumonia in both lungs, multi-organ failure, and even death. The World Health Organization (WHO), on March 11, 2020, declared the novel COVID-19 outbreak a global pandemic. [NALT]
Pathogens
Microorganisms, viruses and parasites that can cause disease.
Vectors and Vector-borne Diseases
Disease Vectors: Invertebrates or non-human vertebrates which transmit infective organisms from one host to another.