Florida Sea Grant
Summary
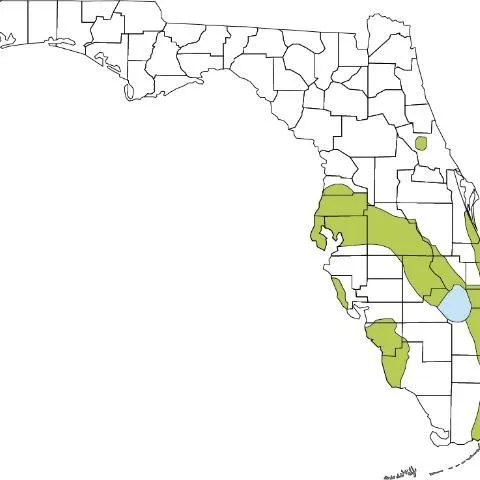
The Florida Sea Grant College Program supports research and education activities that help Florida's shoreline communities, industries and citizens wisely use the state's coastal and marine resources.
Source: Florida Sea Grant Marine Extension
Editorial Team
- Maia McGuire - Editor, Chair, Approver
- Susan Gildersleeve - ICS Editor
- Sherry Larkin - Chair
- Donielle Nardi - Assistant
- Roberto Ferrer - Assistant
New and Revised Publications
The Florida Sea Grant College Program supports research and education activities that help Florida's shoreline communities, industries and citizens wisely use the state's coastal and marine resources.
Source: Florida Sea Grant Marine Extension
Editorial Team
- Maia McGuire - Editor, Chair, Approver
- Susan Gildersleeve - ICS Editor
- Sherry Larkin - Chair
- Donielle Nardi - Assistant
- Roberto Ferrer - Assistant
New and Revised Publications
Showing 100 of 128 Publications
Showing of 33 Experts